File - Mr. Schmitt Biology 12 AP
advertisement

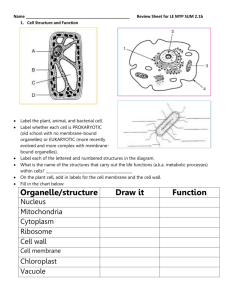
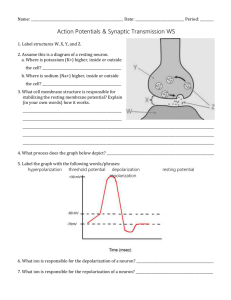
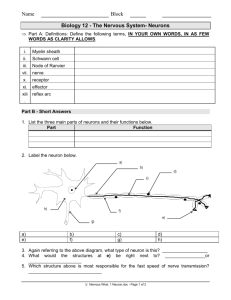
1. Which of the following is a function of structure X? A. to produce neurotransmitters B. to speed conduction of the nerve impulse C. to provide energy for nerve impulse conduction D. to receive stimulation for production of the nerve impulse 2. The structure labelled X is a(n) A. node. B. axon. C. synapse. D. dendrite 3. The structure labelled Y is a A. dendrite B. synapse C. myelin sheath D. node of Ranvier 4. The type of neuron which contains WVZ is a(n) A. interneuron B. motor neuron C. sensory neuron D. oligodendrocyte 5. When a doctor taps below the kneecap and the lower leg jerks forward involuntarily, the pathway that the nerve impulse travels is A. Effector, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, receptor. B. Effector, motor neuron, interneuron, sensory neuron, receptor. C. Receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector. D. Receptor, motor neuron, interneuron, sensory neuron, effector. 6. What is the advantage of reflex arcs? A. They stop the sensation of pain in the brain. B. They provide a quick response to a stimulus. C. They take place independently of any nerve function. D. They allow us to think about an appropriate response to a stimulus. 7. Where in the myelinated axon would an action potential occur? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 8. Which of the following is a characteristic of a resting potential? A. secretion of calcium ions B. neurotransmitters move into the axon C. depolarization of the post-synaptic membrane D. a net negative charge on the inside of the axon 9. In which of the following is ATP required? A. initiation of the nerve impulse B. establishment of the resting potential C. repolarization of the neural membrane D. depolarization of the neural membrane 10. Movement of which of the following ions causes depolarization? A. sodium B. calcium C. hydrogen D. potassium 11. During which of the following times is the membrane’s permeability to sodium ions increasing? A. 0 to 1 milliseconds B. 1 to 3 milliseconds C. 3 to 4 milliseconds D. 4 to 5 milliseconds 12. Which part of the action potential is caused by the opening of potassium gates and potassium rushing out of the neuron? 13. After an action potential is finished, another one cannot be started for a period of time because the ions need to re-establish ion concentration gradients and resting potential. What is this period of time called and which protein in the cell membrane causes the ion concentration gradient? 14. Which of the following events is causing the change within the neuron between time X and time Y? A. Sodium ions are moving into the axon. B. Sodium ions are moving out of the axon. C. Potassium ions are moving out of the axon. D. Large, organic, negative ions are moving into the axon. 15. The graph illustrates changes in membrane potential during the transmission of an action potential. What point on the graph corresponds to the time when repolarization begins? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 16. Which of the following refers to the “threshold” of nerve transmission? A. the frequency of action potentials which occur down a neuron B. the action potential created when potassium ions leave the neuron C. the total polarity change across the membrane during an action potential D. the minimum level of stimulus necessary for an action potential to occur 17. During resting potential, what is the voltage across the membrane? 18. Which ion is responsible for causing the upswing or depolarization phase of the action potential? 19. Molecule X came from a vesicle in the synaptic terminal. What is the general name for molecule X? 20. If molecule X causes depolarization at Y, what could X be? A. sodium ions B. calcium ions C. acetylcholine D. acetylcholinesterase 21. In an excitatory neuron, the molecules labelled X function to A. open sodium ion gates. B. speed up the transmission of impulses. C. provide an energy source for the resting potential. D. tell the brain the kind of stimulus that is being received. 22. In a synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters move to the receptor sites by A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. active transport. D. facilitated transport. 23. Which substance causes the microfilaments to contract and pull the synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane? A. sodium ions B. calcium ions C. noradrenalin D. acetylcholine 24. What is the function of hydrolytic enzymes in the synaptic cleft? A. to increase the threshold level B. to break down neurotransmitters C. to stimulate contractile proteins in the synaptic ending D. to increase the permeability of the presynaptic membrane to calcium ions 25. The structure labelled X above is the A. cerebrum. B. cerebellum. C. hypothalamus. D. corpus callosum. 26. The part of the brain responsible for muscle coordination is the A. cerebellum. B. hypothalamus. C. corpus callosum. D. medulla oblongata. 27. Which part of the brain is responsible for your conscious thoughts, personality and emotions? (What’s the name of this part)? 28. Which of the following structures sorts incoming sensory stimuli and channels them to the appropriate part of the brain? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 29. The portion of the brain involved in speech, vision, learning and memory is the A. cerebrum. B. cerebellum. C. hypothalamus. D. medulla oblongata. 30. If a person’s ability to integrate information from both hemispheres of the brain is impaired, the portion of the brain most likely affected is the A. pituitary. B. thalamus. C. cerebellum. D. corpus callosum. 31. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food through the intestines 32. The parasympathetic nervous system A. controls the central nervous system. B. lowers blood pressure and promotes digestion. C. uses noradrenalin as the neurotransmitter at synapses. D. initiates the “fight or flight” response in times of stress 33. Synaptic vesicles of the sympathetic nervous system contain A. sodium ions. B. acetylcholine. C. noradrenaline. D. potassium ions. 34. After just finishing a large meal, which specific division of your nervous system would be sending signals to your internal organs? 35. Morphine is a drug obtained from the opium plant. It is routinely given to postoperative patients on a short-term basis for pain. At high doses, it causes breathing and heart contraction to become suppressed. What area of the brain is affected by high doses of morphine? A. Pituitary B. Cerebrum C. Cerebellum D. Medulla oblongata 36. Which division of the nervous system is responsible for your voluntary action of moving your arms and legs? 37. Why is the hypothalamus called the master gland? 38. Which part of the brain is responsible for the neuroendocrine system? Key 1B 11B 21A 31B 2B 12 downswing/ repolarization 13 refractory period 22B 32B 23B 33C 3C Recovery phase Na+/K+ pump 4B 14C 24B 34parasympathetic 5C 15C 25D 35D 6B 16D 26A 36somatic 7B 17-65 mV 37effects many glands 8D 18Na+ 27cerebrum /cerebral cortex 28A 9B 19neurotransmitters 29A 10A 20C 30D 38hypothalamus Names: 1 11 21 31 2 12 22 32 3 13 23 33 4 14 24 34 5 15 25 35 6 16 26 36 7 17 27 37 8 18 28 38 9 19 29 10 20 30 1 11 21 31 2 12 22 32 3 13 23 33 4 14 24 34 5 15 25 35 6 16 26 36 7 17 27 37 8 18 28 38 9 19 29 10 20 30 Names: