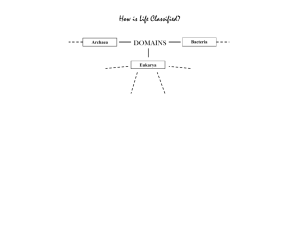
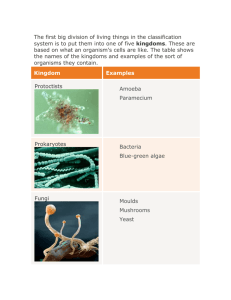
C. Linnaeus's System of Classification
advertisement

Chapter 18 Classification Order From Chaos •When you need a new pair of shoes, what do you do? •You probably walk confidently into a shoe store, past the tens or hundreds of pairs of shoes you don’t want and straight to the kind you do want. How do you find them? •Shoes are organized in the store in categories. People organize objects by grouping similar objects together. 18-1 Finding Order in Diversity Objective • Explain how living things are organized for study • Describe binomial nomenclature • Explain Linnaeus’s system of classification 18-1 Homework Define each vocabulary word in at least one complete sentence. Write out all key concepts. 18–1 Finding Order in Diversity A. Why Classify? B. Assigning Scientific Names C. Linnaeus’s System of Classification A. Why Classify? – – taxonomy – B. Assigning Scientific Names 1. Early Efforts at Naming Organisms 2. Binomial Nomenclature • each species is assigned a two-part scientific name C. Linnaeus’s System of Classification species -genus -family -order -class -phylum -kingdom -- 2 plants and animals Linnaeus’s System of Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Figure 18-5 Classification of Ursus arctos Grizzly bear Black bear Giant panda Red fox Coral Sea star Abert squirrel snake KINGDOM Animalia PHYLUM Chordata CLASS Mammalia ORDER Carnivora FAMILY Ursidae GENUS Ursus SPECIES Ursus arctos 18-1 Homework All 5 questions on page 450 in at least 3 complete sentences. 18–3 Kingdoms and Domains Objective • Name the six kingdoms of life as they are now identified • Describe the three-domain system of classification. 18–3 Homework • Define each vocabulary word in at least one complete sentence. • Write out all key concepts. 18–3 Kingdoms and Domains A. The Tree of Life Evolves B. The Three-Domain System C. Domain Bacteria D. Domain Archaea E. Domain Eukarya A. The Tree of Life Evolves simple view of life 2 kingdoms not sufficient to classify all organism 6 kingdom system of classification B. The Three-Domain System C. Domain Bacteria unicellular and prokaryotic D. Domain Archaea unicellular and prokaryotic E. Domain Eukarya all organisms containing true nucleus Protista- Fungi – Plantae – Animal - Concept Map Living Things are characterized by Eukaryotic cells and differing Important characteristics which place them in Cell wall structures such as Domain Eukarya Prokaryotic cells which is subdivided into which place them in Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea which coincides with which coincides with Kingdom Eubacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Protista Kingdom Animalia Figure 18-12 Key Characteristics of Kingdoms and Domains Classification of Living Things DOMAIN Bacteria Archaea KINGDOM Eubacteria Archaebacteria CELL TYPE Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls of chitin Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts Unicellular Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most multicellular; some unicellular Multicellular Multicellular MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals CELL STRUCTURES NUMBER OF CELLS Figure 18-13 Cladogram of Six Kingdoms and Three Domains DOMAIN ARCHAEA DOMAIN EUKARYA Kingdoms DOMAIN BACTERIA Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Homework 18-3 Answer all 5 questions on page 461 in at least 3 complete sentences. Homework Chapter 18 assessment questions page 465: Multiple choice questions: # 1-5, 6-10 Understanding concepts: # 21-25, 27-28 Each in at least 3 complete sentences.