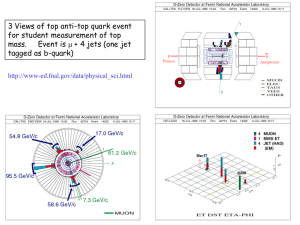
Probing the Higgs sector from Higgs coupling measurements
advertisement
Fingerprinting of the Higgs boson couplings as a probe of new physics models Kei Yagyu (National Central U.) The 11th LHC Physics Monthly Meeting, KIAS, Feb. 18, 2014 1 Congratulation! 이 상화 2 Figure Skating (20 th and 21st) 김 연아 浅田 真央 3 Minimal (1 doublet) Explained EW data, Flavor, … 126 GeV Higgs 4 Extended Higgs sectors Minimal (1 doublet) Extra Singlets Doublets Triplets… Explained EW data, Flavor, … 126 GeV Higgs 5 Beyond the SM Neutrino mass, Dark matter and Baryon asymmetry Introduce Extended Higgs sectors Minimal (1 doublet) Extra Singlets Doublets Triplets… Explained EW data, Flavor, … 126 GeV Higgs 6 Beyond the SM Neutrino mass, Dark matter and Baryon asymmetry Determine Extended Higgs sectors Minimal (1 doublet) Extra Singlets Doublets Triplets… Determine EW data, Flavor, … 126 GeV Higgs Higgs prop. 7 Beyond the SM Determine Extended Higgs sectors Minimal (1 doublet) Extra Singlets Doublets Triplets… Determine EW data, Flavor, … 126 GeV Higgs Bottom up Approach! Neutrino mass, Dark matter and Baryon asymmetry Higgs prop. 8 Bottom up Approach 1. Direct search 2. Indirect search Measuring effects Energy on the 126 GeV Higgs boson Discovery Energy 126 GeV h H++, H+, H, A, … 126 GeV h H++, H+, H, A, ... Studying both ways is important to determine the structure of the Higgs sector. 9 Bottom up Approach 1. Direct search 2. Indirect search Measuring effects Energy on the 126 GeV Higgs boson Discovery Energy 126 GeV h H++, H+, H, A, … 126 GeV h H++, H+, H, A, ... Studying both ways is important to determine the structure of the Higgs sector. 10 Indirect Search Indirect search = Precision test of Higgs couplings Patterns of deviation in various Higgs couplings strongly depend on the structure of the Higgs sector. Experiments Theory hVV Minimal hbb Singlet Models hττ 2HDMs Compare etc… hcc hγγ Triplet Models hhh Make a “Fingerprint” from precise measurements. 11 Higgs coupling measurements ILC, TDR ILC, Higgs White Paper, arXiv: 1310.0763 (300/fb) The hZZ coupling can be measured by 1 % accuracy at the ILC(250) ! 12 Higgs coupling measurements ILC, TDR ILC, Higgs White Paper, arXiv: 1310.0763 (300/fb) The hVV and hff couplings can be measured by 1 % accuracy at the ILC(500) !! 13 Higgs coupling measurements ILC, TDR ILC, Higgs White Paper, arXiv: 1310.0763 (300/fb) The hVV and hff couplings can be measured by 1 % accuracy at the ILC(500) !! 14 Contents Introduction - Bottom up approach (Indirect search) Deviations in the Higgs boson couplings in various Higgs sectors - The hVV and hff couplings at the tree level Higgs boson couplings in the 2HDMs - Tree level - One-loop level Summery 15 Basic Constraints There are two guidelines to restrict Higgs sectors. 1. Electroweak rho parameter ρexp = 1.0004 +0.0003 -0.0004 Models with ρtree = 1 seems to be a natural choice. Satisfy the relation Alignment of (exotic) VEVs T Y 1 0 1/2 1/2 3 2 … … Ex. Model with doublet (Y=1/2) + triplet (Y=1) + triplet (Y=0) (Georgi-Machacek model) if 16 Basic Constraints There are two guidelines to restrict Higgs sectors. 