Impulse and Momentum PP
advertisement

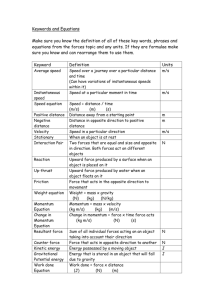
Bellringer Pick up exam (Both Parts) Objectives Make observations about momentum and figure out what factors effect it. Test average: 77% Last year was an 84! What is momentum? Momentum is mass times velocity: p = momentum m = mass v = velocity If all three boats were moving at the same velocity which would be easier to stop? Why? Demonstrations Grab a sheet of paper to record your observation. Which would have more momentum, A linebacker at full sprint or at rest? Bellringer What is the momentum of a 75kg baby crawling at 15m/s? Include units! Objectives Complete collision lab. If all three boats were moving at the same velocity which would be easier to stop? Why? Bellringer What is the momentum of a racecar that is traveling at 30m/s and has a mass of 1,000kg? 30,000kg(m/s) or 30,000N*s Objectives Understand how to use momentum conservation to solve problems. Practice applying this knowledge to help you solve problems. Lab Due tomorrow Only need to show one example calculation for each type of calculation. What is momentum? Momentum is mass times velocity: p = momentum m = mass v = velocity Example If you have a mass of 62 kg and you are running at a constant velocity of 8 m/s what is your momentum If your car has a mass of 2000kg and is parked what is it’s momentum? Total Momentum The total momentum of a system can be found by adding the momentum of each part of the system together? Just like how we added all the forces on a system together to find the net force Total Momentum Conservation of Momentum If two objects, that are not subjected to any external forces, interact, the total momentum of the objects before the interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction. pbefore = pafter pAi + pBi = pAf + pBf mAvAi + mBvBi = mAvAf + mBvBf Is Momentum Always Conserved? Is momentum conserved when a car crashes into a wall? Why? Elastic and Inelastic collisions Elastic Collision: When two or more objects collide and momentum is conserved. i.e. Atoms scattering Inelastic Collision: When two or more objects collide and momentum is not conserved. i.e. Car crash Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Most collisions are inelastic because some energy is lost to some type of friction (sound, heat, etc.) We can treat some problems as elastic collisions to make it easier to solve problems that deal with momentum. Checkpoint 1. Are inelastic or elastic collisions more common in real life? Why? 2. Are inelastic or elastic collisions more common in our little physics world? Why? Exploding Carts - Lab Conservation of Momentum A 90 kg running back is running up field with a constant velocity of 7 m/s. A 105 kg linebacker is running down field with a velocity of 6.5 m/s as he tackles the running back. After they collide find their total velocity. pbefore = pafter pRi + pLi = pRf + pLf mRvRi + mLvLi = mRvRf + mLvf Conservation of Momentum Can you figure out the final velocity of the running back if the linebacker doesn’t make the tackle? What would we need to know? What would be the running back’s final velocity if the linebacker had a final velocity of 3 m/s down field. pbefore = pafter pRi + pLi = pRf + pLf mRvRi + mLvLi = mRvRf + mLvLf Collected Collected! A 5.0 kg gun fires a 0.0020 kg bullet. If the bullet exits the gun at 800 m/s [east], calculate the recoil velocity of the gun. Homework Read pages 244 to 248 (Two-Particle Collisions through Propulsion in Space). Then answer problems 23, 24, and 25 on page 249 Bellringer A 3 kg gun fires a 0.0010 kg bullet. If the bullet exits the gun at 500 m/s, calculate the recoil velocity of the gun. Objective Solidify your understanding and application skill of problems that deal with the conservation of momentum. Explosion Lab Physics Club Today Physics Learning Center Thursday after school Now if you scored a 70 or below on the last exam (without bonus) you must attend. I recommend that anyone who isn’t scoring above an 85 attends. Momentum Practice Questions 10 minutes Momentum Videos Momentum Practice Problems Bellringer Pick up papers Take out and check your homework. Objective Be able to solve conservation of momentum problems Begin to look into situations when momentum is not conserved. Textbook Practice Problems Textbook page 246 17 18 19 20 21 Homework Read pages 244 to 248 (Two-Particle Collisions through Propulsion in Space). Then answer problems 23, 24, and 25 on page 249 Bellringer Bellringer – 2 mins to hand in Take out your homework and start to check it. DO STOP WORK Objective Investigate situations where momentum is NOT conserved. Focus on how force and time effect the change in momentum. What do you know about momentum? So far we have And: pbefore = pafter Is this all there is to know about momentum or is there more for us to discover? Where should we start looking? Momentum and Force How does the force on an object relate to its change in momentum? Crash Test Dummies Why do we have crash test dummies? