Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
advertisement

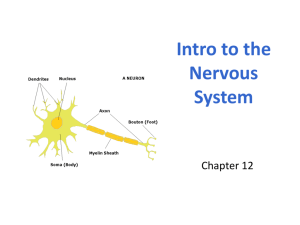
The two functional divisions of the peripheral nervous system are the afferent and efferent divisions. What are their respective functions? 1. 2. 3. 4. Control of the central nervous system/control of the peripheral nervous system Control of neurons/control of neuroglia Sensory input to the CNS/carries motor commands to muscles or glands Carries motor commands to muscles or glands/sensory input to the CNS What would damage to the afferent division of the PNS affect? 1. 2. 3. 4. Ability to learn new facts Ability to experience motor stimuli Ability to experience sensory stimuli Ability to remember past events Which structure of a neuron is capable of propagating an electrical impulse? 1. 2. 3. 4. Dendrites Axon Cell body Perikaryon Which of the following is/are correct concerning structural classifications of neurons? 1. 2. 3. 4. Multipolar neurons control skeletal muscles. Bipolar neurons function in the senses of hearing, smell and vision. Anaxonic neurons have indistinguishable axons and dendrites. All of the above are correct. Are unipolar neurons in a tissue sample more likely to be sensory or motor neurons? 1. 2. 3. 4. They could be either sensory or motor neurons Sensory neurons Motor neurons Neither sensory nor motor neurons One functional classification of neurons is responsible for integrating sensory information with motor output. What is the name of that type of neuron and where are they located? 1. 2. 3. 4. Motor neurons/anterior horn of the spinal cord Proprioceptors/skeletal muscles and joints Interneurons/almost exclusively in the CNS Interocepters/digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular systems Which of the CNS neuroglial cells plays a role in maintaining the blood–brain barrier and repairing damaged neural tissue? 1. 2. 3. 4. Satellite cells Microglia Oligodendrocytes Astrocytes Neuroglia of the PNS include ___ and ___ and their respective functions are ___ and ___. 1. 2. 3. 4. Astrocytes and satellite cells/forming scar tissue and engulfing cellular debris Ependymal cells and Schwann cells/forming cerebrospinal fluid and forming myelin sheath Schwann cells and satellite cells/forming myelin sheath and regulating environment around neurons Microglia and ependymal cells/regulating environment around neurons and forming cerebrospinal fluid Which type of neuroglia would occur in abnormally high numbers in the brain tissue of a person with a CNS infection? 1. 2. 3. 4. Astrocytes Microglial cells Ependymal cells Oligodendrocytes How would a chemical that blocks sodium channels in neuron cell membranes affect its ability to depolarize? 1. 2. 3. 4. It would enhance depolarization. It would completely inhibit depolarization. It would slow depolarization. It would have no effect on depolarization. What effect would decreasing the concentration of extracellular potassium ions have on the transmembrane potential of a neuron? 1. 2. 3. 4. Repolarization Hypopolarization Decreased transmembrane potential Hyperpolarization Which type of gated channel responds to physical distortion of the membrane surface? Where is this ability important? 1. 2. 3. 4. Chemically regulated channels/in dendrites Mechanically regulated channels/sensory receptors Voltage-gated channels/axons of multipolar and unipolar neurons Passive channels/where the channels must remain open Which of the choices below correctly lists the steps of an action potential? 1. 2. 3. 4. Resting potential absolute refractory period relative refractory period All-or-none principle stimulus triggers action potential stimulus does not trigger action potential Depolarization to threshold activation of sodium channels and depolarization inactivation of sodium channels and activation of potassium channels return to normal permeability None of these Why is it impossible for continuous propagation to occur along myelinated axons? 1. 2. 3. 4. Myelin increases resistance to the flow of ions across the membrane. Only nodes along a myelinated axon can respond to a depolarizing stimulus. Continuous propagation uses less energy and fewer sodium ions must be pumped out. 1 and 2 are correct One axon propagates action potentials at 50 meters per second; another carries them at 1 meter per second. Which axon is myelinated? 1. Axon that propagates at 50 meters per second 2. Axon that propagates at 1 meter per second What is the primary distinction between chemical and electrical synapses; which type is more rare? 1. 2. 3. 4. Electrical synapses involve a neurotransmitter/chemical synapses Electrical synapses involve direct connection between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant Excitatory neurotransmitters cause ___ and inhibitory neurotransmitters cause ___? 1. 2. 3. 4. Repolarization/return to resting potential Suppression of generation of action potentials/promote generation of action potentials Synaptic fatigue/synaptic delay Depolarization/hyperpolarization The effects of a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic membrane depends upon ___. 1. The time involved in calcium influx 2. ACh being broken down into AChE 3. The properties of the receptor, not the nature of the neurotransmitter 4. None of these is correct What effect would blocking voltage-regulated calcium channels at a cholinergic synapse have on synaptic communication? 1. 2. 3. 4. Communication would cease. Communication would be enhanced. Communication would be misdirected. Communication would continue as before. One pathway in the central nervous system consists of three neurons, another of five neurons. If the neurons in the two pathways are identical, which pathway will transmit impulses more rapidly? 1. Pathway with three neurons 2. Pathway with five neurons 3. They would transmit at the same rate Which of these is NOT a site at which acetylcholine is released at a synapse? 1. Neuromuscular junctions with skeletal muscles 2. Neuron-to-neuron synapses in the PNS 3. Postganglionic synapses in the sympathetic division of the ANS 4. All of these are true Norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin are all members of which category of neurotransmitter? 1. 2. 3. 4. Hormones Biogenic amines Amino acids Neuropeptides A person you know has experienced sleep problems and prolonged depression. Which neurotransmitter may be in short supply? 1. 2. 3. 4. Dopamine Any of the opioids Acetylcholine Serotonin Which of the following is true concerning neuromodulators? 1. Have short-term effects 2. Act immediately without intermediate steps 3. Affect neither postsynaptic nor presynaptic membrane 4. None of these is correct The relationship between a neurotransmitter, such as NE and cAMP is ____, which is enhanced by a “link” called a ___ ? 1. 2. 3. 4. They are both amino acids/carboxyl group 1st messenger and 2nd messenger/G protein Neurotransmitters/2nd messenger EPSP and IPSP/1st messenger In what way(s) is/are temporal and spatial summation the same? 1. 2. 3. 4. Both require a rapid succession of stimuli at a single synapse. Both are methods by which individual EPSPs combine to result in an action potential. Both occur when simultaneous stimuli are applied at different locations, causing a cumulative effect on transmembrane potential. All of these are correct.