POSTER_RE_Health_FINAL
advertisement

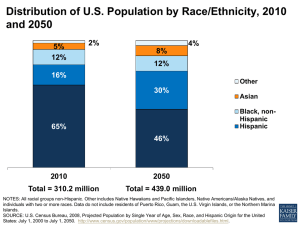
Race/Ethnicity and the Use of Preventive Care Among Adults with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities WHAT IS NATIONAL CORE INDICATORS (NCI)? • Multi-state collaboration of state DD agencies • Measures performance of public systems for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities • Assesses performance in several areas, including: employment, community inclusion, choice, rights, and health and safety • Launched in 1997 in 13 participating states • Supported by participating states • NASDDDS – HSRI Collaboration National Core Indicators (NCI) WHAT IS NATIONAL CORE INDICATORS (NCI)? • Currently 35 states, the District of Columbia and 25 sub-state regions (including all CA Regional Centers) NCI State Participation 2012-13 National Core Indicators (NCI) WHAT IS NCI? • Adult Consumer Survey • Family Survey Adult Family Survey (person lives at home; 18 and older) Family Guardian Survey (person lives out-of-home; 18 and older) Children Family Survey (child lives at home; under 18 years old) • Provider Survey Staff Stability • System Data Mortality Incidents National Core Indicators (NCI) WHAT IS NCI? Adult Consumer Survey • Standardized, face-to-face interview with a sample of individuals receiving services Background Information Section I (no proxies allowed) Section II (proxies allowed) • No pre-screening procedures • Conducted with adults only (18 and over) receiving at least one service in addition to case management • Section I and Section II together take 50 minutes (on average) National Core Indicators (NCI) Methods, Measures and Sample: Data Source • Adult Consumer Survey (ACS), 2011-2012 data collection cycle • Background Information section: demographics, residence, health, and employment information. Generally collected from records by case managers. • 19 states, one regional council • Total N: 11,224 individuals National Core Indicators (NCI) Methods, Measures and Sample: Race/Ethnicity • Source: two items from Background Section Ethnicity (Hispanic, or non-Hispanic) Race (American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, Black or African, American, Pacific Islander, White, or Other race not listed) • Items combined to create: Race/Ethnicity White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic • Other race/ethnic categories too small for analysis National Core Indicators (NCI) Methods, Measures and Sample: Preventive Care • • • • Person has a primary care doctor: No Yes Last complete annual physical exam (routine): In the past year One year ago or more Last dentist visit: In the past year One year ago or more Last eye exam/vision screening In the past year One year ago or more National Core Indicators (NCI) Methods, Measures and Sample: Preventive Care • • • • Last hearing test: Within the past 5 years 5 years ago or more (or never) Flu vaccination in the past 12 months: Yes No Ever had a vaccination for pneumonia: Yes No “Don’t know” responses were excluded from these analysis – i.e. excluded from both denominator and numerator National Core Indicators (NCI) FINDINGS National Core Indicators (NCI) Race/Ethnicity of Sample Race/Ethnicity Frequency Percent of total African American, NonHispanic Hispanic 2,251 20.1% 457 4.1% White, Non-Hispanic 8,516 75.9% 11,224 100.0% Total 20.1% 4.1% 75.9% National Core Indicators (NCI) African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic White, NonHispanic Preventive Care: Primary Care Doctor (p < .001) 100% 95% 96.8% 96.0% African American, NonHispanic Hispanic 91.8% 90% 85% 80% 75% 70% 65% 60% 55% 50% White, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Preventive Care: Physical Exam in Past Year (p < .001) 100% 95% Dentist Visit in Past Year (p < .001) 100% 95% 92.1% 