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8adfGDQ-uRA Crash Test Dummies What is a car’s momentum before a collision with the wall? What is a car’s momentum after a collision with the wall? Is momentum of this system conserved? Crash Test Dummies Where does all the initial momentum of the system go? Crash Test Dummies Does a crash test dummy experience a force as it collides with something else? How do you know? Any evidence? How does this force relate to momentum? Crash Test Dummy Checkpoint Does a larger force or a smaller force change the momentum of a system more? Why? Momentum and Time How does the time of a collision relate to the change of momentum? Tree Jumping Is it possible to jump out of a twenty foot tall tree without hurting yourself? Is it possible to jump out of a twenty foot tall tree and hurt yourself? Do both systems have the same change in momentum? Tree Jumping What can you change to make sure that you do not hurt yourself as you jump out of a tree from 20 feet above the ground? Parkour: The aim to move from one place to another, negotiating the obstacles in between. The discipline uses no equipment and is non-competitive, but still extremely hardcore. Video Clips http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aAhPaiajwDY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Kvw2BPKjz0 What is the difference? Why do hardcore parkour(ers?) not injure themselves when they fall long distances? Does gravity effect them differently? The time of impact changes the force they feel. The Change in Momentum is…? What is Newton’s Second Law? (Yup it’s back again) What is the equation for acceleration? Substitute. How can this be related to the change in momentum? CANNONBALL!!!!!!!!! Use this new equation for the change in momentum to explain how this man is able to pull of this remarkable stunt. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lH45xpTASiw&list =PL311480F303F33687&index=10 Egg Toss Are eggs easy to break? Change in Momentum What is the relationship or pattern between force and time and how do they both relate to the change in momentum of a system? Bellringer Fill out paper Next exam grade must be equal to or higher than your last grade, and must be above a 70. Objectives Practice solving problems using a brand new equation. Solidify your understanding of how your change in momentum can be a life or death situation. Exam This Friday Science Learning Center Thursday after school. 70 or below Any other time we’re both free Physics Club Tuesday after school. Finish application Test GPS Homework Read “What about corked bats?” Write a solid argument about whether or not you believe that a cork bat is easier to hit a baseball with. Make sure to use information from the reading. This will be discussed and collected tomorrow. Momentum Review Five regents physics review questions 5 minutes Solo 3 minutes Partner Impulse The impulse of a collision is the change in momentum of the collision. The change in momentum is equal to the force during the collision multiplied by the time of the collision. Or… Impulse http://www.yout ube.com/watch?v=7RSUjxiZnME Why doesn’t the egg always survive if it always experiences the same impulse? What happens to the impulse if an object experiences the same force for a shorter amount of time? What happens to the impulse if an object a greater force for the same amount of time? Example A 65kg cross country runner is lined up at the starting line. The official shoots the gun to start the race. The runner exerts a constant horizontal force of 200N on the ground for 3 seconds. What is the runner’s impulse? What is the runner’s velocity? Runner 𝐽 = 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 𝑡 𝐽 = 200𝑁 ∗ 3𝑠 𝐽 = 600𝑁 ∗ 𝑠 𝑜𝑟 𝑚 600𝑘𝑔 𝑠 𝐽 = ∆𝑝 𝐽 = 𝑝𝑓 − 𝑝𝑖 𝐽 = 𝑚𝑣𝑓 − 𝑚𝑣𝑖 𝑚 600𝑘𝑔 𝑠 𝑣𝑓 = = 65𝑘𝑔𝑣𝑓 − 𝑚 9.23 𝑠 𝑚 0𝑘𝑔 𝑠 Practice A 500kg car is driving at constant velocity and then hits a wall and comes to rest. The car experiences a 10,000N force for 0.5 seconds. What is the impulse experienced by the car? What was the initial velocity of the car? Car Crash 𝐽 = 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 𝑡 𝐽 = 10,000𝑁 ∗ 0.5𝑠 𝐽 = 5,000𝑁 ∗ 𝑠 𝑜𝑟 𝑚 5,000𝑘𝑔 𝑠 𝐽 = ∆𝑝 𝐽 = 𝑝𝑓 − 𝑝𝑖 𝐽 = 𝑚𝑣𝑓 − 𝑚𝑣𝑖 𝑚 = 𝑠 𝑚 −10 𝑠 5,000𝑘𝑔 𝑣𝑖 = 0𝑘𝑔 𝑚 𝑠 − 500𝑘𝑔𝑣𝑖 Bellringer Take out your homework Objectives Master impulse problems Finish station problems Physics Learning Center on Thursday 70 or below Physics Club Finish application Test GPS Impulse side Stations Bellringer What is a person’s change in momentum if they have a mass of 75kg and are driving at 30m/s then come to a stop. Is this person injured after they stop? Explain Objective Master Impulse and Momentum Friday’s Test 10 Multiple Choice 3 Long Answers 1 Bonus 8 Station Problems Multiple Choice Questions Textbook problems. Happy and Sad Balls Which one has the greatest change in momentum and why? Impulse Practice Problems Bellringer Cart A has a mass of 25kg and an initial velocity of 10m/s before it hits cart B, which has a mass of 10kg and an initial velocity of 5m/s. If cart A has a final velocity of just 7m/s, what is the final velocity of cart B? Air Track Head on collision Why is it safer to be in the more massive car during a head on collision? Trains! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dzoHx29pkbI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UNmt13Y870U https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1mHtOW-OBO4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5WcKIgrRlj8 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vRfbL6memSs Readings Grade Slips Last Lab Lab Time