Organizational Theory * Part 1 Three Early Perspectives
advertisement

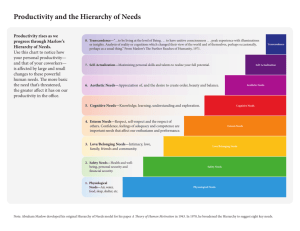
Chapter 3 Lecture/Recap Change with cultures Resources or thinking tools 3 P’s of historical writing Partial Partisan Interpreting meaning of facts > identifying facts Problematic Encourages dialogue Organizations as efficient machines Science used to predict ways to make organization run efficiently Big focus on hierarchy Managers communication deliver orders to employees Employees as wage-maximizing individuals Communication: creativity < constraint Scientific Management Reinforced divisions of labor and strict hierarchy (conflict) New focus: impact of manager/worker relationships Fayol’s Classical Management Five principles: planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling Focused on importance of factors such as: firm hierarchy, centralization of power, rewards for employees, employee morale Bureaucracy Focused on importance of factors such as: fixed division of labor, hierarchy, general rules, separation of personal and work life, personnel selected based on technical qualifications, equal treatment of employees, employment as career, tenure as protection What about the quality of manager/worker relationships? “…emphasized the interpersonal and social needs of individuals…” (p. 78) Focused on: empowering workers, importance of cooperation and strong internal relationships Examples: Chester Barnard: strong interpersonal relationships will help with persuading employees to work towards shared purpose Hawthorne Studies: more attention can lead to more productivity Concerns: What is the organizational climate? ‘How can an organization encourage employee participation and dialogue?’ (p. 82) What are the employees’ individual needs? Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Recognize goals/needs; how can work environment help? Example (figure 3.2, pg. 83): Need for love – respect from colleagues, feeling like you belong t the organization. Need for good self-esteem – salary and responsibilities McGregor’s Theory Y Management Employees = valued human resources. Don’t generally dislike work and plan to slack without constant control More participative and facilitative management style Example of principles/beliefs: the right conditions can encourage employees to accept and seek responsibility, it is natural for people to put effort into work, rewards for achievement can increase commitment Likert’s Principle of Supportive Relationships Four types/systems of organizations System IV – Participative – Principle of Supportive Relationships Stresses importance of open communication, general oversight > close supervision, supportive peer groups Considering one of the theories/approaches, what are issues with this scenario? How should it have been handled and why?