X. VSEPR Theory
advertisement

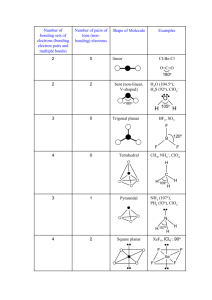
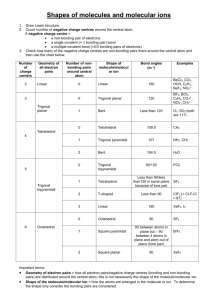
X. VSEPR Theory – Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. [Remember: Like charges repel!] A. A theory to predict the 3-dimensional geometry, ie. the“shape” of a molecule 1. The theory is based on “electrostatic repulsion”: Molecules will adjust their shape to keep the negatively-charged pairs of valence electrons as far apart as possible from each other. B. When NOT to use VSEPR theory: When there are only 2 atoms in a molecule. These molecule’s shapes are called linear – it doesn’t matter if there are single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds, or unshared electron pairs. C. Using VSEPR theory: 1. Draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule. 2. Identify its central atom. 3. Identify the sets of valence electrons as one of two possibilities: A. Those connecting two atoms. B. Those that do not connect two atoms. These are called “unshared pairs”. 4. The unshared pairs found on a central atom strongly repel each other; and molecules that would otherwise be linear, will be forced into a bent (or angular) shape. 5. Unshared pairs also cause a molecule that would be shaped like a flat triangle (trigonal planar), to be forced into a not flat ( trigonal pyramidal) shape. 6.Count the number of connections separately from the number of unshared pairs. 1 single bond counts as 1 connection. 1 double bond counts as 1 connection. 1 triple bond counts as 1 connection. Each unshared set of 2 dots counts as 1 unshared pair. D Predicting Shapes Using VSEPR Table Read horizontally across the table. # of Connections To total the Central Atom atoms Unshared Pairs of Molecular Shape Electrons Around Central Around Central Atom Atom 3 2 0 Linear 4 3 0 Trigonal Planar 5 4 0 Tetrahedral, 109.5o 3 2 1 or 2 Bent 3 1 Pyramidal 4 Shapes: , Linear diatomic E. Shapes: Trigonal planar Trigonal Planar Bent Linear diatomic Linear triatomic Linear triatomic Pyramidal Tetrahedral Trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral bent