American Literature
advertisement

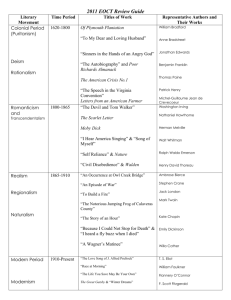
American Literature Periods of Am. Lit. 1. Beginning of American Literature: 1607-1776 Colonial Period 1765-1790 The Revolutionary Age 1775-1828 The Early National Period 2. Romanticism, Transcendentalism 1828-1865 The Romantic Period (Also known as: TheAmerican Renaissance) The Age of Transcendentalism 18651900 3. Realism, Naturalism The Realistic Period 1900-1914 The Naturalistic Period (extreme realism) 1914-1939 1920s 1920s, 1930s: American Modernist Period: Jazz Age, Harlem Renaissance The "Lost Generation" 1939-present 1950s 1960s, 1970s The Contemporary Period: The Beat generation American Literature recognizes works of: African-American Writers Native American Writers Asian-American Writers Colonial Period Periods of Am. Literature vary a lot It´s impossible to give exact dates The first literature started to appear after founding of the first settlement at Jamestown in 1607 It continuoud till the outbreak of the Revolution Literary genres: Historical writings Religious themes – sermons (kázání) tracts Writers: Anne Bradstreet (poet) Benjamin Franklin (The Way to Wealth) William Bradford The Revolutionary Age The greatest documents of American history were authored: Thomas Paine (Common Sense – he urged independence) The Declaration of Independence (Thomas Jefferson - 1776) The Constitution (1789 - ratified) The Early National Period Beginnings The of true Am. Literature writers wrote in th English style but the settings, themes and characters were authentically American Irving – he wrote about Am. Life, biography of G. Washington Washington Fenimore Cooper – The Last of the Mohicans James Edgar Allan Poe E.A.Poe (1809-1849) son of a poor actress (drastic death) his father alcoholic He was taken by his guardian Mr. Allan Studied West Point – kicked out Marriage with 13 year-old cousin She died of TB ten years later – despair, grief was reflected in his works 1849 found delirious in a steet The Raven (poem) - a tired, unhappy student asks if he ever meets his love again His doubts are underlined by the raven´s repetition „nevermore“, symbol of doubts and longing The Golden Bug The Pit and the Pendulum The Black Cat The Murders in the Rue Morgue The Fall of the House of Usher His work: 1. realism: detective stories – logical, brilliant, rational 2. romanticism – irrationalism, mystery, violence, criminality, death, passion Perverse, vulgar, grotesque style. Transcendentalism American reflection of European romanticism Philosophical movement The transcendal philosophy was based on: 1. Free will Humanity Intuition Individual conscience It glories nature 2. 3. 4. 5. All transcendentalists were isolated people They lived in „Utopian Community“ – Brookfarm near Boston The individual can transcend the world and discover union with God and Ideal Main representatives: Ralph Waldo Thoreau Henry David Thoreau Other Romantic Writers Herman Melville – symbolist (Moby-Dick) Nathaniel Hawthorne (The Scarlet Letter) the main theme –sin Hester has te wear letter A – means adulteress Walt Whitman (poet) Emily Dickinson (poet) Realistic Period After Civil War: Social injustice – first millionaires appear (Rockefeller) discoveries in science (railway, telegraph cable, telephone,…) Growth of education Twain called this period „gilded age“ Realism Action against romanticism Main literary form – novel Authors accuse romanticism of falsehood They describe common things, common places, everyday life Mark Twain His real name: Samuel Langorne Clemens He spent his childhood on the Mississippi river Workedon a steamboat on the Mississippi Travelled a lot He recollects his childhood in his books The Innocents Abroad The Gilded Age The Adventures of Tom Sawyer The Advedntures of Huckleberry Finn Tom likes danger, he´s always able to avoid problems, Huck represents social conscience, he´s sensitive to everything around him Naturalism Derived from the word nature (interest in nature) It has its origin in France – Zola Prople are influenced by environmental forces (outside us) and inner drives (inside us) – peole can ´t control them The main drives of characters: hunger, fear, sex, … Their writings are often cruel and tragic. Stephen Crane Jack London (Tjhe Call of the Wild) Theodore Dreiser (An American Tragedy) Upton Sinclair (The Jungle) Lost Generation A term applied for Am. Writers born around 1900, who fought in WWI The term comes from Gertrude Stein Main features: description of the loss of traditional values as the result of the war other social evils Ernest Hemingway Find some info. about him F. S. Fitzgerald Connected with Jazz Age in 20s Wrote many stories about wealthy people The Great Gatsby – masterpiece (a rich man earns money by smuggling, he loves Daisy, but Daisy is married Nick – a narrator is is disgusted) American Dream Other 20th century writers The Harlem Renaissance: Harlem (N.Y.) was a centre of it Motto: Let us return to Africa! (in a literary sense) We all have sth. in common Main representatives: Langston Countee Richard Hughes Cullen Wright The Great Depression = the end of American Modernist Period William Faulkner John Steinbeck Eugene O´Neil (a playwright) Dealt with social and political issues Jewish Writers Big emigration of the Jews to the US Writers explore new themes of identity, psychological problems They are looking at their racial background Saul Bellow J.D. Salinger (The catcher in the Rye) Bernard Malamud Joseph Heller (Cath 22) The Beat Generation The main personalities: A. Ginsberg, W. Boroughs, J. Kerouac, G. Corso Knew each other, travelled through the US by taking drugs and having many sexual affairs SAn Francisco – cradle of the Beats Basic Characteristics Wanted to live life without social conventions Against supermacy of money Their idol = wanderer travelling with his bag from a state to state, listening to JAZZ, being spontaneous, free, sincere Taking drugs, drinking alcohol Jack Kerouac On the Road Written on toilet paper Journeys from East of States to the West