2. Flavor Changing Neutral Current (FCNC) Tree level FCNC process should be absent. In general, multi-doublet extensions cause FCNC at the tree level B0 Φ0 B0 17 Basic Constraints There are two guidelines to restrict Higgs sectors. 2. Flavor Changing Neutral Current (FCNC) Tree level FCNC process should be absent. In general, multi-doublet extensions cause FCNC at the tree level B0 Φ0 B0 Only one Higgs doublet couples to each fermion. 18 Simple Extended Higgs Sectors We consider the following simple Higgs sectors; (with ρtree = 1 and no tree level FCNC) 1. Φ + S (Singlet) 2. Φ + D (Doublet) 3. Φ + Δ (Triplets or larger) [GM model, Septet model] Hisano, Tsumura, PRD87 (2013) Kanemura, Kikuchi, KY, PRD88 (2013) 19 Two mixing angles Mixing between CP-even states VEVs T: isospin, Y:hypercharge where 20 Deviations in hff and hVV Yukawa f α Φ f β Yf = mf /<Φ> Gauge V <Φ> V β α Φ φ <φ> <φ> V φ V 21 Higgs Singlet Model (φ=S) Yukawa f Φ f ★ The singlet VEV α S does not contribute to the EWSB. <S> Yf = mf /<Φ> → β=0 (<Φ>=246 GeV) ★ The hff and hVV couplings are Gauge V <Φ> α Φ V <S> V universally suppressed. S V 22 Two Higgs Doublet Model (φ=D) Yukawa f α Φ (D) Yf = mf /<Φ (D)> f ★ There are 2 patterns in κf D (Φ) β <D (Φ)> for each fermion f. ★ξ=1 Gauge β <Φ> V V Φ V <D> α D V 23 Model with a triplet (or higher) (φ=Δ) Yukawa f α Φ f ★ The hff couplings are Yf = mf /<Φ> universally suppressed. Δ β ★ ξ factor can be larger <Δ> than unity. → κV > 1 Ex. Gauge V <Φ> α Φ V β GM model: ξ = 2*sqrt(6)/3 <Δ> V Septet model : ξ = 4 Δ V 24 SM 25 κF’ SM 26 κF’ SM κF = κF’ 27 κF’ SM κF = κF’ 28 Gauge vs Yukawa -π/4 < α < +π/4 0.1 < tanβ < 100 Singlet Model 2HDM (Type-I) Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] 29 Tau vs Bottom -π/4 < α < +π/4 0.1 < tanβ < 100 Singlet 2HDM (Type-I) Georgi-Machacek Model 2HDM (Type-II) 2HDM (Type-X) 2HDM (Type-Y) 30 Contents Introduction - Bottom up approach (Indirect search) Deviations in the Higgs boson couplings in various Higgs sectors - The hVV and hff couplings at the tree level Higgs boson couplings in the 2HDMs - Tree level - One-loop level S. Kanemura, M. Kikuchi, KY, appear in PLB, arXiv: 1401.0515 [hep-ph] Summery 31 2HDMs In general, Yukawa Lagrangian is given by To avoid the tree level FCNC, one of the Yukawa couplings should be forbidden. Z2 symmetry (softly-broken) Glashow, Weinberg, PRD15 (1977) Z2 symmetry (unbroken) Barbieri, Hall, Rychkov, PRD74 (2006) S3 symmetry Kajiyama, Okada, KY, arXiv:1309.6234 [hep-ph] U(1) symmetry Ko, Omura, Yu, JHEP1201 (2012) … 32 2HDMs with the softly-broken Z2 sym. In general, Yukawa Lagrangian is given by To avoid the tree level FCNC, one of the Yukawa couplings should be forbidden. Z2 symmetry (softly-broken) Glashow, Weinberg, PRD15 (1977) Z2 symmetry (unbroken) Barbieri, Hall, Rychkov, PRD74 (2006) S3 symmetry Kajiyama, Okada, KY, arXiv:1309.6234 [hep-ph] U(1) symmetry Ko, Omura, Yu, JHEP1201 (2012) … There are four independent types of Yukawa interactions. 