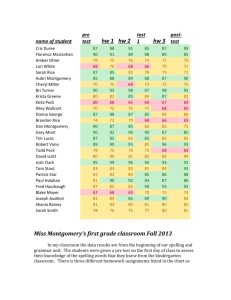
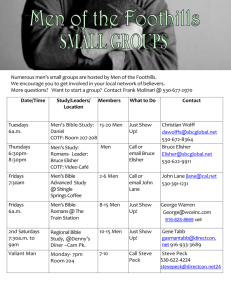
Efficient verifier-based key agreement protocol for three parties
advertisement

Public Key Encryption with Conjunctive
Keyword Search and Its Extension to a
Multi-user System
Source: Pairing 2007, LNCS 4575, pp.2-22, 2007
Author: Yong Ho Hwang and Pil Joong Lee
Presenter: Li-Tzu Chang
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Conclusion
Introduction
B
BB
Bn
[EApub [M], PECK (Apub, (W1 , W2, …, Wm))]
傳送文件
搜尋包含關鍵字
的文件,
產生一個暗門Tw
AA
2
A
3
A
n
傳回Alice的文件
Tw
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Generic Model for PECK
Adversarial Models for PECK
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Conclusion
Generic Model for PECK
KeyGen (security parameter ): pk, sk
Takes as input a security parameter and returns params (system
parameters) and the public/private key pair (pk, sk).
PECK(pk,W ): S
Executed by the sender to encrypt a keyword set W = {w1, . . . , w}.It
produces a searchable keyword encryption S of W with the public key
pk.
Trapdoor (sk,Qi ):TQi
Takes as input the secret key sk and the keyword query Q ={I1, . . . , Im,
wI1 , . . ., wIm} for m ≤ where Ii is an index to denote a location of wIi ,
and returns a trapdoor TQ for the conjunctive search of a given keyword
query.
Test (pk,S): 0,1
Executed by the server to search the documents with the keywords of a
trapdoor TQ. It takes as input the public key pk, the searchable keyword
encryption S, Then output ‘1’ if S includes Q and ‘0’ otherwise.
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Generic Model for PECK
Adversarial Models for PECK
IND-CC-KA
IND-CR-KA
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Construction
Adversarial Models for PECK
IND-CC-KA game
A
Setup
Keygen(1k):pk,sk
(保有)
pk,params
Phase 1
Trapdoor Oracles
Trapdoor Queries (Qi)
Trapdoor (sk,Qi)
TQi
queries a number of keyword sets
Q1,…Qd
Adversarial Models for PECK
A
Challenger C
select w0,w1
w0,w1 (無法區別來自哪個trapdoor)
pick β∈R{0,1}
Sβ =PECK(pk,Wβ)
Phase 2
Trapdoor (sk,Qi): TQi
if TQi 無法區別 w0,w1
Guess
Sβ
Trapdoor Oracles
queries keyword sets Qd+1,…Qr
Trapdoor Queries (Qi ≠w0,w1)
TQi
output β’∈R{0,1}
if β =β’ win the game
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Generic Model for PECK
Adversarial Models for PECK
IND-CC-KA
IND-CR-KA
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Construction
Adversarial Models for PECK
IND-CR-KA game
A
Setup
Keygen(1k):pk,sk
(保有)
pk,params
Phase 1
Trapdoor Oracles
Trapdoor (sk,Qi)
Trapdoor Queries (Qi)
TQi
queries a number of keyword sets
Q1,…Qd
Adversarial Models for PECK
A
select W*
Challenger C
W*
select random keyword set R(W*無法區別來自哪個trapdoor)
pick β∈R{0,1}
Sβ =PECK(pk,wβ),
Sβ
where w0=W*,w1=R
Phase 2
Trapdoor Oracles
queries keyword sets Qd+1,…Qr
Trapdoor Queries (Qi ≠w0,w1)
Trapdoor (sk,Qi): TQi
if TQi 無法區別 w0,w1
Guess
TQi
output β’∈R{0,1}
if β =β’ win the game
Adversarial Models for PECK
Adversary of adversary A
IC-CC-CKA
Adv
1
(1 ) Pr '
2
k
IC-CR-CKA
Adv
IND-CC-CKA
PECK , A
IND-CR-CKA
PECK , A
1
(1 ) Pr '
2
k
In the IND-CC-CKA game the adversary A selects two
target keyword sets, w0 and w1, and gives them to the
challenger C.
