File
advertisement

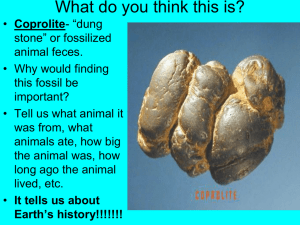
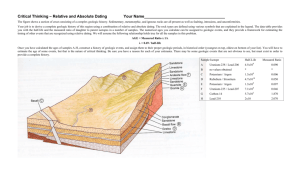
Earth Systems 3209 Unit 2: Historical Geography (14 classes) Unit 2 Outline • • • • • • • • • • • Uniformatarianism Vs. Catastrophism Relative Vs. Absolute time Core Lab 1: Interpreting geologic events Absolute Dating Unit 2 STSE: Absolute Dating CBC Doc: Canadian shield Unit 2 Quiz Fossils Core Lab 2: Estimating Dinosaur size Geologic time scale Unit 2 Test Question! • Where these mountains (Himalayan) formed quickly or slowly? Why? Question! • Did the dinosaurs mass extinction happen quickly or slowly? Why? So do Geologic events happen Quickly? or Slowly? Catastrophism • Is a concept popular in the 1700-1800’s which states that earth’s landscapes had been shaped primarily by great disasters or catastrophes (floods, storms, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions etc.) • James Ussher: Anglican Arch Bishop and scholar attempted to fit the rate of change of Earth processes into a relatively young aged Earth. ** Unknown causes which were fast James Hutton • Scottish Geologist after years of studying landforms and rocks • “ the present is the key to the past” and • “that, the physical, chemical, biological laws that operate today to shape Earth also operated in the past.” Uniformitarianism • two key concepts; 1) the geologic processes at work today were also active in the past. 2) the present physical features of Earth were formed by these same processes, at work • over long periods of time. So is one right and one wrong? • Not necessarily, some geologic events can be explained by catastrophes, wile other through uniformitarianism Question! • How would the ideas of Catastrophism and Uniformitarianism explain the formation of the Hymalayas? Dating geologic events how old are you? • Quantitative measurements: describing something using numbers • how old are you? (use quantitative) • Example: He is 14.5 years old how old are you? • Qualitative measurments: Describing something using words. • Can you describe your age without using any numbers at all? How? Absolute time • Identifies the actual date of an event, & pinpoints the exact time in history when something took place. • For example, the extinction of the dinosaurs about 66 million years ago and the age of • Earth is approximately 4.6 Billion years. . Relative time • Attempts to place events in a sequence of formation, but does not identify their actual date of occurrence. • Comparing events to each other often does this. • Can’t tell us how long ago something happened; only that it followed one event and preceded another. Work in groups • answer questions on Handout