Operations Master / FSMO Roles in Active Directory
advertisement

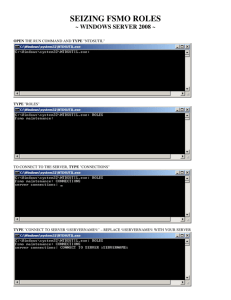
Operations Master / FSMO Roles in Active Directory : Suhail Ashfaq Butt Introduction • In every forest, there are five operations master roles that are assigned to one or more domain controllers. • Forest-wide operations master roles must appear only once in every forest. • Domain-wide operations master roles must appear once in every domain in the forest. • The operations master roles are sometimes called flexible single master operations (FSMO) roles. • By default all roles are assigned to first domain controller. Forest-wide Operations Master Roles Every forest must have the following roles: Schema Master Domain Naming Master Note : These roles must be unique in the forest. This means that throughout the entire forest there can be only one schema master and one domain naming master. Domain-wide Operations Master Roles : Domain-wide Operations Master Roles Every domain in the forest must have the following roles: Relative Identifier (RID) Master PDC Emulator Master Infrastructure Master Note: These roles must be unique in each domain. This means that each domain in the forest can have only one RID master, PDC emulator master, and infrastructure master. Schema Master (Forest Wide) • The schema master domain controller controls all updates and modifications to the schema. • Once the Schema update is complete, it is replicated from the schema master to all other DCs in the directory. • To update the schema of a forest, you must have access to the schema master. • There can be only one schema master in the entire forest. • In order to change or move the Schema Master role to another Server, you must be a member of Schema Administrators Group. • By default, the first server in the forest has Schema Master Role Domain Naming Master (Forest Wide) • The domain controller holding the domain naming master role controls the addition or removal of domains in the forest. • There can be only one domain naming master in the entire forest. • By default, the first server in the forest has the domain naming master role • In order to change or move the Domain Naming Master role to another Server, you must be a member of Enterprise Administrators Group. PDC Emulator (Domain Wide) • The PDC emulator role provides backwards compatibility for Windows NT backup domain controllers (BDCs). • The PDC emulator advertises itself as the primary domain controller for the domain. • It also acts as the domain master browser and maintains the latest password for all users within the domain. • The PDC emulator is necessary to synchronize time in an enterprise. • It processes password changes from clients and replicates updates to the BDCs. • At any time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the PDC emulator master in each domain in the forest. • By default, the first server in the domain has PDC Emulator Master role. • In order to change or move the PDC Emulator role to another Server, you must be a member of Domain Administrators Group PDC Emulator Continued In a Windows 2000/2003 domain, the PDC emulator role holder retains the following functions: Password changes performed by other DCs in the domain are replicated preferentially to the PDC emulator. Authentication failures that occur at a given DC in a domain because of an incorrect password are forwarded to the PDC emulator before a bad password failure message is reported to the user. Account lockout is processed on the PDC emulator. Editing or creation of Group Policy Objects (GPO) is always done from the GPO copy found in the PDC Emulator's SYSVOL share. Infrastructure Master (Domain Wide) The Infrastructure Manager role is responsible for updating references from objects within its domain with objects in other domains. • The infrastructure master compares its data with that of a global catalog. • Global catalogs receive regular updates for objects in all domains through replication, so the global catalog data will always be up to date. • If the infrastructure master finds data that is out of date, it requests the updated data from a global catalog. The infrastructure master then replicates that updated data to the other domain controllers in the domain. • There is one infrastructure operations master in every domain in a forest. • By default, it is placed in the first domain controller in the domain. • In order to change or move the Infrastructure Master role to another Server, you must be a member of Domain Administrators Group. RID Master (Domain Wide) • The RID Master manages the Security Identifier (SID) for every object within the domain. • The RID master allocates sequences of relative IDs (RIDs) to each of the various domain controllers in its domain. • Whenever a domain controller creates a user, group, or computer object, it assigns the object a unique security ID (SID). • The SID consists of a domain SID, which is the same for all SIDs created in the domain, and a RID, which is unique for each SID created in the domain. • By default, the first server in the domain is the RID Operations Master • In order to change or move the RID Master role to another Server, you must be a member of Domain Administrators Group Role Transfer • Used to move a FSMO role gracefully from one live domain controller to another live domain controller. • Transfer a FSMO role to other domain controllers in the domain or forest to balance the load among domain controllers or to accommodate domain controller maintenance and hardware upgrades. • NTDSUTIL Utility is used to perform this task Role Seizure Used only when you have experienced a failure of a domain controller that holds FSMO role and you forced an ungraceful transfer. Seize a FSMO role assignment when a server holding the role fails and you do not intend to restore it. • Seizing a FSMO role is a drastic step that should be considered only if the current FSMO role holder will never be available again. NTDSUTIL Utility is used to perform this task