11.1 Gas Laws Ideal Law Dalton Diffusion part two
advertisement
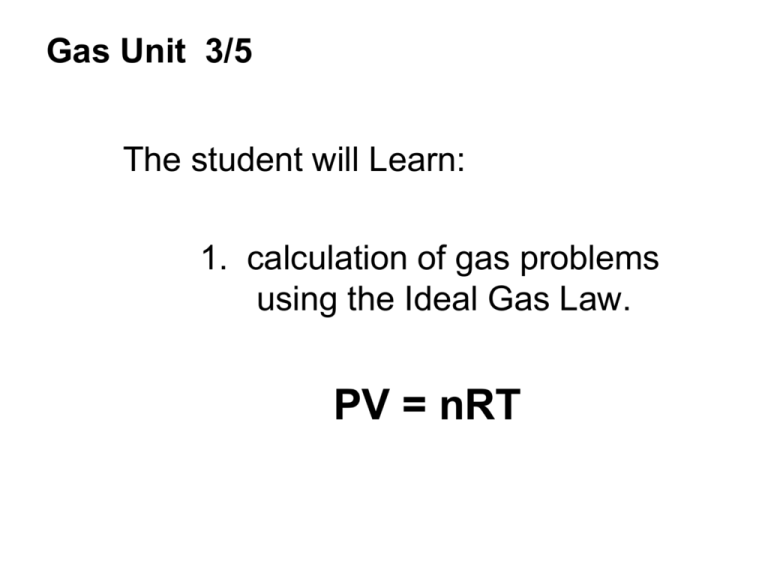
Gas Unit 3/5 The student will Learn: 1. calculation of gas problems using the Ideal Gas Law. PV = nRT Ideal Gas Law Involves P,V,T & …number of moles of gas PV = nRT All units must be : P = atm V = liters T = Kelvin n = #of moles R = .0821 liters x atm moles x K R is a constant …….. Like pi is a constant 3.14 ws.11.21 3 Options for R gas constant 0.0821 L x atm mol x K 8.315 L x Kpa mol x K 62.4 L x mmHg mol x K Ws. 11.21 1. If 6 moles of CO2 gas is contained at a pressure of 7.6 atm and a volume of 20 liters, calculate the temperature of the gas. Answer in Celsius degree. 2. A 31 liter tank contains a gas at 12.2 atm with a temperature of 273k. What is the weight in grams of the dinitrogen oxide, laughing gas, inside the tank? 3. What is the volume of a balloon if it contains 19.2 moles of helium, an internal pressure 770mmHg and the outside temperature is 80oC? 4. If I have an unknown quantity of gas at a temperature 80oC, and a volume of 25 liters and the tank pressure registers at 2000mmHg. How many moles of the unknown Gas? 5. A one liter aerosol can of WD-40 at room temperature (25oC) is thrown into an incinerator. Calculate the temperature of the gas in the can with an internal pressure of 3atms and 0.05 moles of WD-40 were in the can? Assume the can did not explode. ws.11.21 How do I know when to use the Combine Gas Law or the Ideal Gas law? Gas Unit 3/5 The student will Learn: 1. calculation of gas problems using the Ideal Gas Law. PV = nRT Gas Unit 4/5 The student will learn: 1. concept of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure. 2. calculations of Dalton’s law of Partial Pressure. Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure Total pressure of a mixture of gases = sum of partial pressure of the component gases. Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + P4 … 1. If 5 gases in a cylinder each exert 1atm, what is the total pressure exerted by the gases? 2. Three samples of gas each exert 740mm Hg in separate 2-L tanks. What pressure do they exert if they are all placed in a single 2-L tank. 3. A mixture of four gases exerts a total pressure of 860 mmHg. Gases A and B each exert 220 mmHg. Gas C exerts 110mmHg. What pressure is exerted by gas D? Gas Unit 4/5 The student will learn: 1. concept of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure. 2. calculations of Dalton’s law of Partial Pressure. Gas Unit 5/5 The student will learn: 1. concept of rate of diffusion 2. minor calculations in rate of diffusion. Diffusion KMT: 4- No significant forces of attraction or repulsion between gas particles So…..gas particles can flow easily past one another 3- Gas particles are in constant, rapid, random motion. They have KE. So….. motion of gas particles causes the gas particles to evenly mix. Diffusion =movement of one material through another material. “Cooking cookies in the kitchen…others can smell it upstairs in the bedroom.” Rate of Diffusion depends on mass ---Skinny people can run faster than fat people-----So can molecules--- Lighter molecule diffuse faster than heavy molecules @ STP Of the following molecules which would diffuse faster? l. Oxygen or Neon 2 Sulfur dioxide or carbon dioxide 3. Chlorine gas or krypton gas List the following gases in order of increasing rate of diffusion. (a) He (b) Xe (c) HCl (d)Cl2 The two gases in the figure below are simultaneously injected into opposite ends of the tube. They should just begin to mix at which labeled point? H2S SO2 A B C How does the diffusion rate of hydrogen molecules compare with that of oxygen molecules when both gases are at 250C 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. They have equal rates Hydrogen is 1/16 as fast as oxygen Hydrogen is 16 times faster than oxygen Hydrogen is 4 times as fast More information is needed Gas Unit 5/5 The student will learn: 1. concept of rate of diffusion 2. minor calculations in rate of diffusion.




