Class Notes on Reconstruction - Washington Township Public Schools
advertisement

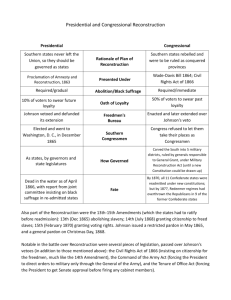
Objectives Describe the United States after the Civil War What questions were answered? What questions still remain? Describe the condition of the South after the War? What were the various plans for Reconstruction and which plan ultimately won out? What were the goals of the “Radical Republicans”? Describe some of the landmark legislation the Republican Congress passed. Post-Civil War America The Civil War settles a key constitutional crisis United States is singular not plural Federal Government supremacy over the states “The Lost Cause” Romanticized the Pre-Civil War South Revered Confederate leaders- Lee, Jackson, Davis Post Civil War South White South In economic ruin 1 in 5 white adult males killed in the war Stripped of capital($) invested in slaves, Confederate bonds and currency Social class structure destroyed Southern code of “honor” dealt a crushing blow Racism and sectional tension intensifies Freed Slaves 13th Amendment- Ends slavery in U.S. Freedmen (4 million) What now? Left plantations during or shortly after the war Some searched for family members Freedom for Freedmen means: Set up their own churches, schools, fraternal societies Freed Slaves Freedmen’s Bureau Distributed food to former slaves Established schools, taught by northern white women Some help to settle freedmen on land Also assisted poor whites Is this enough? Reconstruction Plans Lincoln’s Plan for Reconstruction Conservative Plan- wanted a smooth “readmission” of Southern States 10% Plan Suffrage to freedmen who were educated, owned property and served in Union Army Lincoln Assassination- Conspiracy! Shot in the head by John Wilkes Booth George Atzerodt decided not to go through with plan to kill Johnson, Seward was stabbed and survived. Results? Johnson’s Reconstruction Plan Racist- felt that “White men alone must manage the South” Similar to Lincoln’s Plan Exception- High ranking Confederate officials, any Southerner with land worth $20,000 or more had to apply to the president for an individual pardon. Also opposed by Radical Republicans Stage set for showdown between: “Radical” Republicans’ Plan Pushed for much more harsh treatment of the South Wanted to destroy the political power of Southern slave holders Responsible for many of the legal advancements of African-Americans at the time Led by Thaddeus Stevens (Penn) and Charles Sumner (Mass) Successfully overrode vetoes by Andrew Johnson on Civil Rights Act and Freedmen’s Bureau Act “Radical” Republicans Elections in 1866- Johnson campaigns for conservatives in Congressional elections Radicals win out in elections- carry overwhelming majorities in both the House and Senate “Radical” Reconstruction 14th Amendment- Constitutional definition of American citizenship Anyone born or naturalized in the U.S. is a citizen All citizens are guaranteed equal protection of the laws (by state and nat’l gov’t) Restrictions on former Confederates’ ability to hold office (unless pardoned by 2/3 of Congress) Radical Reconstruction The Reconstruction Act of 1867 Ten Confederate States divided into 5 military districts Military commander governed each district and registered qualified voters Voters would elect conventions (many AA delegates) to prepare new state constitutions Constitutions would have to give AA males right to vote and ratify 14th Amendment Radical Reconstruction 15th Amendment (1870) Forbade states and the federal government to deny suffrage to any citizen on account of “race, color, or previous condition of servitude” Gives all black males the right to vote President Johnson tried to veto Radicals’ bills but was overridden a record number of times Causes Congress to impeach Johnson Johnson’s Impeachment Review of Impeachment rules Impeachment is NOT to be thrown out of office Charges are brought by the House of Reps Senate acts as the jury in an impeachment trial 2/3 of the Senate must vote to convict Johnson’s Impeachment (1867) Radicals pass the “Tenure of Office Act” President could not fire a civil official without consent from the Senate Johnson tries to test it in the courts by firing Edwin Stanton (ally of the Radicals) Vote is 35-19- one short of 2/3 majority Why does this happen? Johnson’s Impeachment Excerpt from Iowa Senator James W. Grimes’ Opinion on the Trial of Andrew Johnson: “[The Tenure of Office Act]was directed against the President alone. It interfered with the prerogatives of his department as recognized from the foundation of the Government. It wrested from him powers which, according to the legislative and judicial construction of 80 years, had been bestowed upon him by the Constitution itself. … This Government can only be preserved and the liberty of the people maintained by preserving intact the co-ordinate branches of it-legislative, executive, judicial—alike. I am no convert to any doctrine of the omnipotence of Congress. I cannot agree to destroy the harmonious working of the Constitution for the sake of getting rid of an Unacceptable President.” Fame or Shame for Grimes? Reconstruction Politics Republicans in South