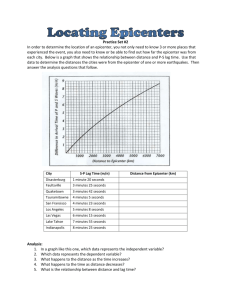
Lab 2: Locating Earthquakes
advertisement

GEOL 108 - Crises of a Planet Lab 2 - Locating Earthquakes Sept. 9 - 14, 2012 Department of Earth Sciences LAB 2 - EARTHQUAKES - KEY CONCEPTS • Reading seismograms • Using travel time curves to triangulate an epicenter • Predicting tsunami arrivals EARTHQUAKES | 2 Department of Earth Sciences SEISMIC WAVES • Release of accumulated energy leads to quake • Energy travels in waves of vibration − Body waves • P-waves - primary • S-waves - secondary − Surface waves • Love • Rayleigh • Waves travel at different known velocities EARTHQUAKES | 3 Department of Earth Sciences DETERMINING QUAKE EPICENTER • Step 1: Identify P and S arrival times 2:37:10 2:41:50 EARTHQUAKES | 4 Department of Earth Sciences DETERMINING QUAKE EPICENTER • Step 2: Subtract arrival times to get S-P delay 2:37:10 S-P delay = 2:41:50 – 2:37:10 S=P delay = 0:04:40 (4 minutes, 40 seconds) 2:41:50 EARTHQUAKES | 5 Department of Earth Sciences DETERMINING QUAKE EPICENTER • Step 3: Use seismic wave travel time vs. distance chart to determine distance to epicenter S-P delay = 2:41:50 – 2:37:10 S-P delay = 0:04:40 (4 minutes, 40 seconds) Find where S-wave line minus P-wave line equals the delay you determined Read what distance that delay corresponds to… ~ 3,600 km here EARTHQUAKES | 6 Department of Earth Sciences DETERMINING QUAKE EPICENTER • Repeat steps 1-3 for two other seismic stations Distance to epicenter (determined from reading seismographs, not shown) Los Angeles: 1800 km Austin: 3150 km Urbana: 3400 km EARTHQUAKES | 7 Department of Earth Sciences DETERMINING QUAKE EPICENTER • Step 4: Use a compass to plot all possible epicenter locations. The epicenter is where they intersect. Distance to epicenter (determined from reading seismographs, not shown) Los Angeles: 1800 km Austin: 3150 km Urbana: 3400 km EARTHQUAKES | 8 Department of Earth Sciences TSUNAMIS Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. Photograph by Sadatsugu Tomisawa, AP • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2uJN3Z1ryck EARTHQUAKES | 9 Department of Earth Sciences PREDICTING TSUNAMI ARRIVALS • Tsunamis are triggered by earthquakes • Tsunamis travel at 600 km/hr on average • Given a known epicenter, you can predict the tsunami arrivals elsewhere by rearranging the equation we used last week (velocity = distance / time) • Assignment will ask you to plot how far a tsunami has traveled in 1, 2, 3 and 4 hours. So what should you solve the above equation for? EARTHQUAKES | 10 Department of Earth Sciences