Animal Systems
advertisement

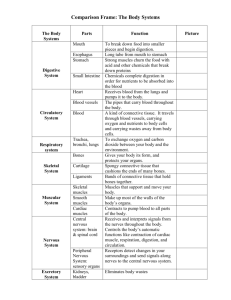
Chapter 1 Lesson 4 What does the digestive system do? • It breaks down food into materials the body can use. Which organ system is most important? • ALL the organ systems are needed for the animal to survive. Look and Wonder p. 60 • What makes a macaw’s wings move? • Muscles make the wings move. Let’s read pgs. 62-63. • What are two functions of the skeletal system? • Protection and Support What animals have skeletons on the outside of their bodies? •Arthropods Look at the illustrations on pgs. 62-63. • Why does the rabbit need opposing muscles in order to run? • One muscle pulls the leg up and the opposing muscle pulls the leg down. • What type of tissue attaches muscle to bone? • tendons Quick Check Questions p. 63. Partners discuss the answers to these questions (3 min.). • Tell what happens to the rabbits muscles as it runs. • A nerve signal arrives at the muscle and causes the muscle to contract. The contracted muscle pulls on the tendon, which pulls the leg bone up. Another muscle, which pulls down, relaxes. This cycle of contracting and relaxing continues as the rabbit runs. Muscles that move your fingers are in your arm. How are your fingers able to move? • The muscles are connected to the bones by the tendons. Let’s read pgs. 64-65. Digestion • Food has nutrients that cells need to stay alive but the body must break down the food to release the nutrients. What body parts does food pass through? • • • • Mouth Esophagus Stomach Intestines What body parts make chemicals that digest food? mouth, stomach, liver, and pancreas Read a diagram p. 64. • What digestive organs do worms and humans have in common? • Mouth, esophagus, and intestines What are three ways humans remove wastes? • Humans remove excess water, salt, and other wastes by sweating, humans breathe out carbon dioxide, and remove excess water and collected wastes from the kidneys as urine. What do the kidneys do? • They filter wastes from the blood to produce urine. Quick Check Questions p. 65 • What key steps take place in the process of digestions? • Chewing in the mouth, chemical breakdown in the stomach, further chemical breakdown in the small intestine and absorption into the bloodstream, and reabsorption of water and removal of undigested waste matter in the large intestine. Why are nephrons surrounded by many tiny blood vessels? • Nephrons have a membrane that allows some substances to flow in and out. Waste products are collected by the nephrons, and useful substances such as nutrients are passed to the blood through blood vessels. Let’s read pgs. 66-67. What is the main respiratory organ in a mammal? The lungs How are the bronchi related to the alveoli? The bronchi are small tubes that empty into thin-walled air sacs called alveoli. Could the lungs supply oxygen to your body cells without the circulatory system? • No • Why? • The lungs need a way to transport the oxygen to other parts of the body. Look at the illustration of the heart and lungs on p. 66. • Let’s name the parts of each organ. • What is the main function of the lungs? • The main function of the lungs is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood. Read a diagram p. 67. • Where is the oxygen-poor blood pumped? • Oxygen-poor blood is pumped to the lungs where the blood picks up oxygen and rids itself of carbon dioxide. Quick Check Questions p. 67. • What steps does the circulatory system take to deliver blood to the body? • The heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body cells. Blood vessels return carbon dioxide-rich blood to the heart and then the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart and is pumped back to the body cells. Is the respiratory system part of the excretory system? Explain. • The respiratory system is part of the excretory system because it removes carbon dioxide from the body. Carbon dioxide is a cellular waste product. Let’s read p. 68. • Animals sense and respond to their surroundings. • What is a stimulus? • Anything in the environment that bring about responses from the body. • What body systems work together to respond to stimuli? • The nervous system, the skeletal system, and the muscular system Look at the illustration of the nervous system on p. 68. • What is the function of the three types of neurons? • Sensory neurons receive stimuli from the body. • Motor neurons carry messages from the brain and spinal cord to the body’s organs and glands. • Associative neurons connect the sensory neurons to the motor neurons. Quick Check Questions p. 68. • What is the function of the nervous system? • The nervous system works with other body systems to help organisms respond to stimuli in their environment as well as stimuli inside their body. How does the nervous system work closely with other body systems? • The nervous system works with the muscular system to help move the body. Messages sent through the nervous system signal muscles to contract. Choose the BEST answer for each question. Which happens first when an animal moves its leg? Which part of the digestive system absorbs nutrients? • A. A muscle contracts. • B. The tendon pulls on a bone. • C. The muscle pulls on a tendon. • D. A nerve impulse reaches a muscle. • • • • A. B. C. D. Mouth Stomach Esophagus Small intestine Choose the BEST answer for each question. Which structure in fish performs the same function as lungs in mammals? Which animal has an open circulatory system? • • • • • • • • A. B. C. D. Fins Gills Veins Swim bladder A. B. C. D. Lobster Sparrow Rattlesnake Timber wolf How might an animal’s damaged sensory neurons affect its safety? • An animal with damaged sensory neurons would not be able to properly receive messages about its body and its environment. If danger were nearby, the animal would likely not be able to detect it and could get hurt or killed.