88.9% 90% 90% 85.2% 85% 85% 80% 80% 75% 75% 70% 70% 65% 65% 60% 60% 55% 55% 50% 50% White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic 84.8% 79.0% 74.7% White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Preventive Care: Eye Exam/Vision Screening in Past Year (p < .05) Hearing Test in Past Five Years ( p < .01) 90% 90% 85% 85% 80% 80% 75% 75% 70.9% 70% 69.3% 70% 66.5% 65% 61.5% 65% 62.8% 60% 60% 55.5% 55% 55% 50% 50% White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Preventive Care: Flu vaccine in past year (p < .001) Ever had pneumonia vaccine (p < .001) 100% 100% 90% 90% 80% 80.5% 70.6% 72.6% 80% 70% 70% 60% 60% 50% 50% 40% 40% 30% 30% 20% 20% 10% 10% 0% 44.9% 34.5% 32.4% 0% White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Preventive Care: Simple binary logistic regressions (odds ratios) White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic * p<.05, ** p<.01, ***p<.001 National Core Indicators (NCI) Primary care doc Phys exam Dental exam Vision Hear test screen Flu vacc Pneum vacc ref ref ref ref ref ref ref 2.66*** 0.69*** 0.53*** 1.06 0.81** 0.58*** 0.65*** 2.13** 0.50*** 0.67** 0.78* 0.92 0.64** 0.59*** BUT: • Differences may be due to other demographic characteristics. • The following demographic variables were tested and found to be significantly different among the three racial/ethnic categories: State Age Gender Individual’s primary language Individual’s primary means of expression Level of intellectual disability Mobility Other diagnoses (in addition to ID/DD) Poor health status Support needed for behavioral issues Residence type National Core Indicators (NCI) Demographic Differences: Average Age (p < .001) 45 Gender (p < .01) 44.8 70% 61.9% 44 60% 43 50% 42 40.9 41 58.5% Female 55.2% 44.8% 41.5% 38.1% 40% 40 30% 39 37.7 38 20% 37 10% 36 35 White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic 0% White, NonHispanic African American, NonHispanic Male Hispanic Demographic Differences: Primary language (p < .001) 100% 99.2% Primary means of expression (p<.01) 99.4% English 100% Non-spoken Spoken other 90% 90% 79.0% 80% 80% 70% 70% 60% 60% 50% 50% 40% 40% 30% 30% 22.4% 21.0% 20% 20% 10% 10% 0.8% 77.6% 74.3% 25.7% 73.3% 26.7% 0.6% 0% 0% White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Demographic Differences: Level of Intellectual Disability (p < .01) 50% White, Non-Hispanic 45% African American, Non-Hispanic 41.6% 40% 35% 34.4% 35.4% Hispanic 37.6% 32.5% 30.4% 30% 25% 20% 16.0% 14.6% 14.5% 15% 17.1% 13.6% 12.4% 10% 5% 0% Mild ID National Core Indicators (NCI) Moderate ID Severe ID Profound ID Demographic Differences: Mobility level (p < .001) 90% 80.9% 81.0% 80% White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic 75.0% Hispanic 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 15.4% 11.1% 11.2% 10% 9.6% 8.0% 7.9% 0% Moves self around environment without aids National Core Indicators (NCI) Moves self around environment with aids or uses wheelchair independently Non-ambulatory, always needs assistance Demographic Differences: Other diagnoses 50% White, Non-Hispanic 45% African American, Non-Hispanic 40% Hispanic 35.7% 35% 30.0% 28.1% 30% 25% 20% 15% 14.0% 10.7% 13.7% 11.4% 10% 5.8% 5% 4.6% 4.0% 8.5% 5.7% 2.3% 0.8% 0.5% 0% Autism-Spectrum Disorder (p < .001) National Core Indicators (NCI) Mental Illness or Psychiatric Diagnosis (p < .001) Hearing Loss- Severe or Profound (p < .01) Down Syndrome (p < .001) Alzheimer's (p < .001) Demographic Differences: Needs support to manage problem behavior (p < .05) Poor health status (p < .01) 50% 50% 45% 49% 40% 48% 35% 47% 30% 46% 25% 45% 20% 44% 15% 43% 10% 42% 5% 5.2% 3.9% 2.7% 0% 46% 46% 42% 41% 40% White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic National Core Indicators (NCI) Hispanic White, NonHispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Demographic