Introduction to Political Science

Introduction to
Comparative Economic Systems
Honors Non-Western Studies
Mr. Tumino
Discussion…
• How would you define economics?
• What is an economic system?
• How does economics impact you?
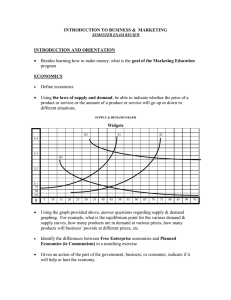
Comparative Economics Systems
•
The major economic systems are traditional economy, market economy, command economy and mixed economy.
•
There are also countries that are said to have developing economies, moving from a traditional to a market economy.
Definitions
• Factors of production:
– Those things necessary to produce goods and services.
» Land
» Labor
» Capital (money, buildings, equipment, etc.)
» Management
Definitions
• Traditional economy:
– An economic system in which the factors of production are settled by rules accepted as good and correct
– Normally used to describe economic systems that pertain in societies with extensive subsistence agriculture
– Used by members of industrialized societies to describe societies deemed "underdeveloped"
Definitions
• Market economy:
– An economy in which the prices of goods and services are determined in a free price system.
– A system in which buyers and sellers exchange on the basis of supply and demand.
– Also known as a capitalist economy.
Market Economy
Definitions
• Command economy:
– An economic system in which decisions regarding the factors of production are made by government leaders.
Command Economy
Command Economies
• Two types of command economies:
– Communist—strict government control of the entire society
Command Economies
–
Socialist—three main goals of this type of economy:
•
An equitable distribution of wealth and economic opportunity
• Society’s control, through its government, makes decisions about public goods.
•
Public ownership of services and factories that are essential.
Definitions
• Mixed economy:
– A combination of market, command, or traditional economy.
– A system in which free enterprise is affected by government regulations.
Mixed Economy
Economic Decisions
• All economic systems must make three basic economic decisions:
–
What and how many goods and services should be produced
–
How should they be produced
–
Who gets the goods and services that are produced
Economic Decision Making
• These decisions are made differently in the three major economic systems:
–
Traditional—habit and custom determine the rules.
–
Market—this economy is based on free enterprise, the idea that private individuals or groups have the right to own property or businesses and make a profit with only limited government interference.
–
Command—the government controls the economy is this system .
Economics and Trade
• Countries with varying levels of economic development have become increasingly interdependent through world trade.
• Geographers and economists classify all of the world’s economic activities into four types:
–
Primary economic activities—taking or using natural resources directly from the Earth
–
Secondary economic activities—raw materials are used to produce something new and more valuable.
Economies and Trade
• Factors affecting trade:
– The unequal distribution of natural resources
– Differences in labor costs
– Differences in education levels
Economics and Trade
• Barriers to trade:
–
Tariffs
–
Embargos
–
A quota on the quantity of a product that can be imported from a country
• Many governments around the world have moved toward free trade.
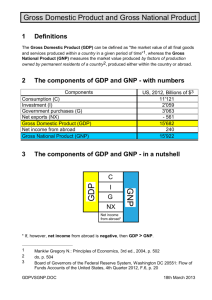
Gross Domestic Product
• GDP -
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living.
Gross National Product
• GNP - Gross National Product is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country
GDP vs. GNP
• Gross National Product (GNP) is often contrasted with Gross Domestic Product
(GDP). While GNP measures the output generated by a country's enterprises - whether physically located domestically or abroad -
GDP measures the total output produced within a country's borders - whether produced by that country's own firms or not.