Nursing care for patients with Urinary Tract Infection
advertisement

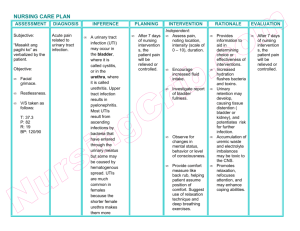
4/8/2020 Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract (the normal urinary tract is sterile above the urethra). UTIs are generally classified as infections involving the upper or lower urinary tract 4/8/2020 4/8/2020 Lower UTIs include bacterial cystitis (inflammation of the urinary bladder), bacterial prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland), and bacterial urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). Upper UTIs are much less common and include acute or chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis), interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidney), and renal abscesses. 4/8/2020 For infection to occur, bacteria must gain access to the bladder, attach to and colonize the epithelium of the urinary tract to avoid being washed out with voiding, evade host defense mechanisms, and initiate inflammation. Most UTIs result from fecal organisms that ascend from the perineum to the urethra and the bladder and then adhere to the mucosal surfaces. 4/8/2020 Ascending infection E.Coli ---> 86% In men , obstructive abnormalitites UTI ---> sepsis and nosocmila infections Upper UTI ---> recurrent bladder infection 4/8/2020 Dysuria, frequency, urgency, nocturia Suprapubic pain or discomofort Microscopic or gross hematuria 4/8/2020 Urine microscopy Urine culture Patients with indwelling catheter---> asypmtomatic 4/8/2020 Antibiotic therapy( follow up culture) 3-7-10 4/8/2020 Pyelonephritis hematogeneuos spread leading to sepsis 4/8/2020 History of recurrent UTI? Voiding habits? Suprapubic pain or tenderness? 4/8/2020 Acute pain R/T inflammation of the bladder mucosa Deficient knowledge R/T prevention of recurrent UTI 4/8/2020 4/8/2020 4/8/2020