Personality Adjustment and Conflict
advertisement

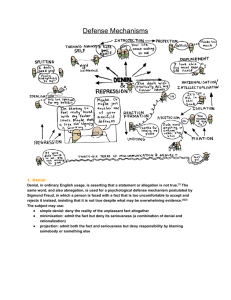
Personality Adjustment and Conflict The Healthy Personality Self Defense Mechanisms Do Now: Who controls what happens in your life? If you’re having a bad day, can you change it? Have you ever blamed someone other than yourself for a bad grade? Are some people luckier than others? How do our learned beliefs and habits help us…or not • There are three habits that have a tremendous impact on our lives: 1. Locus of control 2. Self-efficacy 3. Optimism What is Locus of Control? Individual perception about main causes of events in their life Concept developed by Julian Rotter 1950’s Do you believe outside forces, fate, God, luck or powerful others control your destiny? Do you believe your destiny is controlled by yourself? External Locus of Control Internal Locus of Control What is locus of control? • It is the measure of how responsible you feel for your success and failures. • Internal Locus: believe you are responsible • External Locus: believe others, luck, chance and fate are responsible. What is your locus of control? Page 478 to 480 in your textbook. What is Self Efficacy? The belief in one's capabilities to achieve a goal or an outcome. Students with a Verbal strong sense of persuasion efficacy are Teachers can boost more likely self-efficacy to with challenge credible themselves motivation. with difficult tasks Emotional Vicarious state -A experience Successful Observing a positive mood can experiences peer Be boost one's boost self- succeed at a intrinsically beliefs in efficacy, task can while self-efficacy, strengthen motivated failures while beliefs in erode it. anxiety can one's own undermine abilities. it. Who’s in the Driver’s Seat? • Alfred Adler: psychologist who studied competence and achievement I will win this game if I have good luck I’m not in control I will win this game because I am skilled at it =more possibility of losing I am in some control over it =higher possibility of winning How does this all relate to control? • When we feel we have lost control over our lives – we tend to become ill easier • In cases where control isn’t possible – if there can be information and control of reaction, effects of stress are reduced dramatically. • Difficult people will always exist – how YOU react to them can control your situation better than you think. Do Now: When you feel physically threatened, what do you do? When you feel emotionally threatened, what do you do? Defense Mechanisms • Defense mechanisms help us cope with unbearable thoughts, feelings and wishes. • The idea of this comes from Freud • Some are: repression, suppression, projection, rationalization, reaction formation, displacement and sublimation. Why do we use defense mechanisms? • How do we keep our personalities from getting beat up while we are building them? • Defense Mechanisms do for anxiety, what endorphins do for physical pain – reduce impact • They can be helpful – lead our lives in difficult times • They can be dangerous – distort reality, keep us from taking action in bad situations What are Conversion Disorders? • Serious psychological trauma that converts itself into a real dysfunction. • Severe examples: hysterical blindness, false pregnancy, hysterical paralysis. These physical symptoms DO exist, but are rare. • Hypochondrasis: more common conversion disorder. Over concern about health. Can begin from childhood when great attention was paid to them when they were sick, and not under healthy conditions. How strong is the power of suggestion? • Psychological issues can impact biology • Extreme examples: voo-doo, sudden death syndrome, etc. • Somatoform Disorders: condition in which psychological issues are expressed in bodily symptoms in the absence of any real physical problem. • Mild examples: man feels morning sickness due to wife’s pregnancy, etc. Hey, we only have a week to go! Yes, but mine’s going to be gone after that. What is repression, suppression and denial? • Repression: first line of defense • Pushing out of bad memories after first acknowledging them – actually forgetting them. • Often found in child abuse victims • Suppression: pushing bad memories away while being aware you are doing it. • Denial: Totally denying a problem exists • Freud: “repression is damming up a pool, repressed wishes, thoughts will leak through the barriers that separate the unconscious from the conscious.” What is displacement? I hate this pie!!! I can’t believe Bertha broke up with me. • Venting our feelings on someone or something other than ourselves Separation of emotion from its real object and redirection of the intense emotion toward someone or something that is less offensive or threatening in order to avoid dealing directly with what is frightening or threatening What is Reaction Formation? •Expressing the opposite of what we really feel •Sometimes someone with very vocal and strong opinions about a topic actually practices the opposite of what they preach. Another example of reaction formation? You smell! You have cooties! She’s really pretty, I wonder if she likes me? Wow, he’s talking to me!! The process of expressing the opposite of what we feel What is intellectualization? • The process of removing our feelings about an event and discussing it in a calm rational and unemotional way …and then it burned down, can you believe that? Yup, lost everything. Can I have more iced tea? What is projection? • The process of attributing our own thoughts to someone else. Example: a woman insists that her husband is cheating on her, yet she is the one who is considering it. What is sublimation • The process of channeling emotional energy into constructive or creative activities “Drive past any school playground and find the kid sitting by himself looking miserable…that’s your future successful writer” • Sublimation is probably the most useful and constructive of the defense mechanisms as it takes the energy of something that is potentially harmful and turns it to doing something good and useful. What is rationalization? • The process of explaining a problem so as not to associate blame Victims of domestic violence are often told “You deserved it” or “I didn’t want to hit you, but you asked for it”. This is a form of rationalization. Victims also sometimes exhibit the defense mechanism “Identification with Aggressor” Identification with aggressor Taking on characteristics of someone who • has mistreated us in order to psychologically avoid abuse. • Stockholm Syndrome: The behavior of kidnap victims who, over time, become sympathetic to their captors. The name derives from a 1973 hostage incident in Stockholm, Sweden. The behavior is considered a common survival strategy for victims of interpersonal abuse, and has been observed in battered spouses, abused children, prisoners of war, and concentration camp survivors What is regression? • The process of going backwards in thoughts and behavior to a period when we were taken care of as children. Summary 1. The key to handling life’s problems seems to be actual control, or at least the belief that you are in some control 2. Psychological defense mechanisms are used to protect us– using them in moderation helps to protect our sense of wellbeing to recover from: personality defects, mistakes, emotional pain or problems. 3. Using them for too long or in absence of having a real life can cause long-term damage and impact quality of life. 4. Healthy Personality: accepting yourself and others, being flexible, realistic but still optimistic, and exhibiting control over your life, even when faced with difficulties. A sense of humor helps too!