refocus - Mrs. GM Biology 300
advertisement

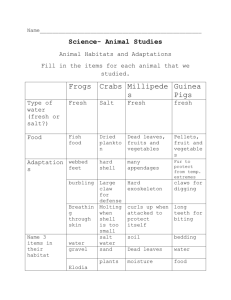
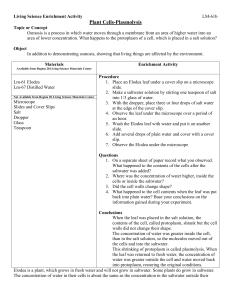
Name___________________________ Date _________ Mrs. Geithner-Marron (Bio 300) Period ________ "Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) Background: Diffusion of water molecules across a cell’s membrane from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration is called osmosis. This movement of water may be harmful to cells. It can result in cell water loss (plasmolysis) when living cells are placed into a hypertonic environment (where the concentration of solute is higher outside the cell and lower inside the cell, therefore, causing the concentration of water inside the cell to be higher than the concentration of water outside the cell). Most cells, however, live in an environment that is isotonic (with the solute concentration being equal inside and outside of the cell, and therefore, the water concentration also being equal on both sides of the cell membrane). Thus, under normal isotonic conditions, there are no harmful effects to the cell. Purpose: In this investigation you will: a. prepare a wet mount slide of an Elodea leaf in fresh water and a wet mount slide of an Elodea leaf in salt water for observation using the microscope. b. observe cells from both wet mounts and draw diagrams of each. c. compare the appearance of normal Elodea cells in fresh water (an isotonic environment) and plasmolyzed (shriveled) Elodea cells in salt water (a hypertonic environment). Materials: microscope (1) microscope slide (2) coverslips Elodea (a freshwater plant) fresh (tap) water (in beaker with a dropper) ~5% salt water solution (in dropper bottle) tweezers/forceps #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) Procedure: 1. Prepare your wet mounts using figure 1 as a guide: a. Put an Elodea leaf on the right side of the slide. i. Add 1-3 drops of the salt water solution to the Elodea leaf on the right side of the slide. ii. Put a coverslip over this leaf. iii. Dry off any excess salt water on the remaining area of the slide. b. Put an Elodea leaf on the left side of the slide. i. Add 1-3 drops of the fresh water to the Elodea leaf on the left side of the slide. ii. Put a coverslip over this leaf. c. Make sure that the salt water and the fresh water do NOT TOUCH! If they do, clean everything off of your slide and start over using fewer drops of water on each side. d. Make sure that you don’t change the position of your slide (right should be salt water and left should be fresh water). #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) 2. After 2 or 3 minutes, observe the leaf on the LEFT (in FRESH water) under LOW power. 3. Diagram ONE cell and LABEL the following parts: a. cell wall (rigid outermost boundary of the cell) b. cell membrane (flexible boundary of the cell… may be flat against the inside of the cell wall) c. chloroplasts (green ovals) 4. Using the knob under the stage, move the slide so that you can observe the leaf on the RIGHT (in SALT water) under LOW power. 5. Diagram ONE cell and LABEL the following parts: a. cell wall (rigid outermost boundary of the cell) b. cell membrane (flexible boundary of the cell… should be pulled away from the inside of the cell wall) c. chloroplasts (green ovals) #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) 6. Using the knob under the stage, move the slide so that the leaf on the LEFT (in FRESH water) is under the objective. 7. Switch to medium power (looking from the side at stage level) and refocus (using only the fine adjustment knob). Then, switch to high power (looking from the side at stage level) and refocus (using only the fine adjustment knob) and observe the leaf using high power. 8. Diagram ONE cell (on HIGH power) and LABEL the following parts: a. cell wall (rigid outermost boundary of the cell) b. cell membrane (flexible boundary of the cell, may be flat against the inside of the cell wall) c. chloroplasts (green ovals) #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) 9. When you are done observing the leaf on the left, switch to low power. 10.Using the knob under the stage, move the slide so that the leaf on the RIGHT (in SALT water) is under the objective. 11.Refocus on low power, then switch to medium power and refocus. Then, switch to high power and refocus and observe the leaf using high power. 12.Diagram ONE cell (on HIGH power) and LABEL the following parts: a. cell wall (rigid outermost boundary of the cell) b. cell membrane (flexible boundary of the cell… should be pulled away from inside of cell wall) c. chloroplasts (green ovals) #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) Analysis and discussion questions: Read/look at the following information before answering the questions (it will be used to help you answer some questions): 1% salt 99% water Elodea in fresh (tap) water: 1% salt 99% water ~5% salt Elodea in salt water solution used in this investigation : ~95% water 1% salt 99% water -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------USE THE DIAGRAMS ABOVE TO HELP ANSWER QUESTION 1 1. For the cell in FRESH water (on the LEFT side of the slide during the lab): a. What is the percentage of water inside of the cell? _________________% b. What is the percentage of water outside of the cell (in the beaker of fresh water)? _________________% c. How do the percentages of water inside and outside of the cell compare? (See # a & b.) ______________________________________________________________________________________ d. The solution is: _____(hypertonic / hypotonic / isotonic) e. Did you see any major changes in the cell? If so, how did the cell change? __________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ i. Explain you’re your answer to part e in terms of osmosis (water movement). ____________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ #_____ Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (300 Bio) Period __________ “Normal & Plasmolyzed Cells” Microscope Lab (Cells in Fresh & Salt Water) USE THE DIAGRAMS ON THE PREVIOUS PAGE TO HELP ANSWER QUESTION 2 2. For the cell in SALT water (on the RIGHT side of the slide during the lab): a. What is the percentage of water inside of the cell? _________________% b. What is the percentage of water outside of the cell (in the beaker of fresh water)? _________________% c. How do the percentages of water inside and outside of the cell compare? (See # a & b.) ______________________________________________________________________________________ d. The solution is: _____(hypertonic / hypotonic / isotonic) e. Did you see any major changes in the cell? If so, how did the cell change? __________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ i. Explain you’re your answer to part e in terms of osmosis (water movement). ____________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Define “plasmolysis”. _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ a. Did either cell show evidence of plasmolysis? ____________________________ i. If so, which one (in fresh water or salt water)? _____________________________________________ 1. How can you tell? ________________________________________________________________ 4. What causes osmosis? _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ a. When osmosis occurs, water moves from ____________________ to _________________ concentration.