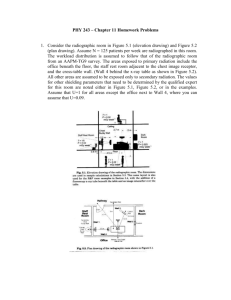
Thyroid ultrasound
advertisement

THYROID DISORDERS Too Hot, Too Cold or Just Right Uzma Khan, MD. Associate Professor of Clinical Internal Medicine University of Missouri-Columbia ACP 2012 On her show, Oprah Winfrey admitted a thyroid problem was the cause of her tiredness Simple case • 45 year old lady, mother of two teenagers, works at Wal-Mart pharmacy • Presents with tiredness, sleepy all the time, weight gain of 10 lbs. over the last 5 years, skin and hair is dry • Her hair dresser advised her to get her thyroid checked History- Questions to ask • No history of radiation to head and neck • No personal history of thyroid problems – During pregnancy? • No family history of thyroid problems --“ goiter” Work up • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH Free T4 Total T4 Free T3 Total T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • • • • • Imaging studies Thyroid uptake and scan Thyroid ultrasound CT scan of neck PET scan • Fine needle aspiration Endocrine Review, 2008 The percentage of subjects with an elevated TSH level by sex and decade of age. Percentages of hypothyroidism ranged from 4% to 21% in women and from 3% to 16% in men. Canaris et al, The Colorado Thyroid Disease Prevalence Study, 2000 The percentage of euthyroid subjects compared with those with an elevated TSH level who reported each symptom. The proportions of elevated, normal, or low lipid levels according to thyroid function status. TSH Subclinical T4 N T3 N Mild N or N or overt Levothyroxine (T4) • Medical situations where T4 medication may be affected. • Estrogen: Pregnancy, OCP, HRT • Drugs that interfere with T4 absorption • Iron, Calcium • Cholestyramine (cholesterol resin Rx) • At least 4h between T4 and these drugs! • Increase TBG: estrogen, heroin, methadone • Decrease TBG: depakote, dilantin, androgens Parameter T3/T4 Combos Production rate nmol/day T3 T4 50 110 • Thyrolar, Armour thyroid -Fraction from thyroid 0.2 • Combo pill of T3 and T4 1.0 • Relative Ratiometabolic of T4:T3potency = 4:1 (not 14:1) • Serum T3 still not slow release concentration • Few small studies showing benefit - Total (nmol/L) • 1999 NEJM study 33 patients 1.8 • Benefit: mood & cognitive function -Free (pmol/L) 5 • Cytomel is only T3………..limited use Fraction of total hormone in free form 0.3 • Only check a TSH…do not check T4 or T3 1.0 0.3 100 20 0.02 Fraction intracellular 0.64 0.15 Half-life (days) 0.75 6.7 Complex Case • 42 year old female presents with left thyroid nodule detected during annual physical exam • She is a country singer , has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has a healthy 2 year old son • There is no history of head and neck irradiation, her mother has hypothyroidism, there is no family history of thyroid cancer • She denies dysphagia, ROS is negative, and states” I did not even know it was there” Thyroid Incidentaloma Palpable: 5% women 1% men Ultrasound: 19-67% Thyroid Nodules Prevalence Autopsy Data Autopsy data from 821 patients at the Mayo clinic with “normal” thyroids on clinical examination ◦ 49% had thyroid nodules 12 % had single nodule 37% had multiple nodules ◦ 35.5% of these nodules were >2 cm Single Nodule Multiple Nodule No Nodules 12 51 37 Mortensen et al. J Clin Endocrinology, 1955 Common Varieties of Thyroid Nodules Technique The location of the thyroid is identified by inspection. Using the anterior or posterior approach, palpate the thyroid to identify nodules Note the size and number of nodules. Note the consistency of the nodule. Palpate regional lymph nodes for consistency and mobility. • Anterior approach • Posterior approach The Pemberton sign Wallace C , Siminoski K Ann Intern Med 1996;125:568-569 Work up • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH Free T4 Total T4 Free T3 Total T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • • • • • Imaging studies Thyroid uptake and scan Thyroid ultrasound CT scan of neck PET scan • Fine needle aspiration Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Free T4: Normal Total T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • • • • • Imaging studies Thyroid uptake and scan Thyroid ultrasound CT scan of neck PET scan • Fine needle