Scalawags- Southern white Republicanssmall minority- stigmatized by the white Southern Democrats (accused them of using positions for personal gain) Carpetbaggers African-Americans Most of white South- Democrats Gains of Reconstruction African-Americans seek to develop their own institutions Black churches give unity and political self-confidence. Key to the Civil Rights Movement later African Americans’ participation in politics- all types of political office Southern whites- “Negro rule” Hiram Revels- First black US Senator Gains of Reconstruction Schools improve in South Northern women come south to work in Freedmen’s schools Public school system established in the South Segregated system African-Americans wanted to establish their own institutions separate from whites Whites refused to attend any schools that were integrated Sharecropping Should land be redistributed to freedmen in the South? Freedmen’s Bureau fails to redistribute land to freed slaves Federal Government gives confiscated land back to Planters Many freed slaves and poor whites worked the land of planters, and in return… President Grant (1869-1877) Ineffective politician- chose a poor cabinet Rampant scandals and corruption within his administration plagues the Republican party for years to come Panic of 1873 takes the focus off of Reconstruction Southern States “Redeemed” Many Southern whites began to regain suffrage Causes Democrats to regain control of Southern state governments Paramilitary organizations forced whites to join Democratic Party The Ku Klux Klan Social society established by former Confederate General Nathan Bedford Forrest Becomes a terrorist organization that attempted to: Overthrow Republican govt’s in the south As more Southern whites regain suffrage, the South is trying to rid itself of Republican rule Abandonment of Reconstruction Many Republicans begin to feel that with the right to vote, Reconstruction had served its purpose Panic of 1873- takes focus off of Reconstruction 1874 elections- Democrats take control of the House Compromise of 1877 Election of 1876- Rutherford B. Hayes (R) vs. Sam Tilden (D) Tilden won an apparent victory but 20 electoral votes were disputed (left Tilden 1 electoral vote short of a majority) Series of Compromises between both parties’ leaders gives Hayes the victory Hayes would: Remove all federal troops from occupied areas in the South Appoint one Southerner to his cabinet Internal improvements for the South (Texas-Pacific RR) Redemption After 1877 and withdrawal of federal troops, Democrats take control of every southern state government South again controlled by a powerful, conservative, oligarchy, known as the “Redeemers” (Southern Democrats) Once again establishes “ home rule ” in the South The Birth of Jim Crow Jim Crow laws- instituted an elaborate system of segregation Involved almost every aspect of Southern life Allowed whites to control social relationships between races Laws enacted between 1876 and 1964 Jim Crow Laws Nurses: No person or corporation shall require any white female nurse to nurse in wards or rooms in hospitals, either public or private, in which negro men are placed. (Alabama) Intermarriage: The marriage of a person of Caucasian blood with a Negro, Mongolian, Malay, or Hindu shall be null and void. (Arizona) Barbers: No colored barber shall serve as a barber [to] white women or girls. (Georgia) Segregation Legalized Court cases take away the significance of 14th Amendment Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)- legalizes segregation in railroad cars Establishes the principle of “separate but equal” Other court cases segregate schools- even when there are no equivalent schools for blacks Brown v. Board of Education (1954) overturns the Plessy decision by ending school segregation Disenfranchisement Voting rights restricted but South had to work around the 15th Amendment Poll tax Property qualifications Literacy tests Courts voided Grandfather clauses but upheld literacy test. Result? Lynchings Used along with Jim Crow laws to inhibit black agitation for equality U.S. averages 187 lynchings per year in 1890’s Sometimes mobs of people from miles around Often carried out by friends or family members of the “victim” Especially used to avenge advances toward white women (Emmett Till) Ida B. Wells- journalist who was a leader of the anti-lynching movement Booker T. Washington Founded Tuskegee Institute in Alabama Committed to economic independence, education and integration; seen as a moderate Encouraged African-Americans to adopt standards of the white middle class Refine speech, improve their dress, and get a solid industrial education The Legacy of Reconstruction Was Reconstruction successful or was it a failure? Why didn’t Reconstruction achieve more? What irreversible gains were made during Reconstruction? The Legacy of Reconstruction Presidency weakened Andrew Johnson’s impeachment Grant’s scandals Election of 1876/Hayes African Americans become 2nd class citizens Tenant farming/sharecropping system lasts until 1960s 14th/15th Amendments bright spots Lead to a “2nd Reconstruction” in the Civil Rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s