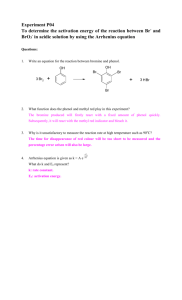
Lecture 8
advertisement

Growth and the envrionment Figure 5.2 Figure 5-3 Psychrophilic environment and psychrophiles. Figure 5-4 Thermophilic environments and thermophiles. Figure 5.5 Figure 5.6 Figure 5-8 Halophilic salt flats and halophilic bacteria. Changes in pH Figure 5.11 Figure 5-15 A soda lake ecosystem. Figure 5-16 Na+ circulation in alkaliphiles. Figure 5.17 Oxygen as an Electron Acceptor • Many microorganisms use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in a process called aerobic respiration. Figure 5.18 Oxygen-related growth zones in a standing test tube Figure 5.19 • Generation and destruction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) Figure 5.20 Humans Influence Microbial Ecosystems • Maximum diversity in an ecosystem is maintained, in part, by the different nutrient-gathering profiles of competing microbes. Figure 5.23 • Microbes die at a logarithmic rate. • Decimal reduction time (D value) is the length of time it takes an agent or a condition to kill 90% of the population. Figure 5.25 The Phenol Coefficient • The phenol coefficient test compares the effectiveness of disinfectants. Table 5.3 Figure 5.30 Antibiotics • Antibiotics are chemical compounds synthesized by one microbe that kill or inhibit the growth of other microbial species. • Penicillin mimics part of the bacterial cell wall. • - Prevents cell wall formation and is bactericidal Figure 5.31 Effect of ampicillin (a penicillin derivative) on E. coli Figure 5.32