In the IND-CR-CKA game A selects a target keyword
set w0 and gives it to C.
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Conclusion
Proposed PECK Scheme
KeyGen(1k):
params=(G1,G2,ê,H1(·),H2(·),g),(pk,sk)
H1(·):{0,1}logw→G1 , H2(·):{0,1}logw→G1 , g is a
generator of G1
select x∈R Zp* ,compute y=gx , (pk,sk)=(y,x)
PECK(pk,W): S=(A,B,C1,…,Cl)
Sender select W={w1,…,w2} ,s,r ∈R Zp*
compute A=gr, B=ys, Ci=hirfis , 1≦i ≦l ,hi=H1(wi),
fi=H2(wi)
Proposed PECK Scheme
Trapdoor (sk,Q): TQ=(TQ,1,TQ,2,TQ,3,I1,…,Im)
select t ∈R Zp*
compute TQ,1=gt ,TQ,2=(hI1,…hIm), TQ,3=(fI1,…fIm),
where Q={I1,…,Im}
Test(pk,S,TQ):
check eˆ(TQ ,1 , i m1CIi ) eˆ( A, TQ ,2 ) eˆ( B, TQ ,3 )
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Generic Model for PECK
Adversarial Models for PECK
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Conclusion
mPECK scheme
KeyGen(1k): params=(G1,G2,ê,H1(·),H2(·),g),
(pk1,sk1),…,(pkn,skn)
H1(·):{0,1}logw→G1 , H2(·):{0,1}logw→G1 , g is a
generator of G1
select x1,…,xn∈R Zp* ,compute yi=gxi ,
(pki,ski)=(yi,xi)
mPECK(pk1,…,pkn ,W): S=(A,B1,…,Bn,C1,…,Cl)
Sender select W={w1,…,w2} ,s,r ∈R Zp*
compute A=gr, Bj=yjs, Ci=hirfis , 1≦i ≦l , hi=H1(wi),
fi=H2(wi)
mPECK scheme
Trapdoor (skj,Q): Tj,Q=(Tj,Q,1,Tj,Q,2,Tj,Q,3,I1,…,Im)
select t ∈R Zp*
compute Tj,Q,1=gt ,Tj,Q,2=(hI1,…hIm)t, Tj,Q,3=(fI1,…fIm)t/xj,
where Q={I1,…,Im}
Test(pkj,S,Tj,Q):
check eˆ(Tj ,Q ,1 , i m1CIi ) eˆ( A, T j ,Q ,2 ) eˆ( B j , T j ,Q ,3 )
Security game for mPECK
A
Setup
Keygen(k):pk1,,…,pkn
sk1 ,…, skn
(保有)
pk1 ,…,pkn , params
Phase 1
Trapdoor Oracles
Trapdoor (skj ,Qi)
Trapdoor Queries (j,Qi)
T j,Qi
queries a number of keyword sets
Q1,…Qd
Adversarial Models for PECK
A
Select W*
Challenger C
W*
select random keyword set R(W*無法區別來自哪個trapdoor)
pick β∈R{0,1}
Sβ =PECK(pk1,…,pkn ,Wβ),
Sβ ,w0,w1
w0=W*,w1=R
Phase 2
Trapdoor Oracles
queries keyword sets Qd+1,…Qr
Trapdoor Queries (j,Qi ≠w0,w1)
Trapdoor (skj,Qi): Tj,Qi
if Tj,Qi 無法區別 w0,w1
Guess
Tj,Qi
output β’∈R{0,1}
if β =β’ win the game
Outline
Introduction
Preliminaries
Generic Model for PECK
Adversarial Models for PECK
Proposed PECK Scheme
Multi-user PECK System
Conclusion
Conclusion
To send an encrypted message with conjunctive
keyword search to n users, the sender has only to
add Bi from the recipient’s public keys.
The server should separately store ciphertexts for
each user.
Introduce a new concept called a multi-user
PECK scheme, which can achieve an efficient
computation and communication overhead and
effectively manage the storage in a server for a
number of users.