33 Four Yukawa Interactions Under the Z2 symmetry, two doublets are transformed as Φ1 → +Φ1 and Φ2 → -Φ2. Type-I Type-II (MSSM) Φ2 Φ2 u e u d Φ1 e Barger, Hewett, Phillips (1990), Grossman (1994) Aoki, Kanemura, Tsumura, KY (2008) d Type-X (Leptophilic) Type-Y (Flipped) Φ2 Φ1 Φ2 u d e u e d Φ1 34 Mass Eigenstates In the Higgs basis, two doublets can be parameterized as: tanβ = <Φ2>/<Φ1> NG bosons CP-even Higgs Charged Higgs CP-odd Higgs SM-like Higgs boson w/126 GeV 35 Yukawa/Gauge Interaction V = (SM) × sin(β-α) h V ξu ξd ξe cotβ cotβ cotβ Type-II cotβ -tanβ -tanβ Type-X cotβ cotβ -tanβ Type-Y cotβ -tanβ cotβ Type-I f = (SM) h f × [sin(β-α)+ξf cos(β-α)] 36 Higgs Potential The Higgs potential under the softly-broken Z2 sym. and CP-invariance We have 8 parameters in the potential. They can be interpreted by v (=246 GeV), mh (=126 GeV), mH, mA, mH+, sin(β-α), tanβ, and M2 Mass formulae with sin(β-α) ~1 mh2 ~ λv2, mΦ2 ~ M2 + λv2 37 SM-like/Decoupling Limit SM-like limit: taking sin(β-α) → 1 All the Higgs boson couplings become the same value as in the SM Higgs couplings at the tree level. Decoupling limit: taking M2 (=mΦ2) → ∞ [mΦ2 ~ M2 + λv2] Decoupling limit can be taken only when the SM-like limit is taken. 38 Decoupling/SM-like Limit 10% dev. cos(β-α) > 0 cos(β-α) < 0 δ= 1% dev. 0.1% dev. (mH = mA = mH+= M =) 39 Decoupling/SM-like Limit 10% dev. κV = sin(β-α) → 1 δ= cos(β-α) > 0 cos(β-α) < 0 1% dev. 0.1% dev. (mH = mA = mH+= M =) 40 Decoupling/SM-like Limit 10% dev. cos(β-α) > 0 cos(β-α) < 0 δ= 1% dev. 0.1% dev. (mH = mA = mH+= M =) 41 Patterns of Deviation in hff Couplings If κV ≠ 1 is found, several patterns of deviation in hff appear. f = (SM) × [sin(β-α) + ξf cos(β-α)] h (SM) × [sin(β-α) + cotβ cos(β-α)] = f δ = 1 - sin(β-α) (SM) × [sin(β-α) - tanβ cos(β-α)] (SM) × For cos(β-α) > 0 ~ δ≪1 Type-I cotβ u d e Type-II cotβ u d cos(β-α) < 0 (SM) × Type-X tanβ e Type-Y cotβ tanβ cotβ u e u d e d tanβ 42 Patterns of Deviation in hff Couplings If κV ≠ 1 is found, several patterns of deviation in hff appear. f = (SM) × [sin(β-α) + ξf cos(β-α)] h (SM) × [sin(β-α) + cotβ cos(β-α)] = f δ = 1 - sin(β-α) (SM) × [sin(β-α) - tanβ cos(β-α)] (SM) × For cos(β-α) > 0 ~ δ≪1 Type-I cotβ u d e Type-II cotβ u d cos(β-α) < 0 (SM) × Type-X tanβ e Type-Y cotβ tanβ cotβ u e u e d tanβ d 43 Bottom vs Tau κV2 = 0.99, 0.95, (δ ~ 0.005, 0.02) cos(β-α) < 0 44 Radiative Corrections • How these predictions can be modified by taking into account radiative corrections? • The hff and hVV couplings can be measured with O(1)% accuracy. • In order to compare precision measurements, to include radiative corrections are essentially important! 