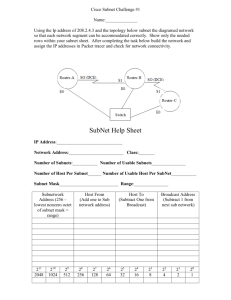
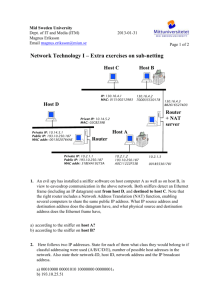
Network Devices
advertisement

IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing What Is TCP/IP? • A large collection of networking protocols and services • The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) handles reliable delivery for messages of arbitrary size, and defines a robust delivery mechanism for all kinds of data across a network • The Internet Protocol (IP) manages the routing of network transmissions from sender to receiver, along with issues related to network and computer addresses, and much more 1 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Origins of TCP/IP • In 1969, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), a branch of the United States Department of Defense (DoD), funded an academic research project for a special type of long-haul network with following objectives: – A desire to withstand a potential nuclear strike – A desire to permit different kinds of computer systems to easily communicate with one another – A need to interconnect systems across long distances • A packet-switched network, which is known as ARPANET, was built as a result of this project 2 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing IP Addressing • An IP address is a numeric identifier assigned to each machine on an IP network • IP address consist of 32 bits divided in to four sections (octets) • Usually depicted in one of three formats Decimal: 172.16.30.56 Binary: 10101100.00010000.00011110.00111000 Hexadecimal: AC 10 1E 38 • 232=4,294,967,296 possible number of addresses 3 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 4 Binary-to-Decimal Conversion Decimal Binary 120,321 101010 + 100×1= 1 101×2= 20 102×3= 300 103×0= 0 4 10 ×2= 20,000 105×1= 100,000 120,321 Practice: Write IP address 10101100.00010001.00011000. 01010011 in decimal numbers. + 20×0= 21×1= 22×0= 23×1= 24×0= 25×1= 00000000= 0 10000000= 128 11000000= 192 11100000= 224 11110000= 240 11111000= 248 11111100= 252 11111110= 254 11111111= 255 0 2 0 8 16 32 58 20 = 0 21 = 2 22 = 4 23 = 8 24 = 16 25 = 32 26 = 64 27 = 128 28 = 256 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 5 Hierarchical Addressing • IP addressing is a hierarchical addressing IP Pool Network Host Host Network Sub-net Host Network Sub-net Host • Hierarchical addressing makes sure efficient routing IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Network Address Ranges • Class A: the first bit of the first byte is always 0 (0xxxxxxx.) – Range • minimum 00000000. =0. • maximum 01111111. =127. – Format: network.node.node.node – Valid Network Addressing • 00000000.- is reserved for the default route for the network • 01111111.- is reserved for diagnostics • What is the maximum usable number of Class A network addresses? – Valid Host Addressing • -.0.0.0 is reserved for network address • -.255.255.255 is the broadcast address • What is the maximum usable number of Class A node (hosts) addresses? 6 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing • Class B: The first byte is always 1 and the second byte is always 0 (10xxxxxx.) – Range • minimum 10000000.=128. • maximum 10111111.=191. – Format: network.network.node.node – Valid Host Addressing • -.-.0.0 is reserved for the network address • -.-.255.255 is the broadcast address • What is the maximum usable number of Class B node (hosts) addresses? • Class C: The first two bytes are always 1 (11xxxxxx) – Range • 11000000. = 192 • 11111111. = 223 – Format: network.network.network.node – Valid Host Addressing • -.-.-.0 is reserved for the network address • -.-.