Differences: Residence Type (p < .001) 50% 46.5% 45% 41.5% 40.4% 40% White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic 35% Hispanic 32.5% 32.3% 29.9% 30% 25% 20% 15% 13.2% 12.4% 8.5% 10% 5% 11.6% 9.0% 8.9% 4.9% 4.6% 3.8% 0% Institution National Core Indicators (NCI) Community-Based Residence Independent Home/apt Parent/relative’s home other Preventive Care: Multivariate Logistic Regressions State Race White, Non-Hispanic African American, Non-Hispanic Hispanic Primary care doc *** Phys exam *** ref 1.5 0.98 1.01 1.24 1.18 ref 0.82 0.95 1.01** 0.96 .35*** Dental exam *** *** ref 0.60*** 0.85 .99*** 0.99 .53** ref 0.69 0.71 0.83 0.58 1.02 0.96 1.1 1.36 *** ref 0.76 0.28*** 0.21*** 0.48* ref 0.76 0.82 0.73 0.91 1.14 1.09 0.95 0.75* *** ref 0.47** 0.15*** 0.11*** 0.29*** ref 1.03 1.21 0.73* 1.11 ref 0.88 0.81 0.98 1.05 Age Gender: male Primary Language: Not English Level of ID Level ID: No ID ref Level ID: Mild ID 0.66 Level ID: Moderate ID 0.67 Level ID: Severe ID 0.46 Level ID: Profound ID 1.01 Other diagnosis: Mental Ill 0.68* Other diagnosis: Hearing loss 0.97 Other diagnosis: Downs 1.66 Poor Health 1.17 Residence Type Residence Type: Institution ref Residence Type: Community Based Residence 1.02 Residence Type: Independent home/apt 0.83 Residence Type: Parent/relative's home 0.9 Residence Type: other 1.06 Mobility Mobility: Moves self without aids ref Mobility: Moves self with aids 1.39 Mobility: Non-Ambulatory 1.19 Expression: Spoken 1.19 Support for behav. problems 1.48* Coefficients for states not shown; * p<.05, ** p<.01, ***p<.001 National Core Indicators (NCI) Vision Hear test Flu vacc screen *** *** *** ** *** ref ref ref 1.25** 1.12 0.68*** 1.2 1.44 0.78 1 1 1.03*** 0.96 1.03 0.85* 0.68 0.64 0.85 * * ref ref ref 1.09 1.08 1.28 0.96 1.15 1.54* 0.81 1.17 1.53* 0.98 1.32 1.90** 1.1 1.20* 1.22* 1.22 3.30*** 1.1 1.19 1.78*** 1.21 0.92 0.82 1.47* *** *** *** ref ref ref 0.95 0.37*** 0.44** 0.58*** 0.17*** 0.17*** 0.40*** 0.11*** 0.15*** 0.87 .22*** .28*** *** *** ref ref ref 0.81** 0.99 1.38** 0.69*** 0.82 1.55** 1.08 1.23 1.02 0.94 1.09 1.14 Pneum vacc *** ref 0.82 0.85 1.04*** 0.94 1.05 ref 0.76 0.86 1.05 0.96 1.21* 1.18 1.19 2.51*** *** ref 0.8 0.59** 0.59** 0.78 *** ref 1.59*** 2.13*** 0.72** 1.14 Conclusions: Effect of race/ethnicity • There are differences in likelihood of receiving preventive care by race/ethnicity • White, Non-Hispanic respondents less likely to have a primary care doc White, Non-Hispanic respondents more likely to have had a physical exam, a dental exam, a flu vaccination and/or a pneumonia vaccination Adults with IDD of different racial/ethnic backgrounds also differ in other demographic factors Where they live Their age Their means of expression Their language Their level of ID Other diagnoses Their level of mobility Their health • It is crucial to control for these demographic factors. National Core Indicators (NCI) Conclusions: Effect of race/ethnicity • Controlling for other demographic factors, racial/ethnic background is a significant predictor for : • Has had dentist visit in past year • African American, Non-Hispanic respondents are significantly less likely to have had a dentist visit in the past year Has had eye exam in past year • African American, Non-Hispanic respondents are significantly more likely than White, NonHispanic respondents to have had an eye exam in the past year Has had flu vaccine in past year • African American, Non-Hispanic respondents are significantly less likely than White, NonHispanic respondents to have had a flu vaccine in the past year Controlling for other demographic factors, racial/ethnic background is no longer a significant predictor for: Has primary care doctor Has had physical exam in past year Has had hearing test in the past five years Has