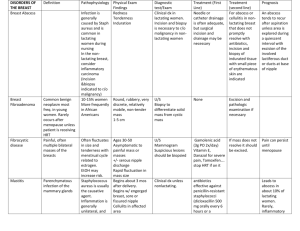
50 Shades of Aging
Kathleen Lindaman Aebischer
PT
What is the pelvic floor and what
does it have to do with my quality
of life?
Much more than you think!
Statistics
2010
40 million adults over the age of 65
(12.9% of the population)
53,364 adults are greater than 100 yrs
old (.13% of the population)
2030
Estimated 72 million over the age of 65
(19% of the population)
Life Expectancy
Adults over the age of 65 have an
average lift expectancy of 78.2 yrs
with women living 20 yrs more on
average and men only 17 yrs on
average
Who do The Seniors Live with?
72% of older men and 42% of older
women live with spouses at home
Widows account for 8.7 million of the
population and widowers 2.1 million
29% over the age of 65 live alone
Nursing Homes
Only 1.5 million (4.1% of the
population) live in nursing facilities
2009 Seniors Living Outside
Nursing Facilities
40% rate their health as excellent or
very good despite having at least one
chronic medical condition
37% of those over 65 categorize
themselves as having a disability vs.
being disabled
A Much Larger Segment of Seniors
17.4% over the age of 65 are working
or seeking work (6.7 million)
Views on Retirement
59% view retirement as a time to be
active and involved
Only 24% see retirement as a time to
relax and enjoy leisure
Older Volunteers
46.6% of seniors from 65 to 74
volunteer in their communities
43% of those 75+ yrs old also
volunteer
The next generation retirees will be
the healthiest and longest lived with
40% of the population expected to
reach 90 by 2050
How Do We Get To That
Healthy
Vigorous Life of Possibilities
?
General Changes as We Age
Loss of Muscle Mass
Weight gain
Decreased skin elasticity
Loss of height
Loss of bladder capacity
Stiffening of the joints and ligaments
General Changes with Aging
Decreased circulation
Glucose tolerance deteriorates
Bones become more brittle
There is a decrease in the immune
response effectiveness
Many of these conditions can be
improved or slowed by remaining
active
Regular exercise
Stretching, aerobics, and strengthening
Dietary Changes
Slow Aging
Sexuality and Aging
Interest and pleasure in sex does not
decrease in healthy aging adults but
sexual behavior does decline
Sex remains a way to communicate
love, affection, warmth, sharing and
bonding
Benefits of Sex
Sex burns fat
Boosts the immune system
Releases brain endorphins
Relieves stress
Slows the pronounced changes that
occurs with aging
Improves flexibility of the tissues
Improves body image
Aging Changes Specific To Women
Low sexual desire/sex drive
Pain due to illness
Lack of mobility
Medications
Poor body Image
Depression
Fatigue and stress
Slower sexual arousal
Low testosterone
Menopause
The largest change in aging for
women
Symptoms
Hot flashes
Worsening of organ prolapse
Incontinence, urgency, frequency
Frequent urinary tract infections
Vaginal dryness
Lack of Estrogen
Causes a cascade of physical
changes in the body
Lean fit women are at more risk for
post menopausal problems
associated with lack of estrogen
Atrophic Vaginitis
The vagina shortens and becomes
more narrow
The tissue is thinner with loss of
elasticity
Vaginal dryness
Intercourse is painful for 25 to 45% of
post menopausal women
Treatments
Vaginal moisturizers
Replens
Dilators
Purchased sets / Candles
Vibrator use
Lubricants
Local estrogen treatment
Vaginal estrogen creams such as
Estrace and Premarin
Vaginal tablets such as Vagifem
Vaginal estrogen rings such as Estring
Vaginal suppositories
Systemic estrogen treatments
Estrogen is absorbed into the blood
stream and reaches all the tissues
Estrogen patches
Hormonal Replacement Therapy or
HRT oral estrogen replacements
Homeopathic remedies
Side Effects Vary
Headache
Stomach upset, bloating, nausea
Weight changes
Breast tenderness
Back and abdominal pain
Respiratory infections
Vaginal itching or yeast infections
Change in sexual interest
Vaginal Irritants
Soaps and laundry detergents with
dyes and perfumes
Lotions
Douches
Condom use
Smoking
Preventative Measures
Use natural oils to hydrate the tissue
in the vulva (area between the inner
vaginal lips)
Exercise regularly including
stretching, aerobics, and
strengthening
Maintain a healthy diet
Work on loving the body you are in
AND
Use It Or Lose It!
