Phylum
advertisement

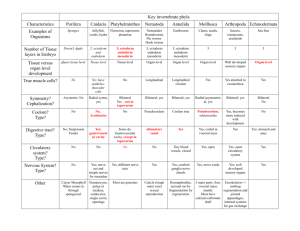
Phylum Classes/Examples Symmetry Body Layers Skeleton Porifera (sponges) Natural bath sponge Glass sponges Calcareous sponges Asymmetrical Some radially semetrical none Spicules of Silicon dioxide, calcium carbonate, or spongin Coelenterata (Cnidaria) hydra, jellyfish, coral Radial symmetry Hydrostatic Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) Planaria, flukes, tapeworms Turbellaria – free living Bilateral symmetry Trematoda- parasitic Cestoda – parasitic Ectoderm, endoderm separated by a layer of mesoglea (non-cellular) Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Nematoda (Roundworms) Ascaris lumbricoides Annelida Earthworm, Leech Neris C. elegans Ascaris Trichina Bilateral symmetry Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Hydrostatic Oligochaeta Polychaeta Hirudinea Bilateral symmetry Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Hydrostatic Mollusca clams, squid, snails Bilvalva Gastropoda Cephalopoda Bilateral symmetry Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Hydrostatic and various forms of a shell secreted by mantle. Arthropoda insects, spiders, crustaceans, millipedes, centipedes Diplopoda Chilopoda Insecta, Arachnida Crustacea Bilateral symmetry Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Chitinous exoskeleton Radial symmetry Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Excoskeleton of ossicles Echinodermata starfish, sand dollar sea urchins None Phylum Respiratory System Circulatory System Nervous System Porifera (sponges) None Cellular diffusion None Coelenterata (Cnidaria) hyrda, jellyfish, coral Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) Planaria, flukes, tapeworms None Cellular diffusion None None Diffusion None Nerve ladder composed of two longitudinal nerve cords and lateral nerves Flame cells Nematoda (Roundworms) Ascaris lumbricoides Annelida Earthworm, Leech Neris None Diffusion None Anterior ganglion and ventral nerve cord Pores Diffusion through skin as respiratory surface Closed 5 “hearts” with ventral and dorsal blood vessel Brain and nerve cords Paired nephridia Mollusca clams, squid, snails Gills in bivalves and cephalopods. Vascularized mantle in gastropods Insect-Trachea & spiracles. Arachnida –book lungs. Crustacea – gills Water-vascular system by diffusion Open system in bivalves and gastropods. Closed in cephalopods Open system with heart and ventral blood vessel Brain and ventral nerve cords Kidney Brain and nerve cords Open system Brain and nerve cords/ring Arachnidia & insect Malpighian tubules Crustacean – green gland Water-vascular system Arthropoda insects, spiders, crustaceans Echinodermata starfish, sand dollar sea urchins None Excretory System None Cellular diffusion None Cellular diffusion Nerve net Phylum Appendages Body Cavity Digestive System Reproductive Means Porifera (sponges) None None Osculum for water to exit None Intracellular (phagocytosis) Asexual- budding and regeneration Sexual – gemmules Coelenterata (Cnidaria) hyrda, jellyfish, coral Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) Planaria, flukes, tapeworms None Tentacles with nematocysts for protection & food capture None Acoelomate Extracelluar digestion in gastrovascular cavity mouth present Asexual – budding and regeneration. Sexual hermaphroditic Acoelomate Turbellaria/planaria Mouth, protrusible pharynx, branched intestine Parasitic - none Complete mouth, pharynx intestine and anus Asexual – regeneration Sexual - hermaphroditic Nematoda None (Roundworms) Ascaris lumbricoides Annelida May have tentacles (clam Earthworm, Leech worm) Neris Pseudocoelomate Sexual with separate sexes Coelomate Complete, mouth, pharynx, crop, gizzard, intestine, anus Sexual hermaphroditic do not self-fertilize Mollusca clams, squid, snails May have tentacles Coelomate Sexual with both hermaphroditic and separate sexes Arthropoda insects, spiders, crustaceans Legs, wings, antenna, tail Coelomate Complete, mouth and anus. Specialization of feeding for different classes see notes Complete, mouth to anus. Variations among classes see notes Echinodermata starfish, sand dollar sea urchins Tube feet, spines Coelomate Complete, mouth and anus Sexual separate sexes Sexual with separate sexes