ever had pneumonia vaccine National Core Indicators (NCI) Conclusions Other Findings • Speaking a language other than English has a negative effect on receipt of preventive care. • Residence type is strongly related to use of preventive care. • Individuals with less mobility are significantly more likely than those who are selfmobile (without using aids) to have been vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia. • Age is significantly related to receipt of physical exam, dentist visit and flu and pneumonia vaccines. • Being in poor health is a significant predictor of receiving flu and pneumonia vaccinations. • State in which individual resides is a highly significant predictor of receipt of all preventive care variables – much state to state variation. National Core Indicators (NCI) Limitations • “Don’t know” responses are excluded from analyses. For some health care variables, the rate of “don’t know” responses are fairly high. • Data less likely to be available in independent/family home settings – i.e. higher rates of “don’t know” responses. • Choice is not taken into account - what if person does not want to get a specific test? • There may be other pertinent factors affecting likelihood of receipt of care that were not controlled for. • Standards regarding recommended frequency of care used are for general population. • No data on income or SES. Previous research has shown that racial/ethnic disparities are often confounded by disparities based on SES. National Core Indicators (NCI) References • • • • • • • • • Ashton, C., Haidet, P., Paterniti, D., Collins, T., Gordon, H., O’Malley, K., Petersen, L., Sharf, B., Suarez-Almazor, M., Wray, N., Street, R. (2003). Racial and ethnic disparities in the use of health services: Bias, preferences or poor communication? J Gen Intern Med. 18:146-152 Bershadsky, J. & Kane, R. (2010). Place of residence affects routine dental care in the intellectually and developmentally disabled adult population on Medicaid. Health Services Res. 45(5 pt 1: 1376-89 Bershadsky, J., Taub, S., Bradley, V., Engler, J., Moseley, C., Lakin, K. C., Stancliffe, R. J., Larson, S., Ticha , R. & Bailey, C. (2012). Place of residence and preventive health care for developmental disabilities services recipients in twenty states. Public Health Reports, 127, 475-485. Bonito, A., Eicheldinger, C., Lenfestey, N. (2005). Health disparities: Measuring health care use and access for racial/ethnic populations. Final Report, Part 2. Retrieved on March 4, 2013 from http://www.cms.gov/ResearchStatistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/Reports/downloads/bonito_part2.pdf Havercamp, S., Scandlin, D., Roth, M. (2004). Health disparities among adults with developmental disabilities, adults with other disabilities, and adults not reporting disability in North Carolina. Public Health Reports. 119 418-426 Jones, C. (2000). Levels of racism; A theoretic framework and a gardener’s tale. American Journal of Public Health. 90(8): 1212-1215 Kawachi, I., Daniels, N., Robinson, D. (2005). Health disparities by race and class: Why both matter. Health Affairs. 24(2):343-352 Magaña, S., Parish, S., Rose, R., Timberlake, M., Swaine, J. (2012). Racial and ethnic disparities in quality of health care among children with autism and other developmental disabilities. Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. 50 (4) 287-299 Newacheck, P., Hung, Y., Wright, K. (2002). Racial and ethnic disparities in access to care for children with special health care needs. Ambulatory Pediatrics. 2 (2): 247-254 National Core Indicators (NCI) Contacts • HSRI Julie Bershadsky: jbershadsky@hsri.org Dorothy Hiersteiner: dhiersteiner@hsri.org • NASDDDS Mary Lee Fay: MLFay@nasddds.org • NCI website: www.nationalcoreindicators.org National Core Indicators (NCI)