Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation
advertisement

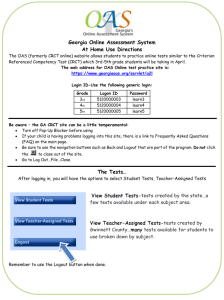
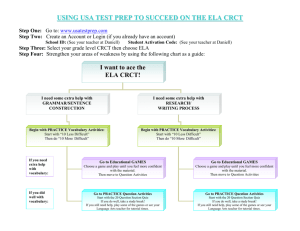
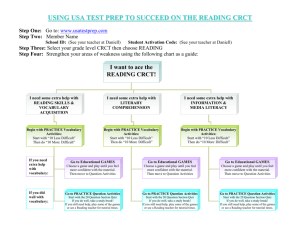
Chapter 15 Chemical Compounds Preview CRCT Preparation < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 1. What kind of carbon backbone does the figure represent? A an alkyne chain B a ring chain C a branched chain D a straight chain < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 1. What kind of carbon backbone does the figure represent? A an alkyne chain B a ring chain C a branched chain D a straight chain < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 2. Antacids usually contain bases. Which of the following best describes the reaction between antacids and stomach acid? A A neutralization reaction occurs, producing neutral compounds. B The products formed are more acidic than stomach acid. C The antacid becomes bright red in the presence of stomach acid. D The products formed contain different elements than those contained in antacid and stomach acid. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 2. Antacids usually contain bases. Which of the following best describes the reaction between antacids and stomach acid? A A neutralization reaction occurs, producing neutral compounds. B The products formed are more acidic than stomach acid. C The antacid becomes bright red in the presence of stomach acid. D The products formed contain different elements than those contained in antacid and stomach acid. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 3. Which of the following substances is a lipid? A glucose B carbohydrate C fat D protein < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 3. Which of the following substances is a lipid? A glucose B carbohydrate C fat D protein < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 4. A compound dissolved in water turns red litmus paper blue and changes the indicator bromthymol blue to dark blue. What kind of compound is it? A an acid B a base C lemon juice D table salt < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 4. A compound dissolved in water turns red litmus paper blue and changes the indicator bromthymol blue to dark blue. What kind of compound is it? A an acid B a base C lemon juice D table salt < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 5. A salt solution conducts an electric current, but a sugar solution does not. Which of the following statements best describes why a sugar solution does not conduct an electric current? A Sugar molecules are held together by ionic bonds. B Covalent compounds cannot conduct electric currents. C Sugar molecules form ions in water. D Sugar molecules are not charged. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 5. A salt solution conducts an electric current, but a sugar solution does not. Which of the following statements best describes why a sugar solution does not conduct an electric current? A Sugar molecules are held together by ionic bonds. B Covalent compounds cannot conduct electric currents. C Sugar molecules form ions in water. D Sugar molecules are not charged. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 6. The pH of some common household substances is listed in the table. Which substance would most likely feel slippery? A lemon juice B vinegar C milk D ammonia < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 6. The pH of some common household substances is listed in the table. Which substance would most likely feel slippery? A lemon juice B vinegar C milk D ammonia < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 7. What factor does the pH scale measure? A the concentration of sodium ions in a solution B the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution C the concentration of glycogen ions in a solution D the concentration of hydronium ions in a solution < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 7. What factor does the pH scale measure? A the concentration of sodium ions in a solution B the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution C the concentration of glycogen ions in a solution D the concentration of hydronium ions in a solution < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 8. All organic compounds are based on which element? A hydrogen B carbon C oxygen D nitrogen < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 8. All organic compounds are based on which element? A hydrogen B carbon C oxygen D nitrogen < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 9. A chemist is identifying an unknown white solid. The sample consists of a single compound. The first step in the identification process involves deciding if the compound is covalent or ionic. Describe two pieces of information the chemist could gather in order to decide if this compound is covalent or ionic. Explain your answer. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 9. Answer - Full-credit answers should include two of the following points: • The chemist could measure the compound’s melting point. Melting points of ionic compounds are usually higher than those of covalent compounds. • The chemist could see if the substance dissolves in water. Many ionic compounds dissolve in water, while most (but not all) covalent compounds do not. • The chemist could measure the electrical conductivity of a solution containing the compound. Solutions of ionic compounds conduct electric current, while solutions of covalent compounds do not. < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 10. When you add a small amount of a weak acid to a sample of seawater, a neutralization reaction occurs. What can you conclude about the pH of seawater? < Back Next > Preview Main Chapter 15 CRCT Preparation 10. Answer - The seawater must be basic if a neutralization reaction happens when an acid is added. So, the pH of the seawater must be greater than 7. < Back Next > Preview Main