Building a National CTSA Consortium: Goals and
advertisement

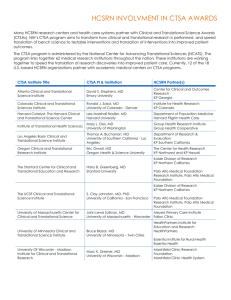
National Center for Research Resources NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Accelerating and enhancing research from basic discovery to improved patIent care Building a National CTSA Consortium: Goals and Opportunities January 8, 2009 Indiana Clinical and Translational Science Institute First Annual Meeting Barbara Alving, M.D., MACP Director National Center for Research Resources The Translational Research Gap Source: Butler D. Translational research: Crossing the valley of death. Nature. 2008;453:840–2. The Translation Gap Source: Butler D. Translational research: Crossing the valley of death. Nature. 2008;453:840–2. U.S. Hispanic Population by County, 1980 1980: Hispanic population concentrated in a few counties, mostly near Mexican border Source: Where Latinos Live: Pew Hispanic Center. 2008. Available at http://pewhispanic.org/states/population. U.S. Hispanic Population by County, 2007 2007: Hispanic population has spread substantially Source: Where Latinos Live: Pew Hispanic Center. 2008. Available at http://pewhispanic.org/states/population. National Health Expenditures as a Percent of GDP 20% Percent of U.S. GDP 18% 16% 14% 12% 10% 8% Actual Projected Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSAs) Educate the next generation of clinical researchers Improve clinical research management Build diversity in leadership Assemble interdisciplinary teams Enhance public trust Forge partnerships with private and public health care organizations CTSAWeb.org CTSA – Creating National Partnership Opportunities Consortium Governance Advisory: providing guidance and input to the NCRR Director Oversight: identifying and selecting collaborative opportunities to facilitate research, coordinating Consortium-wide approaches to research, and overseeing topicspecific efforts across the Consortium www.ctsaweb.org Steering: coordinating institutional topic-specific efforts with the national CTSA Consortium; each Steering Committee has an Operations subgroup that takes timely action on emergent topic issues CTSA National Strategic Plan Priorities Goal One: Enhancing National Clinical and Translational Research Capability Clinical research management Research infrastructure Phenotyping – human and preclinical models Goal Two: Enhancing Training and Career Development of Clinical and Translational Investigators CTSA National Strategic Plan Priorities Goal Three: Enhancing Consortium-Wide Collaborations Social networking Inventory of resources Data sharing Goal Four: Enhancing the Health of Our Communities and the Nation Community engagement Public health policy Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) Clinical Research Ethics Biomedical Informatics Trial Design Advanced Degree-Granting Programs CTSA HOME Clinical Resources Biostatistics NIH & other government agencies Industry Participant & Community Engagement Regulatory Support Each CTSA academic health center will create a home for clinical and translational science Healthcare & community organizations CTSA – Providing Local Leveraging Opportunities Atlanta Clinical and Translational Science Institute (Atlanta-CTSI) at Emory University Kaiser Permanente Georgia Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Complex Carbohydrate Research Center at U Georgia Yerkes National Primate Research Center CDC Emory University Atlanta VA Medical Center Morehouse School of Medicine Georgia Tech Georgia Research Alliance Georgia Bio Indiana CTSI – Providing Leveraging Opportunities Throughout the State Biocrossroads Wellpoint, Inc. Roudebush VA Medical Center Clarian Health Partners Indiana University Regenstrief Institute Eli Lilly and Company Purdue University Richard M. Fairbanks Foundation Notre Dame Wishard Health Services Cook Group, Inc Indiana State Government Indiana Health Study Indianapolis is a health challenged community with some of the highest rates of obesity, heart disease, smoking, and diabetes in the country. Indiana Health Study Longitudinal study of the population of Indianapolis and surrounding communities Collaboration between Fairbanks Institute, Biocrossroads, Indiana University School of Medicine, Regenstrief Institute, and other community health leaders in Indiana Focus is on coronary artery disease Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI) and CTSA Partnership Example Vanderbilt University and Meharry Medical College Community Engagement and Research program Promotes educational and research activities that will enhance translation of basic research into the clinic and into the community A “bench to bedside to community” project RCMI-CTSA Partnership Example CTSA at Weill Cornell Medical College Partnership includes Weill Cornell Medical College, other Cornell University schools and hospitals, and the Hunter College Center for the Study of Gene Structure and Function Clinical and Translational Science Center, a unique and diverse biomedical complex