AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
advertisement

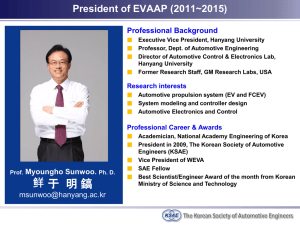
AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Emrah KUTLU Zeynep AVCIOĞLU AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY • • • • Key driving sector of the economy Closely tied to other sectors of the economy Prime buyer in basic industries Requires complex and multidisciplinary technology AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY • Intense competition in the market • Intensive R&D • Fastest developing sector in the global economy AROUND THE WORLD • 1800’s Europe • US Mass production • 1990’s Globalization TURKEY • mid 1950’s • 1954 Türk Willys Overland Ltd. • Tofaş, Renault, Ford • Joint ventures MARKET STRUCTURE • Highly labor and capital intensive • Majority of costs for producing - Labor - Materials - Advertising MARKET STRUCTURE PORTER’S FIVE FORCES MODEL MARKET STRUCTURE • The auto industry is considered to be an oligopoly. • Today there are 15 companies in production of which 5 are automotive producers and 10 are commercial vehicle producers. MARKET STRUCTURE • The automotive industry is one of the four largest exporters. • Significant contribution to: - National production and development - Employment - Level of technology MARKET STRUCTURE Table- 1 PRODUCTION IN TURKEY Source: OSD, MVI Monthly Report MARKET STRUCTURE • The companies in the sector are mainly located in the Marmara Region. • Existing motor vehicle production capacity of the automotive industry in Turkey is 1,015,000 units per year, as of 2002. Table- 2 The Firms in the Automotive Industry Source:OSD, 2002 Table- 3 The Leading Firms in the Industry and Their Sales 2004 yılı ilk 500 firma sıra no. 2003 yılı 500 Büyük Firma Sıra No Firma ve Müessese Adı Bağlı Bulunduğu Oda Özel Firma Sıra No Üretimden Satışlar Net (YTL) 2 2 FORD OTOMOTİV SAN. A.Ş. İSTANBUL 1 4,445,190,178 3 11 TOYOTA OTOMOTİV SANAYİ TÜRKİYE A.Ş. ADAPAZARI 2 3,348,031,394 4 4 OYAK-RENAULT OTOMOBİL FABRİKALARI A.Ş. İSTANBUL 3 2,966,839,536 9 7 TOFAŞ TÜRK OTOMOBİL FABRİKASI A.Ş. İSTANBUL 7 2,146,938,617 16 17 MERCEDES BENZ TÜRK ANONİM ŞİRKETİ İSTANBUL 12 1,218,993,109 Source: ISO, 500 Büyük Sanayi Kuruluşu Anketi, 2004 CONDUCT LEADING EXPORTING COUNTRIES • • • • France Germany Italy UK Table- 4 Source: www.wbr.co.uk, About the Turkish Automotive Industry Table- 5 Automobile Imports( in units) Years Imports from EU Total Imports Share of Imports from EU 1997 93,811 135,795 69% 1998 93,549 110,552 84% 1999 102,662 121,309 84% 2000 236,902 272,110 87% 2001 66,405 74,165 89% 2002 53,121 61,294 86% Source: OSD, 2005 CONDUCT PRODUCT DESIGN -Design of Textile and Textile-Based Products Used in Automotive -Designing Commercial and Public Transport Vehicles Like Trucks, Buses,etc. - Development and Redesign Work for Currently Produced Automobiles Towards New Markets -Design Work Towards Developing Accessories and Products of Special Functions - Prototype Processes of Vehicles Designed Abroad and Design Work Concerning Test Production CONDUCT PARTNERSHIPS • Tofaş- Fiat • Otosan- Ford • Oyak- Renault PERFORMANCE SWOT ANALYSIS The Strength of the Turkish Automotive Industry Economically a) Third major sector in Turkish manufacturing industry b) Leading private sector investor c) Driving force in manufacturing industry with its high value added d) A reliable source of tax revenue with its totally registered production PERFORMANCE Human Knowledge a) High-skilled human resources both in production and management b) Sustainable and improvable competitive workforce with low labor cost and culture of productivity c) Accumulated technological know-how and rapidly growing investments in R&D d) Quality management systems e) Widespread distribution and marketing networks f) Integration with world automotive industry since 1990s PERFORMANCE Geostrategic Importance a) The most developed automotive industry and a unique export and production base in the region with close bilateral relations with EU, G8, Eurasia b) Export experience and strong export markets c) Easy access to potential emerging markets PERFORMANCE The Weakness of the Turkish Automotive Industry a) Unstable domestic market b) Loss of quality and quantity in manpower as a result of the crises caused by the weak economy of the country c) In adequate investments in the sector d) High costs of raw materials due to capacity utilization and production below economies of scale e) High sales taxes and gasoline prices f) Lack of international strategy g) Excess capacity h) Insufficient export incentives GROWTH AND FUTURE - The automotive industry in Turkey has a significant potential for progress and export capacity. With the completion of global vehicle projects currently under progress, Turkey will soon reach an annual vehicle export capacity of at least 500,000 units. - In the near future, Turkey will be the world‘s alternative production center of vehicle and parts, and the automotive sector will become one of the leading sectors of the manufacturing industry, with exports of $8-8.5 billion. GROWTH AND FUTURE Basic elements of the national export strategy to reach these goals are; • • • • • • • • Exporting of knowledge-intensive products with high added value Focusing on markets with high purchasing power Reaching the end consumer Adopting quality by all industrial institutions Establishing sales prices based on market conditions and customer requirements Following new developments Focusing on R&D Investing more in technology, human resources, information, and quality training CONCLUSION Globalization will continue increasingly in the automotive sector. The automotive industry in Turkey is in a position where it can produce at global standards. It has developed its competitive capabilities, and a structure that can apply common marketing strategies with licensing countries. The sector is able to create more added values. Having a competitive structure, having the power to manufacture quality and consistent products with new technologies, and most effectively, having the cost-price advantage, puts Turkey in a position of being an important manufacturing base and an important market, from the perspective of the global automotive. THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION…