Ch. 17 Notes - Mr. Lamb

APUSH Notes – Ch. 17
The Gilded Age . . . Continued.
The struggle between business and working class continues.
Property rights (Business owners) vs. economic freedom for laborers
Farmers struggle
In the South:
Sharecroppers (white and Black) locked into a fairly hopeless system
Cotton prices keep falling
World cotton production expanded during the Civil War; Worldwide surplus afterwards
1881 – 11 cents per pound
1894 – 4.6 cents per pound
Farmers everywhere are pissed at railroads (high freight rates)
Early 1890s: the Farmers Alliance Organization evolves into the Populist Party
They try to attract ALL workers – not just farmers
Populist proposals o Direct election of US Senators o Government control of currency o Graduated income tax (rich pay a higher tax rate) o Right to form labor unions o Public ownership of railroads
Colored Farmers Alliance – black farmers in South
Economic Depression of 1893 – provokes protests
Coxey’s Army – 1894 – first protest march on Washington
Pullman strike – 1894 – 150,000 railroad workers go on strike (American Railway Union)
They refuse to handle trains with Pullman cars
Federal troops mobilized; Eugene Debs jailed
Republican Party attracts working class with promises to increase tariffs
(would protect workers from foreign competition)
Election of 1896
William Jennings Bryan – Democrat & populist o Bryan calls “free Silver” “bimetallism” in his “Cross of Gold” speech o (he really wants expanded money supply and inflation)
William McKinley – Republican
McKinley wants higher tariffs; continuation of Gold standard
McKinley raises $10 million; Bryan $1/3 million
McKinley wins in a sectionally-divided election – Map page 645
South after 1877
Redeemers in control – reconstruction reforms are on the way out.
State taxes cut – less money for public schools
Vagrancy laws allow state to arrest unemployed o Many states provide “convict’ labor to businesses
Black farmers in South are the worst off – trapped in the bottom of the economy
1890-96 – laws passed to effectively eliminate Black voting
1883 – US Supreme Court overturns Civil Rights Act of 1865
(Which outlawed discrimination in public businesses (hotels, theatres)
1896 – Plessy v. Ferguson – “Separate but equal” accommodations are okay.
South passes segregation laws - (legally!) Foner podcast #3
White intimidation and lynching (KKK) maintain separate white/black society
Most Reconstruction gains are gone by 1890-1900 Foner podcast #5
Chinese discrimination in the West
1882 – Chinese Exclusion Act – restricts Chinese immigration
1890 – California requires separate schools for Chinese
Nativist or Nativism = Anti-immigrant (especially poor, Irish, Chinese, Jews)
Rise of Booker T. Washington (Frederick Douglass dies in 1895)
Born a slave in Virginia - His autobiography is titled, “up from slavery”
Educated at Hampton Institute – Virginia
Founder of Tuskegee Institute – Alabama (technical school for Blacks)
His philosophy: Blacks can’t attempt to achieve full equality; must settle for economic gains; live in separate spheres and hope for full equality in the future. Page 659
He will disagree with W.E.B. Dubois – He wants Blacks to demand full equality.
The Rise of the American Federation of Labor (AFL) Samuel Gompers
Gomper’s strategy: o Focus on unionizing SKILLED workers in trades – printers; construction trades o Unskilled workers are too easily replaced; have little bargaining power o Disagrees with Idea of IWW and socialist reforms o Limit negotiations to wages, hours, working conditions
1874 - Women’s Christian Temperance Movement
Starts as anti-drinking movement
expands to advocate for womens’ rights in general Foner podcast #4
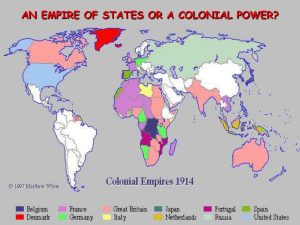
Imperialism – powerful nations controlling weaker nations
1884-85 - Berlin Conference – Eurpoean powers agree to divide up Africa
Main imperialistic nations: Britain, France, Spain, Japan, Belgium, Germany.
3 reasons for US imperialism:
economic competition (imports, exports, raw materials)
political & military competition o claim lands before some other country did o (continue Manifest Destiny) o establish strong navy – refueling bases (Admiral Mahan)
Need to improve lives of “backward” people o (Racial superiority + social Darwinism) o This is the White man’s burden – Kipling
Key point: conquered areas entitled to eventual self government
(That’s the philosophy presented in the Declaration of Independence)
(but how far into the future will that take?)
The US takes Hawaii:
Hawaii is independent monarchy
Economy is dominated by US-owned sugar growers
1890- Change in US tariff taxes imports from Hawaii
1891- Liliuokalani (Lil) becomes queen
she proposes new constitution; Hawaiian democracy
1893- sugar growers + marines overthrow Queen Lil.
Queen gives up without a fight (save lives)
New government: Sanford Dole becomes president; asks US to annex Hawaii
1893– President Cleveland refuses to annex; wants to restore Queen Lil to power
1897- McKinley becomes pres.; he favors annexation
1898- Congress votes to annex Hawaii
Spanish-American War
1860s - Cuba and Puerto Rico want independence
Spain uses harsh tactics to crush revolt
Concentration camps; Gen. “Butcher” Weyler
Yellow journalism: Pulitzer & Hearst exaggerate events in Cuba to sell more newspapers
De Lome Letter: Spain’s ambassador calls McKinley “Weak”
Feb. 1898: Battleship Maine blows up in Havana harbor
US declares war – “Remember the Maine!”
April 20, 1898: US Congress declares war
US Navy destroys Spanish fleet in the Philippines
US Navy blockades Cuba; land invasion follows
T. Roosevelt – Rough riders; San Juan Hill
August 12, 1898: Armistice (cease-fire)
Dec. 10, 1898: Treaty of Paris ends war
1.
Cuba becomes independent
2.
US gets Puerto & Guam
3.
US pays Spain $20 million for Philippines
After the war ends…
Puerto Rico becomes US territory
Cuba becomes a US protectorate
Platt Amendment: o No foreign control in Cuba o US has right to intervene in Cuba o US can buy or lease land for military or naval bases
Philippines revolt against US - Turns into ugly Vietnam-style war
US sends 70,000 troops; spends $400 million
China:
1899 - US establishes “Open Door Policy”
All nations allowed to trade with China (no imperialism allowed)
1900 – US and other nations send troops to put down Boxer rebellion
Big Question: What’s the future of Conquered possessions????
The right of self-government is in the Declaration of Independence
Spanish-American war looks more like a battle to gain empire than defending democracy
Insular cases – Supreme court rules that constitutional rights do not fully apply to conquered lands
Election of 1900
Bryan – Democrat – Against imperialism
McKinley/ T. Roosevelt – favor benevolent imperialism!!!!