on Manhattan’s Upper East Side State-of-the-art resources for clinical/translational research Nurtures minority talent and has an effective electronic network with minority scientists nationwide CTSAs – Building a National Consortium of Academic Health Centers Currently 38 CTSAs Sites Across the Country WA MT ME ND OR VT MN ID NH WI SD NY WY MA RI MI PA IA NE NV IL UT OH IN CO MD WV KS CA NJ MO CT DE VA KY NC TN OK AZ AR NM SC MS TX AK AL GA LA FL HI Participating Institutions Members 2006 & 2007 New Members 2008 PR CTSA – Creating Regional Partnership Opportunities University of Washington Oregon Health & Science University University of California, Davis University of Iowa Mayo Clinic College of Medicine University of Wisconsin University of Chicago University of Rochester Yale University Weill Cornell Medical College Columbia University University of California, San Francisco Rockefeller University Albert Einstein College of Medicine Stanford University = CTSA Institutions = East Coast Consortium The Scripps Research Institute = Midwest Consortium = West Coast Consortium Washington University in St. Louis Educational Impact of CTSA Program Doubled the clinical and translational training workforce from 2006 - 2008 Increased the number of regional training interactions among consortium sites Awarded a supplement to develop a National CTSA Educational Resource Program (NCERP) that will: Identify, catalog, and assess training modules in clinical and translational research Enhance and broaden training opportunities for clinicianscientists across the CTSA consortium Educational Impact of CTSA Program (Based on 2008 Annual Progress Reports from first 24 CTSAs) Field of Training Clinical Disciplines (includes 37 subcategories) Pediatric Disciplines Public Health Stats, Res Methods, Informatics Genetics Allied Health Immunology Nursing Bioengineering Neuroscience Psychology, non-clinical Physiology Microbiology and Infect Diseases Pharmacology Molecular Biology Other Total # of Investigators # of Trainees and Scholars 3,948 272 516 29 317 50 176 10 134 9 121 16 115 7 110 20 108 10 108 18 93 5 77 5 69 8 61 10 53 7 250 37 ______ ______ 6,256 513 Multiple Principal Investigators Traditional single-PI model does not always work well for multidisciplinary efforts and collaboration Growing consensus that team science would be encouraged if more than one PI could be recognized on individual awards Overarching goal: maximize the potential of team science efforts, responsive to the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century http://grants2.nih.gov/grants/multi_pi/index.htm CTSA Consortium – Building Connections at Columbia University Irving Institute for Clinical and Translational Research CTSA Program: Helped inspire Columbia neurologist Petra Kaufmann, M.D., to reach outside her discipline to find a collaborator to build an apparatus to help children with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) Partnered with Elisa Konofagou, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Biomedical Engineering and Radiology to design the prototype Resulted in a device to help SMA patients use their arms Support for CTSA Consortium-Wide Projects Administrative supplements $2.5 million in FY 2008 to support consortium-wide projects including: Informatics – National web portal for research volunteers Education – National CTSA Educational Research Program (NCERP) Communications – Exploring web-based methods to maximize sharing in the CTSA consortium Encouraging and Enhancing Collaboration CTSA Consortium – Informatics Pilots Clinical and Translational Information Exchange Environment Informatics Pilots Implementation and development of tools for clinical investigators to facilitate small and medium sized research studies Enhance the collection and management of data in small and medium sized studies Requirements At least three CTSA must collaborate Data and software sharing Must incorporate institutional database support that is flexible, secure, and easily accessible on demand Informatics Pilot Projects Under Development PhysioMIMI at Case Western Reserve University Includes investigators from Marshfield Clinic, University of Wisconsin and University of Michigan Collects, manages, and analyzes diverse data types across institutions Allows secure, safe and regulated transfer of information from clinical care systems and research databases Sharing Clinical Data at University of Washington Includes investigators from University of California, San Francisco, University of California, Davis Allow researchers to access large shared datasets Assist with designing research studies and generating hypotheses Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) at Vanderbilt Includes investigators from Oregon Health and Sciences University and Mayo Clinic Provides workflows to develop secure, web-based applications for collecting, managing and sharing of clinical study data Informatics Pilots Under Development University of Washington WA MT ME ND Oregon