Water Movement Through Soil

Water Movement Through Soil
Or… Why did that bucket of water
I spilled disappear into the ground.
Porosity
The movement of water through the soil is controlled by certain characteristics.
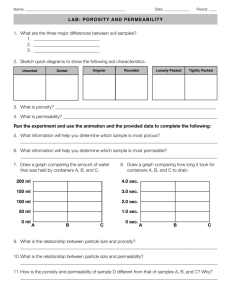
Well sorted
Porosity – The number of pores in a material compared to its volume.
Unsorted
Usually expressed as a percentage.
Well sorted
Unsorted
Sorting
• Well sorted soils contain rounded particles similar in size not closely packed. They are the most porous.
• Unsorted soils which contain different sized particles and are more closely packed are less porous.
• Soils with flattened or angular grains, such as clay soils, can pack closely together and have a low porosity.
• Important – particle size alone may not affect the porosity of the soil.
• Soils with different particle size but with similar shape and packing can have the same porosity.
48% 48%
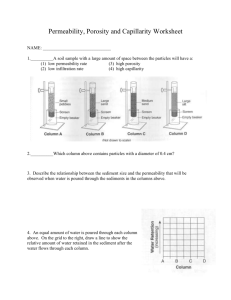
Permeability
• The ability of a soil to transmit water.
• The rate of permeability, or how fast the water moves through the soil, depends on the size of the pores and how the pores are connected.
• For example: sandy soils have large well connected pores buy clay soils do not.
Therefore, sandy soils have a higher permeability than clay soils.
Permeability is Directly Related to Porosity
PERMEABILITY
POROSITY
Runoff
• Occurs when rainfall exceeds permeability.
• Or when a soil is saturated and cannot retain more water.
• Or when the slope of a soil’s surface is too great to allow infiltration.
Capillary Action in Soil
• The movement of a liquid along the surface of a solid caused by the attraction of molecules of the liquid to the molecules of the solid.