Textbook Chapter Ten Notes
advertisement

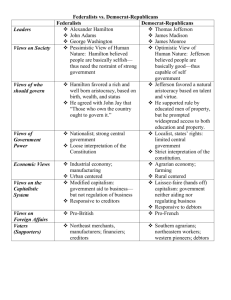
Growing Pains Population was rising rapidly Most lived in rural areas west of Appalachian mountains Washington for President Unanimously elected Was no so into politics and not so smart. More of a strength of character than politician Welcomed to NY with a huge ceremony Washington established the cabinet – advisors The Bill of Rights Constitution did not allow all individual rights like freedom of religion and trial by jury James Madison was leading figure First 10 amendments to constitution (Bill of Rights) were established and included Madison protected minority and individual rights while preserving a strong central government First Congress also established effective federal courts Hamilton Revives the Corpse of the Public Credit Alexander Hamilton was doubted to have loyalty Wanted to fix debt from AOC by favoring the wealthy so they would be nice to government and send them money Wanted congress to first finance entire national debt “Funding at par” meant paying off debts at face value Convinced Congress to fund the states debts because it was a “national cause” – lost money fighting for independence - this really helped link the state and federal government more States with huge debts liked this obviously but Virginia did not have a huge debt and only agreed when they said they would but the federal government near them Custom Duties and Excise Taxes Debt was swelling but Hamilton was not concerned and thought it was good Wanted to get money from foreign tariffs Passed first tariff law – imposed a small tax but didn’t have much of an impact since the economic depended on agriculture and commercial Also had a tax on domestic items Hamilton Battles Jefferson for a Bank Hamilton wanted to build a national bank that would hold surplus federal funds, keep money in circulation and therefore stimulate business, and print money Jefferson opposed and said that there was no authority for this and power not specifically to the federal government were with the states – so if any bank was happening it should be by the states – strict interpretation of constitution Hamilton said that Congress can pass anything “necessary and proper.” Congress was instructed to collect taxes and regulate trade and needed a bank to do so – loose interpretation of Constitution Washington accepted and bank was passed. North was mostly in favor and South was mostly opposed. Chartered for 20 in Philadelphia and had capital of 10$ dollars Mutinous Moonshiners in Pennsylvania There was a whiskey rebellion in 1794 - it was a burden on economic necessity and medium of exchange instead of just a tax Washington was alarmed and called in the militia Whiskey rebellion had big consequences – there was a new respect for the government yet people were angry because of the way they forced the law The Emergence of Political Parties Hamilton boosted sound credit – treasury could now borrow money from Netherlands Thought successful, Hamilton challenged the states rights. Some didn’t even want the constitution in the first place, and now he was slowly taking away more rights – made for organized opposition There were always different parties with different ideas but they were never official Having parties seemed disloyal Jefferson and madison had first opposition and then put ideas in newspaper and different parties began to emerge Ever since there have been 2 parties – but usually the one that is not in power balances the government so everyone is happy The Impact of the French Revolution Washington had to deal with the 2 parties French revolution was a big deal and made everyone scared When France became a republic Americans were happy King was beheaded and federalists were scared of the Jeffersonian masses Jeffersonian thought that getting freedom was not that easy – has to be some fighting involved FR didn’t hurt America but Britain was sucked in Washington’s Neutrality Proclamation Many liberals wanted to take the side of the French and against the British Neutrality Proclamation – America had to remain neutral and not get involved Genet, representative of the French republic tried to get rid of Washington and neutrality proclamation but was taken out Embroilments with Britain British sold Miami Indians weapons and the Indians attacked Americans In Treaty of Greenville we got most of Ohio and Indiana and gave the Indians money, right to hunt on land they gave British attacked Americans because they thought they would be on the French side Washington sent John Jay to London to try and avert war which made the Jeffersonians unhappy British finally agreed to evacuate US soil to pay for the damages they caused Jeffersonians were really angry and thought what Jay did was basically surrender to the British Spain was afraid of an Anglo-American alliance so they made a treaty with the US that basically gave them everything they wanted Washington decided to retire eventually Washington had huge contributions – solidified the central government, expanded west, established good merchant marine John Adams Becomes President Federalists nominated John Adams for next election because Hamilton was so unpopular and democratic-republicans nominated Jefferson The election was extremely passionate Adams, who was very stubborn and an intellectual aristocrat won slightly and Jefferson became vice It was hard for Adams because Hamilton hated him and tried to get cabinet members against him Also, Adams had a violent quarrel with France Unofficial Fighting with France French hated Jay’s treaty and saw it as an alliance with British John Adams sent 3 men to France and they met men there that said they would have to pay a lot of money to even speak with foreign minster of France (XYZ affair) Thought the bribes were intolerable Sent a wave of hysteria and military was established Lots of bloodshed at sea that was thought could become a full-fledged war Adam Puts Patriotism above Party France was already fighting England – didn’t want to fight America too Adams could have been really popular if he engaged in war but didn’t because he realized war had to be avoided and sent the name of a new minster to france Wanted to get land in America again and end war Convention of 1800- treaty signed in paris agreeing to annul marriage and US would pay for war damages Adams was good because he kept peace and allowed the purchase of lousiana Adams traded peace for popularity The Federalist Witch Hunt Federalists thought of laws to diminish their Jeffersonian foes and do antifrench stuff Raised citizenship wait from 5 to 14 years which went against American hospitality President could deport dangerous foreigner during peace or deport/imprison them in a time for hostility – gave huge powers to president Sedition Act went against freedom of speech and press – anyone who went against government/officials had to pay a heavy fine and imprisonment Jeffersonians were indicted in the Sedition Act Went against constitution but supreme court had federalists so they would never go against it Acts got a lot of popularity and federalists had a huge victory in congressional elections The Virginia (Madison) and Kentucky (Jefferson) Resolutions Jeffersonians realized they had to get rid of Alien and Sedition acts before more of their rights were taken away Jefferson secretly planned resolutions that were approved by Kentucky/Virginia Compact theory – 13 colonies came together to create a contract, so the national government was the creation of this. Thus, the states were final judges on of the government was overstepping authority and breaking the “compact.” So government overstepped and so states had to nullify the acts These resolutions were later used to secession – but Jefferson used it to make sure federalists didn’t take over Federalists versus Democratic Republicans Parties were stabilized Hamilton federalists wanted to crush democratic revolts, protect lives of wealthy. States should help support private enterprise. Hamiltonians lives near sea, ports Jefferson lead middle class and underprivileged and poorer Jefferson was an aristocrat who owned slaves but still had sympathy for the lower class Jeffersonians wanted a weak central government with no special privileges for the rich and big supporter of agriculture based economy Jefferson thought that government was for people but not everyone – ignorant, illiterate should not be able to vote Jefferson also thought that landless people should not vote because they should not go against those who own land – only could be solved by slavery Big believer in free everything and thought people could rise and newspapers should not be from the government Hamilton wanted to expand foreignly and expand trade with british Jefferson was pro French then British, and wanted to expand democracy at home Everything was conflict and unstable