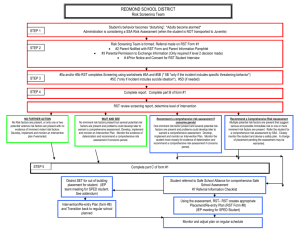
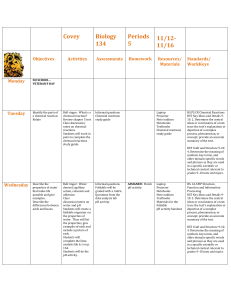
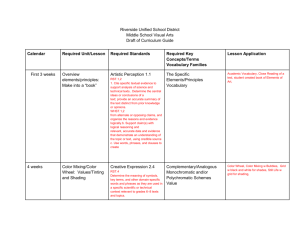
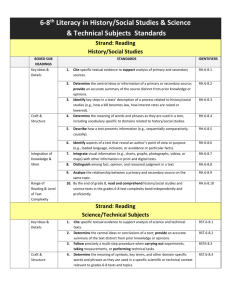
Pairing Gizmos with ELA and SMP's in Science
advertisement

Join ExploreLearning as they showcase how to use math and science simulations (Gizmos) to deepen students conceptual knowledge. Discover how to use Gizmos as a vehicle through which to teach concepts while incorporating standards of mathematical practices (SMP’s), STEM engineering practices, and english language arts (ELA) standards. Experience the versatility of Gizmos as classroom applications are addressed - whole classroom instruction, flipped classrooms, computer labs, or BYOD. During this session, EL trainers will share their secret tips and tricks while showcasing practical teacher and student examples, including but not limited to inquiry, technology integration, claim-evidence-reasoning, incorporation of new national/state standards, STEM, and continuous improvement/RtI. Tuesday, July 7, 2015 Upstate Technology Conference Greenville, South Carolina Corey J. Peloquin Assistant Implementation Coordinator Manager North Florida Project Manager, PD Corey.Peloquin@explorelearning.com Participating, Growing, and Developing As A Professional • Do Not Distract Learners • Keep cell phone on vibrate/silence, text and/or return calls during breaks. Put away all electronic devices. Limit sidebar conversations to content and at a whisper • Be An Active Collegial Learner • Participate in discussion and activities with a positive attitude • Seek first to understand • Watch your own “air time” inviting colleagues to share and balance discussion between participants • Value Your Learning Time • Put away work and non-training materials • Return from breaks on time • Care about improving your skills and sharpening your knowledge RST.3 Follow precisely a multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks. RST.4 Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domainspecific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context RST.5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms RST.7 Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually. RST.9 Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gained from reading a text on the same topic. RST.10 Comprehend science/technical texts in the text complexity band independently and proficiently. WHST.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Introduce claim(s) about a topic or issue, acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically. Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant, accurate data and evidence that demonstrate an understanding of the topic or text, using credible sources. ELA-Literacy.W.8.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. The Student Will: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3. Construct viable arguments. 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning (hook, demonstration, free write, brainstorming, analyze a graphic organizer, KWL, etc) Engage (hook, demonstration, free write, brainstorming, analyze a graphic organizer, KWL, etc) What are you wondering? Engage (hook, demonstration, free write, brainstorming, analyze a graphic organizer, KWL, etc) (investigation, solve a problem, collect data, construct model, etc.) Materials • Toy race track • Small toy trucks • Lego figurine • Different masses (washers) • String/thin wire • Scissors • Meter stick or tape measure • An object to stop the motion Directions • Design a model that will affect the change of motion of an object (Lego figurine) • Collect data each time the model is changed and record on chart paper Explore (investigation, solve a problem, collect data, construct model, etc.) (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) Explain (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) Explain (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) Explain (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) Vehicle Mass Hill # 1 Height Maximum Speed Time Explain (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) Explain (student analysis, structured questioning, reading and discussion, teacher explanation, compare, classify) (problem solving, decision making, experimental inquiry, compare, classify, apply) Challenge 1 – Identify as many possible variables affected when friction is introduced. Challenge 2 – Construct a diagram showing how the height of the hills affects whether or not the egg breaks. Include labels such as gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, friction. Challenge 3 - Provide evidence from the Gizmo that is consistent with your observations from the car crash challenge on the role velocity plays in affecting the motion of an object (Lego figurine/car passengers/roller coaster physics egg). Elaborate/Extend (problem solving, decision making, experimental inquiry, compare, classify, apply) (develop a scoring tool or rubric, performance assessment, produce a product, journal entry, portfolio, etc.) Evaluate (develop a scoring tool or Rubric, performance assessment, produce a product, journal entry, portfolio, etc.) RST.3 Follow precisely a multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks. RST.4 Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domainspecific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context RST.5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms RST.7 Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually. RST.9 Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gained from reading a text on the same topic. RST.10 Comprehend science/technical texts in the text complexity band independently and proficiently. WHST.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Introduce claim(s) about a topic or issue, acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically. Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant, accurate data and evidence that demonstrate an understanding of the topic or text, using credible sources. ELA-Literacy.W.8.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. The Student Will: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3. Construct viable arguments. 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning DEBRIEF From this session, what are some of your biggest “take-aways” or “ah-ha” moments? Content Pedagogy DEBRIEF How will using Gizmos change your instructional strategies to support Math, Science, or ELA standards? Content Pedagogy http://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/scienceflowchart http://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/scienceflowchart http://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/scienceflowchart http://undsci.berkeley.edu/article/scienceflowchart