1-loop level 45 Radiative Corrections in the 2HDMs There are papers for 1-loop corrections to the Higgs boson couplings in 2HDMs. hhh Hollik, Penaranda, Eur. Phys. J. C23 (2002) [in the MSSM Higgs sector] Kanemura, Kiyoura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan PLB558, (2003); Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004). hVV Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004). hff Guasch, Hollik, Penaranda, PLB515 (2001) [in the MSSM Higgs sector] We discuss 1-loop corrections to the hff couplings in the four types of the 2HDM. 46 Decoupling/Nondecoupling Decoupling theorem Appelquist, Carazzone (1975) NP loop effects to the low energy obs. vanish when new particles are heavy. SM SM NP+SM SM 1/Mn → 0 (M → ∞) SM SM M→∞ SM SM Violation of the decoupling theorem If a particle mass is (mostly) given by the Higgs VEV, the particle loop effect does not vanish even in rather large mass case. E.g., Top mass:mt = ytv Scalar boson mass:mφ2 = λv2 + M2 (with λv2 > M2 ) 47 The hhh coupling @1-loop in the 2HDM Φ = H, A, H± Kanemura, Kiyoura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan PLB558 (2003) 48 The hhh coupling @1-loop in the 2HDM Φ = H, A, H± Kanemura, Kiyoura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan PLB558 (2003) 0 In the case with M2 >> λv2, we can see the decoupling behavior. 49 The hhh coupling @1-loop in the 2HDM Φ = H, A, H± Kanemura, Kiyoura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan PLB558 (2003) ~1 In the case with M2 < λv2, nondecoupling effects (quartic power of the masses) appear. 50 Renormalized hff vertices Renormalized hff vertex Renormalized scale factor at on-shell The counter term contribution 51 Parameter Shifts Fermion masses and wave functions Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004). CP-even Higgs sector and mixing angle β The VEV 52 On-shell Renormalization Conditions =0 f f f f p2=mf2 =0 p2=mf2 δmf and δZVf h h =0 p2 =mh2 h H = h p2=mh2 H =0 p2=mH2 δZh, δα and δCh The counter term δv G0 A = p2=mZ2 G0 A =0 p2=mA2 is determined from the EW on-shell RCs. Hollik, Fortsch. Phys. 38, 165 (1990). δβ (and δCA) 53 Decoupling [sin(β-α)=1, mH+=mA=mH (=mΦ) and mΦ2-M2 = (300 GeV)2] Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 tanβ = 1 tanβ = 3 SM 54 Nondecoupling [sin(β-α)=1, mH+=mA=mH (=mΦ) and M2 = 0] Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 55 Nondecoupling [sin(β-α)=1, mH+=mA=mH (=mΦ) and M2 = 0] Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 56 Fingerprinting at the tree level Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 cos(β-α) < 0, tanβ = 1, 2, 3 and 4, 57 Fingerprinting at the 1-loop level Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 cos(β-α) < 0, tanβ = 1, 2, 3 and 4, mH+ = mA = mH (=mΦ), 100 GeV < mΦ < 1 TeV, 0 < M < mΦ, Unitarity + Vacuum stab. 58 Fingerprinting at the 1-loop level Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 cos(β-α) < 0, tanβ: Scanned mH+ = mA = mH (=mΦ), 100 GeV < mΦ < 1 TeV, 0 < M < mΦ, Unitarity + Vacuum stab. 59 Fingerprinting at the 1-loop level Shinya Kanemura, Mariko Kikuchi and KY, arXiv: 1401.0515 cos(β-α) < 0, tanβ: Scanned mH+ = mA = mH (=mΦ), 100 GeV < mΦ < 1 TeV, 0 < M < mΦ, Unitarity + Vacuum stab. 60 One-loop corrected hZZ coupling Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004). Tanβ = 2, mΦ = 300 GeV 1 - sin2(β - α) Even taking the maximal nondecoupling case (M2=0), the amount of correction is less than 1%. 