Porosity & Permeability Lab: Soil Science Worksheet
advertisement

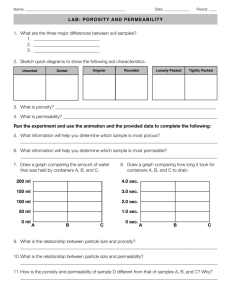
Name _______________________________________________ Date ______________ Lab # _______________ Virtual Lab – Porosity and Permeability Purpose: To investigate how different types of soil hold water. Question: How does soil type affect the movement of groundwater? Background Information: Groundwater is water that moves through soil and rocks below Earth's surface. When groundwater moves through soil, the structure of the soil affects its movement. Groundwater moves through the spaces between soil particles. These spaces are called pores. Not all soils have the same amount of pore space. The amount of pore space, or porosity depends on the number and size of pores in soil. If the pores in soil are all connected, allowing water to pass through them. This means that soil is permeable. The ease with which water moves through the soil is called permeability. Explain porosity and permeability in your own words. Porosity – Permeability - A soil with high porosity and many small pores can hold a lot of water, but it takes longer for the water to enter all the pores. This means that when a soil has higher porosity it has lower permeability. A soil's porosity and permeability are important to many people. Farmers must be aware of soil conditions so they can determine the best way to grow crops. Builders also consider these conditions in the area they plan to build. Environmentalists are concerned with porosity and permeability when there is a risk that a pollutant might be introduced into the groundwater supply. Pre-Lab : Describe the difference between a well sorted sediment sample and a poorly sorted sediment sample. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Part 1 Procedure: 1. Color in the pore spaces between the particles blue to see which has the highest porosity. 2. Label the diagrams below either Sorted or Unsorted 1. Which has the most open space? Sorted or Unsorted sediments? Circle one 2. Which would hold the most water? _______________ Why? ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the relationship between sorting and porosity? ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What would this look like on a graph? Porosity Pore size Part 2: Get a chrome book and log on. 1. Go to http://hmxearthscience.com/Warehouse/geology/surface_processes/animations/perm.poros.swf Before you release the water, answer the questions below. 2. Which tube do you think will flow the fastest? ____________________ Explain why ______________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Which tube do you think will flow the slowest? ____________________ Explain why ____________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Release the water and watch, repeat to see which tube is the fastest / slowest. 4. Where your predictions correct? ______________________ Why or why not? ________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Complete the column below Table 1 Column A B C D Bead Size and color Infiltration time (seconds) 4mm Red 8 mm yellow 12 mm Green Mixed Are these particles Sorted or unsorted? Pore size S,M, L 3 2 1 4 6. Compare the amount of water stored in the three sorted samples to the amount of water in the unsorted sample. ____________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is the relationship between bead/sediment size relate to Infiltration time? ____________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What would this look like on a graph? Infiltration time 9. Sediment/bead size Describe the difference between the infiltration rate of a well sorted sediment sample and an unsorted sorted sediment sample. _________________________________________________________________________ Part 2 1. Go to http://regentsearth.com/ILLUSTRATED%20GLOSSARY/Infiltration.htm 2. Before you release the water, use page 6 & 7 of the ESRT to fill in the grain size on the table below and answer questions 3 and 4. 3. Predict which column will empty the slowest_________________________ why? _______________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Predict which column will empty the fastest_________________________ why? _______________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Table 2 Sediment Name Grain Size Gravel 5-10 mm Rate of permeability of 1 meter of water Sand Silt Clay 5. Where your predictions correct? ______________________ Why or why not? ________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is the relationship between the grain size and rate of permeability of water? ________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What would this look like on a graph? Be sure to label axis. Permeability Rate Grain Size 8. Based on this investigation, which type of soil is the most permeable? Which is the least permeable? How do you know? Support your statement with evidence. _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________