Chromosomes, Mitosis & Meiosis
advertisement

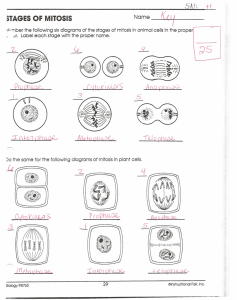
Chromosomes, Mitosis & Meiosis Chapter 9 Chromosomes • Located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells • Visible only when the cell is dividing • Made of chromatin – DNA + proteins – Chromatin is just the chromosomes in an extended, partially unraveled state • Chromosomes contain genes – Humans have less than 30,000 – Genes provide information on cellular function • Chromosomes package a lot of information into a small space Packaging of Chromosomes • Histones – help to coil the DNA molecule – Histones have a slight + charge – DNA has a slight – charge – This attraction forms a clump of 146 base pairs of DNA wrapped around 8 histones – a nucleosome – Nucleosomes help prevent tangling of the DNA • Scaffolding proteins – nonhistone proteins that bundle the nucleosomes and help maintain the chromosome structure Nucleosomes During cell division • Chromosomes consist of identical halves called sister chromatids • Sister chromatids are held together at an area called the centromere • The centromere has a protein disk called a kinetochore The Cell Cycle – the life cycle of a cell • Interphase – – – – Between one cell division and the next The majority of a cell’s life When the cell is doing its work Consists of three phases: • G1 phase S phase G2 phase • M phase – Division of the cell – Consists of two phases: • Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) • Cytokinesis The Cell Cycle Interphase – G1 Phase • G = gap (no DNA synthesis) • Growth and normal metabolism occurs • Cells that are no longer actively dividing (nerve, skeletal muscle, red blood cells) are arrested in this stage – These cells are said to be in the G0 phase • At the end of this phase necessary enzymes are synthesized Interphase – S phase • Synthesis • DNA replicates and histone is synthesized • This is when the sister chromatids are produced Interphase – G2 phase • Cell is entering final preparations for cell division M phase – Mitosis: Prophase • Nuclear envelope breaks down • Nucleolus disappears • Chromosomes (made of two identical sister chromatids) appear as chromatin condenses • Spindle fibers form between centrioles which are now at the poles of the cell Prophase whitefish cell mitosis. LM X360 Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited M phase – Mitosis: Metaphase • Spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes (located at the centromere of the two sister chromatids) • Chromosomes line up along the equatorial plane of the cell, midway between the two poles Metaphase whitefish cell mitosis. LM X360 Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited M phase – Mitosis: Anaphase • Sister chromatids separate at the centromeres • Each chromosome is pulled toward the opposite poles Anaphase whitefish cell mitosis. LM X360 Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited M phase – Mitosis: Telophase • Chromosomes arrive at the poles (now each is a single sister chromatid) • Nuclear envelope begins to re-form around each set of chromosomes • Cytokinesis begins Telophase whitefish cell mitosis. LM X360 Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited M phase – Cytokinesis • The division of the cytoplasm • Two new cells are called daughter cells • In animal cells: – A cleavage furrow pinches in around the midline of the cell and divides the two cells • In plant cells: – A cell plate forms in the midline and grows across to divide the two cells Daughter Cells whitefish cell mitosis. LM X360 Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Regulation of the cell cycle • Different types of cells have different time frames for the cell cycle • Cell cycle checkpoints help regulate the cell cycle • Some chemicals can affect the cell cycle: – Drugs that stop the cell cycle are used in cancer treatment • These can cause nausea and hair loss sideeffects – Hormones may stimulate mitosis • Cytokinins in plants • Certain steroids in animals Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Name that stage… Onion root tip mitosis Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited Confocal image of dividing cell. The markers are mitotic spindle (red), chromosomes (blue) , and peroxisomes (green). Credit: © Carolina Biological/Visuals Unlimited