Thermo notes 2016 - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
advertisement

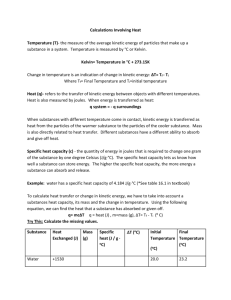
Welcome Wednesday! 1-27-16 • Get ready for warm up #1 • Get ready to take notes on our new unit: Thermodynamics Warm up #1 • A 0.75-kg coconut falls out of a tree from a distance of 8.0 meters. Determine the coconut’s kinetic energy the instant before it hits the ground. Thermodynamics • Essential question: What is thermodynamics? • The study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy) Key terms: • • • • Kinetic molecular theory Temperature Heat Phase changes Kinetic-molecular theory • Essential question: What is the kinetic molecular theory? Theory that states that all atoms/molecules of a substance are constantly in motion Faster movement of atoms = greater kinetic energy Kinetic energy is related to 2 things: 1. the temperature of a substance 2. the state of matter of a substance kinetic/molecular theory Temperature Essential Question: What is temperature? Temperature – a measure of the AVERAGE molecular KE Faster molecular movement = more kinetic energy More kinetic energy = higher temperature The hotter it is, the faster the molecules are moving Colder = slower moving molecules Essential question: how is the kinetic molecular theory related to states of matter and phase changes? As atoms/molecules increase their velocity, two things happen: 1. They get hotter 2. They change state Slowest moving atoms are solids Faster moving atoms are liquids Even faster moving atoms are gases Fastest moving atoms are in the form of plasma • Solid –Atoms close together • Liquid – movement Dance Floor Analogy • • • • Number of molecules = people Volume= size of dance floor Temperature= speed of music Pressure= closeness of people/collisions of people • More movement = more heat http://www.brianmichaelsdj.com/chicken.htm Plasma - formed at high temperatures; ionized phase of matter as found in the sun; most common state of matter in the Universe Phase changes • • • • • • • Melting Freezing Evaporation Condensation Sublimation Deposition vaporization • change from (s) to (l) • change from (l) to (s) • change from (l) to (g) • change from (g) to (l) • change (s) to (g)dry ice Example offrom sublimation: • changeoffrom (g) to (s)frost Example deposition: • change from (l) to (g) Essential Question(s): 1.What is heat? 2. What is the difference between temperature and heat? • Temperature tells you the amount of KINETIC ENERGY something has • HEAT - Energy that flows as the result of a difference in temperature • Heat is the transfer of energy from one object to another Heat & Temperature • Heat and temperature are NOT the same thing! • Heat – refers to total amount of thermal energy in a substance • Temp. – refers only to average kinetic energy • Q: Which has more heat: 2L of boiling water or 1L of boiling water? Essential question: how do we measure temperature? • 3 main systems: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Essential question: How are the temperature scales similar and different? • In the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees • The Celsius scale divides the difference between the freezing and boiling points of water into 100 degrees (instead of 180). • With the Kelvin scale, water freezes at 273 K and boils at 373 k Kelvin • The Kelvin temperature scale is useful for many scientific calculations because it starts at absolute zero. • It is the universal temperature measurement used in science. • The Kelvin scale is used because it measures the actual energy of atoms. Kelvin scale • “Absolute Zero” = 0 K –i.e., no molecular motion, therefore no KE on the molecular level –0 K is the lowest you can go! You can’t stop motion more than 0. –What would happen if we reached absolute zero? TEMPERATURE VS HEAT • If a substance has a temperature, then the substance’s particles have kinetic energy. Therefore, the particles are moving. • Absolute zero – 0 K – all motion of all particles stops completely. Essential question: What is thermal energy? Heat & Temperature • Heat (Q) and temperature are NOT the same thing! • Heat – refers to total amount of thermal energy in a substance • Temp. – refers only to average kinetic energy • Q: Which has more heat: 2L of boiling water or 1L of boiling water?