OR Health & Science University ID MN SD WY Clinic College of Medicine Mayo University of California, Davis IA NE NV Mansfield Clinic University of WI Wisconsin– Madison University of MI Michigan IL UT CO University of California, San Francisco KS CA MO MD DE VanderbiltNC University AR TX NJ PA KY SC MS AK MA CT RI Case Western ReserveWV University VA OK NM NH NY OH IN TN AZ VT AL GA LA FL HI PR Regenstrief Institute Medical Informatics The Regenstrief Medical Record System, a dynamic electronic medical record system, has helped physicians manage health care information for over a quarter century and provides unique research opportunities to fellows Led by Director J. Marc Overhage, MD, PhD, Indiana University Professor of Medicine and Regenstrief Professor of Medical Informatics Comprise one of the largest medical informatics physician brain trusts in the United States Identified information technology, including medical informatics, as a priority area of study to improve the quality of the U.S. health care system Technology Resource Cores Workshop: Designs for Efficient Management and Utilization In collaboration with the CTSA consortium, NCRR is planning a 2-day conference in July 2009 Topics to address include: Academic institutions’ policies Sharing experiences of using cores (Mayo Clinic, for example) Service contracts Equipment Demand for core services Personnel NIH I/C Issues National Cancer Institute Translational Research Working Group (TRWG) TRWG conceptualized translational research as a set of developmental processes focused on different goals (ie, developmental pathway for anticancer agents –drugs or biologics) The pathways are graphically represented in Clin Cancer Res 14: 5664-5672, September 15, 2008 Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Example: The West Coast Licensing Partnership Oregon CTSA is part of a group of institutions willing to designate a subset of their technologies for marketing and licensing purposes Adds value by bundling related technologies over individual tools and technologies Strengthens inter-institutional relationships between member partners Increases global access to research tools by promotion of non-exclusive licensing Provides simple one-stop licensing of technologies from multiple institutions Saves time and money from negotiating multiple license agreements CTSA Consortium – Building Connections with Business Schools CTSA are partnering with business schools to: Develop business plans, design, and implement community surveys Create innovative cross-educational programs Develop case studies to pilot programs Collaborate with international colleagues Prepare cost analyses Protect CTSA-developed patents Form industry partnership programs CTSA Consortium – Building Connections at University of California, Davis Center for Entrepreneurship seminar to explore links between research and inventions– topics included: Dynamics of the commercialization process of new inventions Moving along the path of research to market Purpose of intellectual property in the commercialization process When is an idea worth protecting and why Options for faculty, students, and staff in commercializing their research Resources available to navigate the journey from research to commercialization Thomas Edison: A Design Thinker Design Thinking Methodology imbues the full spectrum of innovation activities with an understanding of what people want and need Edison’s Approach Team-based Multidisciplinary Good business sense Nimble budget Full product launch — light bulb, electric power system, etc. Source: Brown T. Design thinking. Harvard Business Review. June 2008. “Hell, there are no rules here — we’re trying to accomplish something.” Thomas Edison Design Thinkers: Personality Profiles (Harvard Business Review June 2008, Tim Brown) Empathy Look at work from multiple perspectives (colleagues, clients, end users, and customers) Integrative thinking See salient and contradictory aspects of problem and find novel solutions Optimism Assume that at least one potential solution is better than the existing alternatives Experimentalism Pose questions and explore constraints in creative ways that proceed in entirely new directions Collaboration Have significant experience in more than one discipline (engineers & marketers; anthropologists & industrial designers; architects & psychologists) Taking a Global View of Design Thinking: Aravind Eye Care System in India More than an eye hospital Aravind is: A social organization committed to the goal of elimination of needless blindness through comprehensive eye care services An international training centre for ophthalmic professionals and trainees who come from within India and around the world An institute for research that contributes to the development of eye care An institute to train health-related and managerial personnel in the development and implementation of efficient and sustainable eye care programs A manufacturer of world class ophthalmic products available at affordable costs