61 Summary Indirect Search = Comparing fingerprints of the Higgs couplings. Typical patterns of deviations in extended Higgs sectors at tree level Points: CP-even Higgs mixing and VEV sharing 1. Higgs singlet model → κf and κV are universally suppressed. 2. Two Higgs doublet models → 4 patterns in κf’s. 3. Triplet models → κf are universally suppressed and κV can be larger than 1. Radiative corrections to the Higgs boson couplings Points: (Non)decoupling property of extra Higgs bosons 1-loop corrections from extra Higgs bosons to the hhh, hff and hVV couplings can be maximally O(100)%, O(10)% and O(1)%, respectively. If 1% deviation in the hZZ couplings is found at the ILC(250), we can discriminate the four types of 2HDM by precisely measured hff couplings at ILC(250) or ILC(500). 62 63 Vacuum stability + Unitarity 64 Unitarity bound for the Singlet Model Kang, Park, arXiv:1306.6713 [Singlet] 65 Gauge vs Yukawa -π/4 < α < +π/4 0.1 < tanβ < 100 Unitarity const. w/ 300 GeV. Singlet Model 2HDM (Type-I) Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] Kang, Park, arXiv:1306.6713 [Singlet] Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004) [2HDM] Aoki, Kanemura, PRD77 (2008) [GM] 66 Gauge vs Yukawa -π/4 < α < +π/4 0.1 < tanβ < 100 Unitarity const. w/ 500 GeV. Singlet Model 2HDM (Type-I) Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] Kang, Park, arXiv:1306.6713 [Singlet] Kanemura, Okada, Senaha, Yuan, PRD70 (2004) [2HDM] Aoki, Kanemura, PRD77 (2008) [GM] 67 Top Yukawa 68 Tanβ dependence 69 τ vs b 70 b vs c 71 τ vs c 72 On-shell Renormalization Scheme Parameters shift: g → g + δg, g’ → g’ + δg’, Wμ → ZW1/2 Wμ , 2-point function = IPI diagram + Counter term v → v + δv, Bμ → ZB1/2 Bμ 3-point function = IPI diagram + Counter term 73 Higgs coupling measurements Peskin, 1207.2516[hep-ph] LHC: 14 TeV, 300 fb-1 ILC1: 250 GeV, 250 fb-1 ILC: 500 GeV, 500 fb-1 ILCTeV: 1 TeV, 1000 fb-1 74 Signal Significance @125 GeV Obs. (Exp.) ATLAS γγ 7+8TeV, ~25/fb CMS 7.4σ (4.3σ) 3.2σ (4.2σ) [CONF-2013-012] [PAS-HIG-13-1] ZZ* →4l 6.6σ (4.4σ) 6.7σ (7.1σ) [CONF-2013-013] [PAS-HIG-13-2] WW* →lvlv 3.8σ (3.8σ) 4.0σ (5.1σ) [CONF-2013-030] [PAS-HIG-13-3] bb No excess 2.1σ(2.2σ) 1.4 (1.3)×SM exc. [PAS-HIG-13-012] [CONF-2013-079] ττ Spin 1 is excluded Higgs mechanism Yukawa? 4.1σ (3.2σ) 2.9σ (2.6σ) [CONF-2012-160] [PAS-HIG-13-004] There is no room for doubt that it is a Higgs boson. 75 Gauge vs Yukawa Singlet Model 2HDM (Type-I) Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] For details, see Prof. Chiang’s talk 76 Fingerprinting (Gauge vs Fermion) -π/4 < α < +π/4 Singlet Model 2HDM Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] 77 Fingerprinting (Gauge vs Fermion) -π/4 < α < +π/4 0.1 < tanβ < 100 Singlet Model 2HDM Georgi-Machacek Model [ξ = 2*Sqrt(6)/3] 78