Endocrine lab - PCC - Portland Community College
advertisement

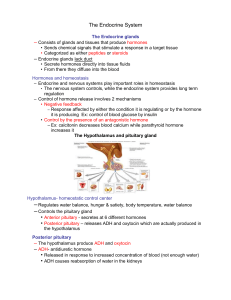
Exercise 28 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 The endocrine system • Diverse collection of organs and tissues that contain endocrine glands. • Glands secrete chemicals called hormones into blood capillaries • Hormones are transported to target cells at a distant location • Hormone binds to a specific receptor and the cell responds to message. 2 Endocrine and Exocrine • Exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts, which transport the secretions internal cavities of organs or to surface of the skin. 3 Effects of Hormones • Areas receptive to hormones are called target cells and may be tissues or organs. • Can have many effects such as growth, development, metabolism, etc. • Many organs produce hormones such as heart, stomach and kidneys. 4 5 Pineal Gland • Secretes: • Melatonin • Involved in circadian rhythms • Day melatonin, Night melatonin • Produces sleepiness 6 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) • Hypothalamus produces a number of releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones. • Stored in posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) • • ADH (antidiuretic hormone) • Reduces urine output by increasing water reabsorption in the kidney • Plays small role in blood pressure regulation • Also called vasopressin Oxytocin • Causes uterine contractions in labor • Causes milk let down in lactating mothers 7 Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis) • • • ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) • Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) • Stimulates production and release of thyroid hormone GH (growth hormone) • Stimulates growth of bones, cartilage, muscle • Timing and amount released determines body size 8 Endocrine Organs in Head • • • PRL (prolactin) • Stimulates breast development • Promotes and maintains lactation after childbirth FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) • Causes formation of ovarian follicles and stimulates them to produce estrogen • Stimulates sperm development in men LH (luteinizing hormone) • Initiates ovulation, maintains corpus luteum • Regulates testosterone production in males 9 Pituitary Histology Intermediate lobe (part of the anterior lobe) produces melanocyte stimulating hormone 10 Thyroid Gland • Secretes: • Thyroid Hormone • Regulates metabolic rate of the entire body • Important in development of the nervous system • • Calcitonin • Decreases bone reabsorption, lowering serum calcium levels PTH (parathyroid hormone) • Increases serum calcium • Decreases serum phosphorus 11 Thyroid Histology 12 Thyroid Histology • Follicular cells produce the colloid (contains precursors to thyroid hormone) • Parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin 13 Parathyroid Histology 14 Thymus • Active in young individuals and plays a part in immunocompetency. • Produces thymosin which causes maturation of T cells. • T cells start out in bone marrow and migrate to thymus The T cells migrate to lymph nodes and spleen to carry out their functions. 15 Hormones secreted by heart • Heart: If blood volume is elevated above normal, cardiac muscle cells in the heart was secrete natriuretic peptides. • Act on the kidneys to promote the loss of sodium ions and water. 16 Pancreas • Secretes: • Insulin (alpha cells) • Released in response to high blood sugar • Increases cellular absorption of glucose • Increases rate of lipogenesis and formation of glycogen in the liver Glucagon (beta cells) • Released in response to low blood sugar • Elevates blood glucose levels by promoting the breakdown of glycogen. Somatostatin (delta cells) inhibit both Insulin and glucagon and may increase efficiency in digestion. • 17 Pancreas •Acinar cells secrete digestive enzymes (exocrine) •Islet cells secrete insulin (beta cells) and glucagon (alpha cells) 18 Adrenal Glands 19 Adrenal Glands • • • Secrete: Glucocorticoids (Cortisone) • Released in response to stress • Increases formation of glucose from protein and fat breakdown • Decreases inflammation Aldosterone • Increases blood volume by causing kidneys to retain sodium (where sodium goes water goes too) in exchange for potassium • Increased blood volume will increase blood pressure 20 Adrenal Glands • Androgens • Are male sex hormones that are produced in small quantities and converted to estrogens (female sex hormones) when they enter the blood • Epinephrine & Norepinephrine • Fight or flight response • Increase heart rate, increase skeletal muscle blood flow, decrease skin blood flow 21 Adrenal Histology 22 Adrenal Cortex Zona Reticularis: Androgens Zona Fasiculata: Glucocorticoids (Cortisone) Zona Glomerulosa: Aldosterone 23 Hormones from the Kidneys • Erythropoietin • Stimulates RBC production • Calcitriol • Stimulates calcium and phosphate absorption • Stimulates calcium release from bone • Inhibits PTH secretion 24 Gonads • Ovaries in females produce estrogens • Testes in males produce testosterone • Both are stimulated by FSH from anterior pituitary • Influenced by LH which increases the level of hormone produced 25 Testis • Produce testosterone responsible for secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair and expansion of larynx. • Inhibin involved in negative feedback providing regulation of testosterone production 26 Testes • seminiferous tubules where the sperm are produced • The interstitial areas contain interstitial (Leydig) cells where the testosterone is produced. 27 Ovary • Produce oocytes (eggs) and have an endocrine function by producing estrogen and progesterone • Responsible for secondary sex characteristics in women. • 28 Endocrine physiology experiment • LH stimulates the final maturation of the oocyte and causes ovulation. • About 24-36 hours prior to ovulation there is a spike. • Are there any students in the middle of your ovarian cycle like to volunteer to test for the presence of LH? • If a woman has significant amounts of LH then the test strip produces a color (usually blue) 29 Glucometer Exercise • We need 4 volunteers to let us test their blood glucose levels at 30 minute intervals. • Measure glucose level • Drink soda or juice • After 30 min test again • 1 hour after drinking test again • If levels haven’t gone down after test again after 2 hours 30 Diabetes • • • • Type 1: Insulin Dependent Diabetes AKA: juvenile diabetes Caused by a lack of insulin Autoimmune disorder • Immune system destroys beta cells in the pancreas 31 Diabetes • Type 2: Non-Insulin Dependent • Caused by an insensitivity of cells to insulin. • Diabetes mellitus marked by hyperglycemia • urine production (polyuria) • thirst (polydipsia) • eating (polyphagia) 32 Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus • Normal blood glucose levels: 70-100 mg/dl • Diabetes mellitus: • A fasting glucose level above 140 mg/dl on two separate occasions, or • A blood sugar over 200 mg/dl 2 hours after oral glucose tolerance test with 75gm of glucose • Impaired Glucose Tolerance (Pre-Diabetes) • A fasting glucose level between 100-126 mg/dl on two separate occasions, or • A blood sugar between 140-200 mg/dl 2 hours after oral glucose tolerance test with 75gm of glucose 33 The End 34