Plants as Living Organisms Plant Parts and Their Functions
advertisement

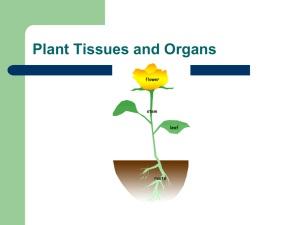
Plants as Living Organisms Plant Parts and Their Functions Plant and Soil Science Topic 2014 Basic Parts of the Plant Roots Stems Leaves Flower (not included in this lecture) Root Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Anchor Plant Absorb water and minerals Translocate water and minerals to stem Store Food Root Parts Primary root – – Secondary root – First root that the seed sends out Anchors root Branches off of primary root Root Cap – Protects roots while they grow Root Parts Root hairs: Tiny one celled hair like extensions of the epidermal cells located near the tips of the roots where vascular tissues have formed. – Increase surface area – Absorb water and minerals from soil Adventitious roots Roots that begin growth from the stem – Different type of Roots A. Tap Root – – – – Continuation of the primary root Ideal for anchorage Penetration is greater for water Storage area for food made by photosynthesis Different type of Roots B. Fibrous Roots – – Many finely branched secondary roots Shallow roots cover a large area More effective absorption of water and minerals Roots hold the soil to prevent erosion Types of Roots Stem Function 1. Translocate water, minerals and food to the leaves 2. Support the leaves and display them to light 3. Store food and water 4. Produces new stem tissue Stem Tissues Xylem – – Provide structural support Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves Phloem – Transports food made in leaves to the rest of the plant Buds Bud scales – Terminal Bud – Primary growing point Lateral buds – Tip of twig Apical Meristem – Protect under developed parts Can develop into secondary branches Apical dominance – Hormones that prevent lateral buds from developing Buds Leave Function 1. Make food through photosynthesis 2. Provide site of gas exchange 3. Store food Cross section of Leaf Principal Tissues of the Leaf Epidermis – Cuticle – Stomata – Waxy substance covers the leaves and stems Waterproof layer that keeps water in plants Openings in the epidermis mainly located on underside of leaves Exchange of gases Guard Cells Two cells located on each side of stomata Open and closes stomata Principal Tissues of the Leaf Mesophyll layer – Palisade mesophyll – Spongy mesophyll Primary site of photosynthesis Contains air and chloroplasts Site of photosynthesis and gas exchange Veins or vascular bundles – – – In spongy mesophyll Phloem tissues conduct food from photosynthesis to rest of plant Xylem tissues conduct water and minerals up to cells in leaves and stems Simple vs. Compound Simple – Single leaf blade and a petiole Compound – A petiole and more then one leaf blades Shapes of leaves