Chapter 4
advertisement

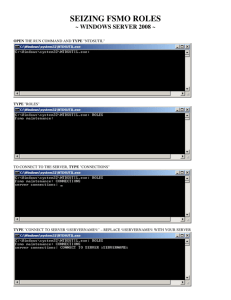
CN1276 Server Kemtis Kunanuraksapong MSIS with Distinction MCTS, MCDST, MCP, A+ Agenda • Chapter 4: Global Catalog and Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) Roles • Quiz • Exercise Global Catalog (GC) • Four main functions: ▫ Facilitating searches for objects in the forest ▫ Resolving User Principal Names (UPNs) ▫ Maintaining universal group membership information ▫ Maintaining a copy of all objects in the domain Global Catalog (Cont.) • Universal group membership caching ▫ Store universal group memberships on a local DC • In Win 2k3 and 2k8, A user must have successfully logged on when a GC server was available and universal group membership caching was enabled • Enabled on a per-site basis. • By default, cache is refreshed every eight hours. Additional GC servers • Each site should contain a GC server to facilitate user logons • When placing a GC at a remote site, you should consider the amount of bandwidth needed Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) Roles • Provides a critical task such as schema update to be assigned by a single DC in each domain or in a forest • Five roles: ▫ Domain specific (one per domain) Relative Identifier Master Infrastructure Master Primary Domain Controller (PDC) Emulator ▫ Forest-wide authoriy Domain Naming Master Schema Master Relative Identifier (RID) Master • Responsible for assigning relative identifiers to domain controllers in the domain • Relative identifiers are assigned by a domain controller when a new object is created • If RID Master is unavailable ▫ unable to create new objects ▫ Unable to move objects between domains Infrastructure Master • Responsible for reference updates from its domain objects to other domains ▫ Assists in tracking which domains own which objects Primary Domain Controller (PDC) Emulator • Provides backward compatibility • Manages time synchronization for the domain • Manages password changes and account lockouts ▫ it provides immediate replication to other domain controllers in the domain. • Managing edits to Group Policy Objects (GPOs) Domain Naming Master • Has the authority to manage the creation and deletion of domains, domain trees, and application data partitions in the forest. ▫ When any of these is created, the Domain Naming Master ensures that the name assigned is unique to the forest. Schema Master • Responsible for managing changes to the Active Directory schema. Placing FSMO Role Holders • When you install the first domain controller in a new forest, that domain controller holds all five of FSMO Roles ▫ Number of domains that are or will be part of the forest ▫ The physical structure of the network ▫ The number of DCs in each domain Managing FSMO Roles • Role transfer ▫ Used to move a FSMO role gracefully from one domain controller to another • Role seizure ▫ Used only when you have experienced a failure of a domain controller that holds a FSMO role and you forced an ungraceful transfer ▫ After the seize, the original holder must be removed from AD before being returned to the network • See Table 4-3 on Page 91 Viewing or transferring Domain-Wide FSMO Role Holders • Open the AD Users and Computers • Right-click the AD Users and Computers node > All Tasks -> Operations Masters Viewing or Transferring the Domain Naming Master FSMO Role Holder • In AD Domains and Trusts • Right-click the AD Domains and Trusts -> Change Operations Master Viewing or Transferring the Schema Master FSMO Role Holder • Open the AD Schema • Right-click AD Schema -> Change Operations Master • You need to register the schmmgmt.dll DLL file using the following syntax: regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll Seizing a FSMO Role • Use the ntdsutil command to access the fmso maintenance prompt and use the seize command. ▫ *See full step on Page 96 or Lab 4 Assignment • Fill in the blank ▫ 1-10 • Multiple Choice ▫ 1-10 • Online Lab 4