-.255 is the broadcast address • What is the maximum usable number of Class A node (hosts) addresses? • Class D: Reserved for multicast address (224-239) • Class E : Reserved for scientific purposes (240-255) 7 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Subnetting • Breaking a large network into smaller networks • Benefits – Reduced traffic – Optimize network performance – Simplified management – Helps expending the network • To create subnetworks, bits from the host portion is revered to define the subnet address 8 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Subnet Mask • 32-bit information to distinguish the network and host portions of the IP address 9 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 10 Subnetting Class C Binary Subnet mask Shorthand Subnets on Hosts per the subnet network -.00000000 255.255.255.0 Default Subnet mask -.10000000 255.255.255.128 /25 -.11000000 255.255.255.192 /26 2 62 -.11100000 255.255.255.224 /27 6 30 -.11110000 255.255.255.240 /28 14 14 -.11111000 255.255.255.248 /29 30 6 -.11111100 255.255.255.252 /30 62 2 Last two digits are reserved for hosts Subnetting formulas x=number of masked bits Number of subnets on the network= 2x-2 Number of hosts per subnet=28-x-2 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 11 Example Network address=192.168.10.0 Subnet mask=255.255.255.192 Subnet 64 01xxxxxx 01 000000=64 01 000001=65 01 111110=126 01 111111=127 The The The The network (192.168.10.64) first valid host (192.168.10.65) last valid host (192.168.10.126) broadcast (192.168.10.127) Subnet 128 10xxxxxx 10 000000=128 10 000001=129 10 111110=190 10 111111=191 The The The The network (192.168.10.128) first valid host (192.168.10.129) last valid host (192.168.10.190) broadcast (192.168.10.191) IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 12 Fast Way: Subnetting a Class C 1. Find the network addresses Subnet mask=192 256-192=64 based number and .64 is the first subnet 64+64=128 the second subnet .128 is the second subnet 128+64=192 (subnetmask. Stop) 2. Find the broadcast address for each subnet The number immediately preceding next subnet number 3. Find the valid host addresses Valid host are numbered between the subnets. 192.168.10.64 192.168.10.65 192.168.10.126 192.168.10.127 The network The valid host addresses The broadcast address Subnet 64 192.168.10.128 192.168.10.129 192.168.10.120 192.168.10.191 The network The valid host addresses Subnet 128 Network 192.168.10.0 Mask 255.255.255.192 The broadcast address IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Example Network address=192.168.10.0 Subnet mask=255.255.255.224 The numbers of subnets and host? Network and Broadcast Addresses for each subnet? Valid Host Addresses? 13 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 14 Subnetting Class B Binary Subnet mask Shorthand -.0000000.00000000 255.255.0.0 Default Subnet mask -.10000000. 00000000 255.255.128.0 /17 -.11000000. 00000000 255.255.192.0 /18 2 16,382 -.11100000. 00000000 255.255.224.0 /19 6 8,190 -.11110000. 00000000 255.255.240.0 /20 14 4,094 -.11111000. 00000000 255.255.248.0 /21 30 2,046 -.11111100. 00000000 255.255.252.0 /22 62 1,022 -.11111110. 00000000 255.255.254.0 /23 126 510 -.11111111. 00000000 255.255.255.0 /24 ? ? -.11111111.10000000 255.255.255.128 /25 510 126 -.11111111.11000000 255.255.255.192 /26 1,022 62 -.11111111.11100000 255.255.255.224 /27 2,046 30 -.11111111.11110000 255.255.255.240 /28 4,094 14 -.11111111.11111000 255.255.255.248 /29 8,190 6 -.11111111.11111100 255.255.255.252 /30 16,382 2 Number of subnets on the network= 2x-2 Number of hosts per subnet=216-x-2 Subnets on the network Hosts per subnet IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing 15 Example Network address=180.168.0.0 Subnet mask=255.255.192.0 Subnet 64 01xxxxxx.xxxxxxxx 01000000.000000=64.0 The network (180.168. 64.0) 01000000.000001=64.1 The first valid host (180.64.1) 01111111.111110=127.254 The last valid host (180.168.127.254) 01111111.111111=127.255 The broadcast (180.168.127.255) Subnet 128 10xxxxxx.xxxxxxx 10000000.000000=128.0 10000000.000001=128.1 10111111.111110=191.254 10111111.111111=191.255 The network (180.168. 128.0) The first valid host (180.128.1) The last valid host (180.168.191.254) The broadcast (180.168.191.255) IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Example •Network Address=172.16.0.0 •Subnetmask=255.255.240.0 The numbers of subnets and host? Network and Broadcast Addresses for each subnet? Valid Host Addresses? 16 IST 228\Ch3\IP Addressing Example •Network Address=172.16.0.0 •Subnetmask=255.255.255.192 (/26) The numbers of subnets and host? Network and Broadcast Addresses for each subnet? Valid Host Addresses? 17