aspiration Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Total T4 Free T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • Imaging studies • Thyroid uptake and scan ? Toxic multinodular goiter? • Thyroid ultrasound • CT scan of neck • PET scan • Fine needle aspiration Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Total T4 Free T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • Imaging studies • Thyroid uptake and scan ? Toxic multinodular goiter? • Thyroid ultrasound – Multiple thyroid nodules with concerning features in left thyroid nodule • CT scan of neck • PET scan • Fine needle aspiration Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Total T4 Free T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • Imaging studies • Thyroid uptake and scan ? Toxic multinodular goiter? • Thyroid ultrasound – Multiple thyroid nodules with concerning features in left thyroid nodule • CT scan of neck • PET scan • Fine needle aspiration – Indeterminate! Genetic medicine Era…New tools!! • She declines surgery, wants to know if we can be more “sure” about cancer • The endocrinologist says “ will assess the cells for mutations”……? Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Total T4 Free T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • Imaging studies • Thyroid uptake and scan ? Toxic multinodular goiter? • Thyroid ultrasound – Multiple thyroid nodules with concerning features in left thyroid nodule • CT scan of neck • PET scan • Fine needle aspiration – Indeterminate! Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Total T4 Free T4 Total T3 Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • Imaging studies • Thyroid uptake and scan ? Toxic multinodular goiter? • Thyroid ultrasound – Multiple thyroid nodules with concerning features in left thyroid nodule • CT scan of neck • PET scan • Fine needle aspiration – Indeterminate! Thyroid Cancer Incidence and Mortality, 1973-2002 •10th leading cancer type in women •22590 new cases/year •2400 deaths/year •50% increase in incidence in 25 years Davies, L. et al. JAMA 2006;295:2164-2167. Trends in Incidence of Thyroid Cancer (1973-2002) and Papillary Tumors by Size (1988-2002) in the United States Davies, L. et al. JAMA 2006;295:2164-2167. Risk of Malignancy A study of 317 thyroid incidentalomas by Nam-Goong et al in 2004 48 50 Percentage 40 44 % Patients % Papillary Thyroid Cancer 30 20 10 0 8 12 <0.5 cm 15 13 0.5-1 cm > 1 cm Size of incidentaloma Nam-Goong et al. Clinical Endocrinolog. 2004 Radioactive iodine management • Consensus: – Fine needle aspiration---if shows malignancy – Total thyroidectomy – Ablative doses of radioiodine – Suppressive treatment – Periodic follow up with thyroglobulin and imaging with radioiodine scans Close follow up rhTSH • recombinant form of human TSH • Thyrogen® (thyrotropin alfa for injection) is a highly purified • Thyrotropin alfa is synthesized in a genetically modified Chinese hamster ovary cell line • Can be used for – Remnant ablation – Follow up WBS/thyroglobulin Scheduling of rhTSH Doses and Diagnostic Procedures • Recommended dose: 0.9mg IM q24 hr x 2 doses • Serum Tg protocol is identical for both Tg alone testing and when combined with WBS • 4 mCi 131I should be used for scans; which should be acquired for 30 minutes and/ or 140,000 counts Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 rhTSH 0.9 mg rhTSH 0.9mg 131 I (if WBS is performed) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Day 4 Day 5 Serum Tg with or without WBS Thursday Friday Maximum Percent Change from Baseline in the Sum of the Longest Diameters (SLD) of Target Lesions Motesanib Diphosphate in Progressive Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Sherman S et al, NEJM, July 2008 Know the thyroid well!! You may need it as the next White House Physician TSH: 6.1 mIU/ l ( 0.40-4.5) TSH : first line test ◦ 2nd generation: good immunometric, sandwich assays: up to 0.1 ◦ 3rd generation: ? Varying sensitivity immunochemiluminometric Assays: up to 0.01 • TSH: normal range: 0.40 4.5 m IU/L • <0.1: Hyperthyroidism • 0.1 – 0.3: subclinical hyperthyroidism • 0.32-5.6: normal vs central hypothyroidism • 6-10: subclinical hypothyroidism • > 10: primary hypothyroidism Know what you are “fishing for”…………………………………………….. T4 or T3 