Protein mteabolism
advertisement

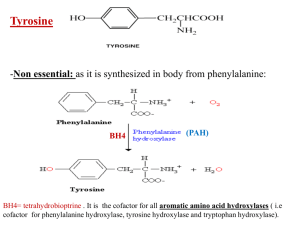
Conversion of amino acids into specialized products Glycine amino acid I- Non essential amino acid: as it is synthesized in the body from serine Serine ↔ glycine +CHO The reaction is reversible so each of them can be converted to each other II- glucogenic : Being converted into serine which is converted into pyruvate Functions of glycine: 1- Synthesis of heme: Glycine + Succinyl CoA → → → → → →Heme 2- Bile salt formation: Cholic acid (bile acid) +glycine → glycocholate (bile salt) 3-Purines: C4, C5 and N7 of purines are derived from glycine 7 5 4 4- Serine: Glycine is converted into serine by the enzyme serine hydroxymethyl transferase. Serine is then converted into pyruvate so both glycine and serine are glucogenic ↔ 5- Creatine: - Creatine is formed of glycine + arginine + methionine amino acid Creatine is present in blood in the free form, while in muscles it is gained phosphate group from ATP by creatine kinase (CK) to give creatine phosphate (creatine ~ p) or called phospho creatine (PCr.) and ATP is converted into ADP. creatine ~ p is the main storage form of energy in muscles and used during muscle contraction. During intense physical exertion, ATP is rapidly recreated from ADP by the donation of a phosphate group from Phosphocreatine (PCr). Creatinine: Is the anhydrous form of creatine and formed in muscles by nonenzymatic dehydration of creatine - Creatinine is excreted in urine. It is one of the kidney function tests. - Elevated creatinine levels in blood than normal indicates renal disease. -Normal creatinine levels: 0.8- 1.2 mg/dl. -II- Glycine participates in detoxification reactions in the body. It detoxify aromatic acids such as benzoic acid (toxic) converting it into hippuric acid (less toxic) which is excreted in urine. Conversion of aromatic acids into specialized products 1- Phenylalanine amino acid Essential amino acid Converted into tyrosine (major pathway ) Minor pathway of phenylalanine: occurs normally in liver tissues via transamination giving phenylpyruvate (a metabolite with minor significance) transaminase Phenylketonuria (PKU): PKU is a genetic disease caused by a defect in the gene responsible for synthesis of PAH enzyme (97% of cases) or by deficiency of the BH4 cofactor (3%). As a result phenylalnine not converted into tyrosine and accumulated in blood, tissues and brain. Phenyl pyruvate (a minor metabolite of phenyalanien will also acumulate and secreted in urine hence the name of the disaese, phenylketonuria). Symptoms of PKU: -Excess phenylalanine leads to mental retardation and delay in growth, talking and walking. -Hypopigmentation (light hair, skin and eye) is also present because tyrosine is not synthesized. Tyrosine is important for synthesis of melanin pigment, so no tyrosine , no melanin. -Musty odor of urine due to excess phenylalanine and phenylyruvate -Treatment of PKU - Diet low in phenylalanine - Aspartame (artificial sweetening agent) is contraibndicated because it contain phenylalanine 2-Tyrosine -Non essential: as it is synthesized in body from phenylalanine: BH4 (PAH) BH4= tetrahydrobioptrine . It is the cofactor for all aromatic amino acid hydroxylases ( i.e cofactor for phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase and tryptophan hydroxylase). Functions of tyrosine: tyrosine enter in the synthesis of: 1- catecholamines 2- melanin pigment 3- thyroid hormones 1- Catecholamines: dopamine, epinephrine and nor epinephrine Epinephrine and nor epinephrine are secreted from adrenal medulla in response to fear, stress, anger, low blood glucose and hypotension. They stimulate degradation of glycogen and TAG (stimlate glycogenolysis and lipolysis). Synthesis of catecholamines also called tyrosinase ↓ tyrosinase 2-Synthesis of melanin: Melanin is aromatic quinone. It is black or brown pigment present in skin, hair and eyes. Its function is to protect underlying cells from the harmful effects of sun light ( UV radiation). ↓ tyrosinase → dopachrome →→ Melanin dopaquinone Albinism: Genetic disease due to genetic deficiency of tyrosinase enzyme and lack of melanin synthesis. This leads to hypopigmentation of skin, hair and eyes making the albino are sensitive to sun light (photophobia), increasing the incidence of skin burns and cancer. 3- Synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4): - Tyrosine +I2 gives monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT) - one MIT + one DIT gives T3 - 2 DIT gives T4 (structures not required) Tryptophan amino acid - Essential amino acid - Both glucogenic and ketogenic (gives pyruvate and Acetyl CoA). Functions: 1- Synthesis of serotonin (5-hydroxy tryptamine) in gut, CNS, platelets (BH4) THB= BH4 (tetrahydrobioptrine) AAAO= aromatic amino acid decarboxylase Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, vasoconstrictor. Regulate mood and sleeping. Its deficiency lead to depression. It is used as antidepressant Research found that fruits (like dates, banana and papaya), turkey, peanuts, almonds, green leaves increase the synthesis of serotonin Serotonin is popularly thought to be a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness. Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the intestine, where it is used to regulate intestinal movements. The remainder is synthesized in neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of mood, appetite, and sleep. Serotonin also has some cognitive functions, including memory and learning. Increasing serotonin is the mechanism of action of several classes of antidepressants. 2- Synthesis of melatonin: Melatonin is N-acetyl 5-methoxy tryptamine - ↓↓ 1) N-acetylation 2) O-methylation Synthesis and secretion of melatonin is regulated by dark/light cycle. Production of melatonin by the pineal gland in brain is inhibited by light and stimulated by darkness. For this reason melatonin has been called "the hormone of darkness. - Melatonin is sleep-inducing molecule -So ingestion of food rich in tryptophan leads to sleepiness. It is powerful antioxidant It has important role in protecting skin from damaging effect of UV radiation: 3- Synthesis of nicotinic acid (niacin) - Niacin (vitamin B3) is a member of vitamin B complex. -Coenzyme NAD and NADP are derived from niacin. NAD (to remember the structure, not required) - Niacin is important for skin health, regulate intestinal movement and energy production particularly in brain (because NAD and NADP are imprtant cofactors in glycolysis) - Deficiency of niacin leads to pellagra (dermatitis, diarrhea and Dementia). Insomnia and high sensitivity to sunlight. - Pellagra occurs also in case of deficiency of dietary tryptophan which converted into niacin - Pellagra occurs in areas where people eat mainly maize (corn, the only grain low in digestible niacin)