Green - Assignment 8
advertisement

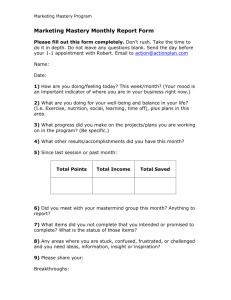
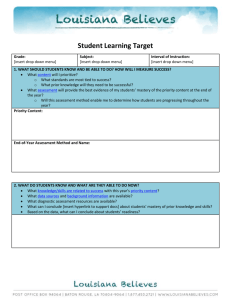
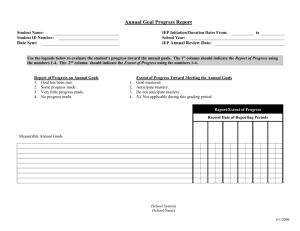
Complete Unit Ewing Coleman Green EDD 8112 CRN 22080 Assessment Centered Curricular Design Nova Southeastern University November 15, 2013 Algebra 1 Unit 2 Linear and Exponential Relationships Linear and Exponential Relationships Linear – constant rate of change Exponential – non-linear rate of change (exponent other than 1) Backward Unit Design Founded on three basic elements (1) Desired Results Assessment Evidence Learning Plan “Backward design yields greater coherence among desired results, key performances, and teaching and learning experiences, resulting in better student performance – the purpose of design.” (1) Wiggins and McTighe (2005, p. 33) Unit Design Wiggins & McTighe’s original three design elements expanded to six stages Stage 1: Enduring Understanding Stage 2: Essential Questions Stage 3: Assessment Stage 4: Learning Experiences Stage 5: Resources Stage 6: Reflection Stage 1 Enduring Understanding Common Core Standards Stage 2 Essential Questions Stage 3 Assessment Strategies Diagnostic Formative Mid-Module Summative Performance/Authentic Self Diagnostic Assessment Purposes Determine mastery of content entering the unit Inform individual learner needs Remedial Enrichment into Geometry Guided independent study and self-assessment Form Written assessment similar to unit summative assessment Grade only informs instructional strategies Formative Assessment Purposes Empower students to own the learning process Provide structured practice to construct understanding Provide descriptive feedback Inform student and teacher on mastery development Determine next steps for mastery attainment Forms Collaborative cluster problem solving Online Gizmos Learning Assignments (not “homework”) Mid-Module Assessment Purposes Gather evidence of mid-unit mastery attainment Provide descriptive feedback Inform student and teacher on mastery development Determine next steps for mastery attainment Document level of demonstrated mastery (“grade”) Form Written assessment Summative Assessment Purposes Gather evidence of end of unit mastery attainment Provide descriptive feedback Inform student and teacher on mastery development Determine next steps for mastery attainment Document level of demonstrated mastery (“grade”) Form Written assessment Unit Summative Assessment Performance/Authentic Assessment Purposes Individualize student expression of mastery Bring personalized meaning to learning Appeal to individual student passion Engage whole brain development Build cross-curricular understanding Link to real-world relevancy Forms Varied Self-Assessment Purposes Empower students to own the learning process Build lifelong learning and achievement skills Build intrapersonal intelligence Develop student self-efficacy Help students chart their own journey toward mastery attainment Forms Varied, frequently using an exemplar Three self-assessment formats included in this unit Unit goals Action Oriented Reflection Prompts on assessments Stage 4 Lesson plans and learning engagements Lesson plan elements Collaborative clusters Investigation SmartBoard lesson Explore Learning Gizmo Lesson Plans Collaboratively designed with subject partner Lesson plan elements: Previous learning assignment review Concept introduction via SmartBoard lesson Investigation/exploration Explore Learning Gizmo focused on concept Problem solving at collaborative table clusters Self-assessment New learning assignment Mr. Green’s SmartBoard and collaborative clusters High Jump record investigation – men versus women!! SmartBoard lesson pages Explore Learning Gizmo (2) (2) www.explorelearning.com Gizmo online formative assessment with immediate feedback and explanation Stage 5 Resources Stage 6 Reflection Calendars Unit Quality Two self-assessments Entire Unit Using Assignment 2, 3, and 4 rubrics Unit summative assessment evaluated along three dimensions Distribution of items – learning outcomes Enduring Understanding Common Core Mathematics Standards Distribution of items – difficulty Bloom’s Taxonomy Entire Unit Entire Unit Overall rubric total score of 29 out of 30 Improvement area: More comprehensive performance tasks with GRASPS (3) prompts (3) Goal, Role, Audience, Situation, Performance, and Standards (Wiggins & McTighe, 2005, p. 157) Unit Summative Assessment Quality – Learning Outcomes Learning Outcomes Analysis showed The enduring understanding and all five essential questions were addressed across the 32 items EQ #5 (how rate of change effects shape of graphs) may be over-represented 9 of 22 Unit Common Core Mathematics Standards addressed Appropriate since this assessment measures understanding across the Linear concepts -Exponential to be studied next Unit Summative Assessment Quality – Item Difficulty Bloom’s Taxonomy Analysis showed All six Bloom’s levels are addressed 18 of 31 graded items address Application level Is this an appropriate cognitive distribution given the audience and subject matter? Approximate normal distribution when viewed as a sideways histogram Slight bias toward higher cognitive end of Bloom’s versus lower Overall Unit Quality Analysis of the unit self-assessment showed: Comprehensive backward-designed template Standards-based learning focus Balanced assessment strategies Varied self-assessment formats Varied whole brain learning engagements Effective use of digital resources Include more comprehensive performance tasks with GRASPS, authentic assessment Further analyze assessment item balance across Common Core standards and Bloom’s levels Image URLs Slide 2. Anonymous student at SmartBoard. Retrieved from https://encryptedtbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSzeS1qe0FJDkCFN_pKUgJxrvbB51JB7cOHp6bMsGf AubXJYA_z4w Slide 2. Bridge. Retrieved from http://blog.keycurriculum.com/2012/03/what-do-you-wonderreal-world-math-problems-are-everywhere/ Slide 2. Parabolic rollercoaster. Retrieved from https://encryptedtbn1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSxX_MWbDefsXeVGepCnZ5oaU9hUfX3uSkSf29jxB9 DQRtoiRG8Cw Slide 3. Airplane takeoff. Retrieved from https://encrypted-tbn2.gstatic.com/images q=tbn:ANd9GcR8P6YyJHaVmV3Sel6ya8m4C8czyW3cJ_vybo7DmbwZ8EtJqLZM Slide 3. Very large array. Retrieved from https://encryptedtbn2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQHTrN8LiLopFi7jMnTes7z2MT6syWnW7wYNkVWtkNl 8oDwXsfWiA References Explore Learning Gizmos. www.explorelearning.com Wiggins, G., & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by design. (2nd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.