Pelvic Floor Function
Supports the
internal organs
Assists the round
sphincter muscles
in clamping tubes
so we don’t loose
urine or feces
Assists with sexual
function
Pelvic Floor Muscles
3 muscle layers
Superficial External Genital Muscles
Urogenital layer (Perineal Membrane)
Pelvic layer
Supportive Dysfunctions
Incontinence
Stress
Urge
Mixed
Overflow
Treatment
Physical Therapy
Medication
Botox and other injections
Surgery
Supportive Dysfunctions
Organ Prolapse
Uterine prolapse
Bladder prolapse
Rectal prolapse
Vaginal vault prolapse
Treatment
Physical Therapy
Pessary use
Surgery
Signs and Symptoms of Supportive
Pelvic Dysfunctions
Painful intercourse (dyspareunia)
Pressure against the vaginal wall
Full feeling in the lower belly
Groin stretching pain
Feeling like something is falling out of
the vagina
Incontinence
Contributing Factors to Supportive
Pelvic Dysfunctions
Obesity
Long lasting coughing bouts
Frequent constipation
Pelvic Organ tumors
Difficult vaginal delivery
Hypertonus Pain Dysfunction
Signs and Symptoms
Pain
Dyspareunia/sexual dysfunction
Difficulty with defection/urination
Difficulty with sitting
Hypertonus Treatments
Relaxation and biofeedback
Physical Therapy
Trigger point injections
Epidurals
Anti-depressant medication
Pain medications and regular muscle
relaxants do not work well on the
pelvic floor
Hypertonus Contributing Factors
History of rape, abuse or incest
Post surgical pain
Scar tissue restrictions
Fractures of the coccyx (tailbone)
Pain due to hemorrhoids or severe
constipation
Unknown
Incoordination
(Muscle Dys-synergy)
Inappropriate use of muscles of the
pelvic floor and core
S & S of Muscle Incoordination
Val salva
Improper tissue contractility
Neurologic disorders
Adhesions
CNS disorders
Disuse
Contributing Factors
Incoordination/Disuse Dysfunction
Lack of awareness:
Weakness, lack of coordination of
muscles
Muscle disuse atrophy
Muscle imbalances: post-op
reconstruction,
Lack of training
Neurological diseases
Incoordination Treatment
Physical Therapy
Muscle re-education
Muscle coordination
Relaxation
Postural education
Electric stimulation
Biofeedback
Visceral Pelvic Dysfunction
Abnormal mobility of the pelvic organs
Endometriosis is the most common
cause
Adhesions, trauma, surgery and
childbirth
Congenital muscle imbalances
S & S of Visceral Dysfunction
Weakness
Decreased sensation
Constipation or diarrhea, or both
Flatulence
Pain in the back, abdomen, thigh and
leg
Visceral Dysfunction Treatment
Physical Therapy
Acupuncture
Surgery
Hormonal Treatment
Incontinence
What population has the greatest %
of incontinence in women?
Treatment (Physical Therapy)
Behavioral Therapy
Toileting schedules
Dietary changes
Pelvic floor and core exercises
Biofeedback
Coordination of exercise
Treatment continued
Teach how to avoid holding your
breath and why
Pessary use
Surgery for bladder suspension
Injections
Our perception and
attitude toward any
situation will
determine the
outcome!