Free T4 : normal • T4 – Free T4 : good – Total T4: make sure you know about TBG • T3 – FT3: very minute amounts – TT3: helpful in T3 thyrotoxicosis, remember TBG! Thyroid Function T4 Protein* binding + 0.03% free T4 Protein* binding + 0.3% free T3 80% (peripheral) 20% T3 * Thyroid hormone Binding: Ratio of T4:T3 -stored in thyroglobulin: 15:1 -secreted in blood: 10:1 Increased production due to any reason Leads to an increase in T3 TBG 75% Transthyretin 15% Albumin10% Serum TSH range in the US population Not a Gaussian curve…………… Tail Hollowel et all, NHANES III survey, JCEM 2002 Thyroid tests • Thyroglobulin – Large glycoprotein – Only source: thyroid follicular cell - Assay limitation: - Tg Ab - >variability 25% - Know why you are doing it - Thyroid cancer - Exogenous TH? • Antibodies – 10% of general population – TPO> Hashimotos – TSI > Graves – Tg> non specific • Remember PGAs Utility of Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) RAIU RAIU Grave’s Thyroiditis Toxic MNG Exogenous Toxic adenoma Iodine ingestion Struma ovarii Metastatic thyroid Ca Hyperemesis gravidarum Trophoblastic tumor Your Interpretation 24 hour RAIU = 25%. TSH 0.2 mU/L. Thyroid palpably “cobblestone” texture. Thyroid Ultrasound (US) Normal Ultrasonographic Anatomy • Current resolution of US allows demonstration of thyroid nodules as small as 1 mm. Transverse right lobe of the thyroid gland Features of a Benign Nodule • Hyperechoic nodule • Halo sign or a smooth margin • Thin walled cyst without solid component • Calcification with acoustic shadowing • Colloid within nodule • Low vascularity • Multiple nodules Longitudinal image of thyroid nodule with peripheral calcification and halo Features of a Malignant nodule • Hypoechoic or heterogeneous nodule • Microcalcification without shadowing • Increasing size on TSH suppression • Cervical lymphadenopathy Intranodular vascularization • Invasion of muscle • Irregular border • Thick walled cyst Longitudinal image of a solid thyroid nodule with incomplete halo and coarse calcifications Your interpretation Left thyroid longitudinal TSH: 0.2 mIU/L ( 0.40-4.5) Higher Serum Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Level in Thyroid Nodule Patients Is Associated with Greater Risks of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Advanced Tumor Stage • The likelihood of thyroid cancer increases with higher serum TSH concentration: 29 % ( 241 of 843 patients) • Even within normal TSH ranges, a TSH level above the population mean is associated with significantly greater likelihood of thyroid cancer than a TSH below the mean. • Higher TSH level is associated with advanced stage DTC – Stage III/IV---- mean TSH was 4.9 ± 1.5 mIU/ml – Stage I/II--- mean TSH was 2.1 ± 0.2 mIU/ml . Haymart et al, 2008 Not useful Techniques for FNA Manual Ultrasound-Guided Management Guidelines for thyroid cancer repeat surgery Cooper et al, 2006 Not helpful results • Mutational analysis : shows: positive for BRAF: V 600 E mutation Three distinct pathways lead to neoplastic proliferation of thyroid cells Asa S, Ezzat S, and Kondo T, 2006 BRAF Mutation One of the three RAF genes ( ARAF and CRAF) -Mutated in about 7% of human cancers -- V600E is the most common mutation--oncogene -Most common mutation in PTC -Unique to PTC - -Santisteban, 2007 BRAF negative PTC -BRAF mutations are not a major event in post-Chernobyl childhood thyroid carcinomas. Lima J, et al. 2004 -Low frequency of BRAF mutations in childhood thyroid carcinomas. Kumagai A, et al. 2004 -Low prevalence of BRAF mutations in radiation-induced thyroid tumors in contrast to sporadic papillary carcinomas. Nikiforova MN, et al. 2004 Thyroid tests • Thyroglobulin – Large glycoprotein – Only source: thyroid follicular cell - Assay limitation: - Tg Ab - >variability 25% - Know why you are doing it - Thyroid cancer - Exogenous TH? • Antibodies – 10% of general population – TPO> Hashimotos – TSI > Graves – Tg> non specific • Remember PGAs Work up- Next step • • • • • • • • • Lab tests TSH: 0.2 mIU/L Free T4: Normal Total T4: normal Total T3: Normal Free T3 TPO antibodies Thyroglobulin Thyroglobulin Antibodies • • • • • Imaging studies Thyroid uptake and scan Thyroid ultrasound CT scan of neck PET scan • Fine needle aspiration