Stargazing on Mars - NexStar Resource Site
advertisement

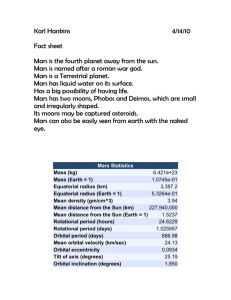
Stargazing on Mars Top Page Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Stargazing on MARS Your imaginary observatory location, 360 degrees unobstructed view, True dark sky. Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Environment on Mars • Thin atmosphere, no industrial smog, no light pollution, • Excellent seeing and transparency (in absence of sand storms, etc.). • Average temperature on Mars is -63ºC/-81.4ºF • Atmosphere is composed of 95.32% carbon dioxid and 7.2% nitrogen • Average atmospheric pressure is 0.007 bars (about 1/100th of Earth) • Gravity is 0.379 of Earth's. • A year on Mars is 1.881x of Earth, a day is about 40 minutes longer. Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Different Constellations? It’s only a small step to Mars, but no giant leap into space. Therefore, the constellations appear like as seen from Earth. Reason being: Parallax angles to Proxima Centauri: on 1 AU base (Earth orbit): 0.773” on 1.524AU base (Mars orbit): 1.178” Mars Rover Spirit’s image of Orion as viewed from 15 deg southern latitude on Mars. Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Mars’s Polar Axis North South RA: 21h10m43s, Dec: 52º53’09 RA: 09h10m43s, Dec: -52º53’09 • The orientation of Mars’s axis is different from Earth, • Mars has no obvious Pole Stars, • Inclination to ecliptic is 1.85º – same zodiac constellations, but different equinoxes and solstices, • Mars, too, is subjected to precession and axial tilt variation. Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Observing the Martian Moons Moon Orbits to-scale Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Observing the Martian Moons Apparent Angular Sizes Influence of altitude Influence of latitude Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Observing the Martian Moons Fact Sheet Phobos (‘fear’) Deimos (‘panic’) Image: Viking 2 Orbiter Image: Viking Orbiter 27 x 22 x 18 km 15 x 12 x 11 km Surface distance 5,980 km 20,060 km Center distance 9,378 km 23,459 km 12.58’ 2.43’ -9mv max. -5.5mv max. 0.32 days 1.26 days Dimensions Apparent size* Visual magnitude Orbit period Axial rotation of Mars: 1.026 days rises in the west *In the meridian on 45º latitude, measured on longest axis. Angular size variations: Phobos: 45%, Deimos: 1.8’ to 2.6’ Image: Phobos-2, Feb 28, 1989 Image: Viking 2, h=30km, 1.2km wide Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Observing Mars from its Moons From Phobos Simulated view on Valles Marineris FOV: 120º Mars’ angular size: 42.5º (85x the full Earth moon) From Deimos Simulated view on the Hellas region FOV: 120º Mars’ angular size: 16.7º (33x the full Earth moon) Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth From Moon to Moon Influence of relative orbit position Visibility Condition Phobos: 8.2º E/W elongation Deimos: 20º E/W elongation Apparent Sizes Min Distance Max Distance Phobos 6.59’ 2.83’ Deimos 3.66 1.57 • An exciting performance of fast changes, • Observing Phobos from Deimos is most dynamic • Phobos - Deimos minimum distance is 14,081km, • Phobos - Deimos maximum distance is 32,837km. Stargazing on Mars Solar Eclipses on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Phobos Eclipse Mars Rover Opportunity On March 10, 2004 • Sun size is 2/3rd • Phobos’s is half of Earth Moon Deimos Eclipse Mars Rover Opportunity On sol 39 of its mission • Sun size is 2/3rd • Deimos size is half of Phobos Phobos eclipse shadow Mars Global Surveyor. August 26, 1999 over Western Xanthe Terra. 250km (155mi across) • Eclipses occur several times a day • No total eclipses on Mars • Less spectacular than on Earth Stargazing on Mars Observing Earth from Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth • Earth is an inner planet, • Shows phases like Venus/Mercury, • Mean greatest elongation is 41º, • Earth transits observable but rare. (last: May 11, 1984; next: Nov 10, 2084) Mars Global Surveyor. May 8, 2003 13:00 UTC Earth of the Past • Earth-Mars light time varies between 3 and 22 minutes. • In 22 minutes Earth rotates 5.5º towards East (1º in 4 minutes). Venus transit in 2004. Courtesy K. Spencer. Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars Our Mars Observatory Mars Rover Spirit Spirit’s two panoramic CCD cameras. Spirit’s field of view • Location: • Mounting: • Pixel area: • Field of view: • Resolution: • Equivalent: • Cost: Gusev Crater, 15º south of equator altazimuth, no tracking 1,024 x 1,024 pixels 16.8º 59” per pixel 35mm SLR with 125mm lens 400 million US$, excluding shipment Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars Orion Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars Phobos and Deimos Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars Phobos and Deimos Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars Phobos Lunar Eclipse Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Imaging on Mars South Celestial Pole Region Stargazing on Mars Cover Page Environment Constellations Polar Axis Observing Moons Observing Mars Moon to Moon Solar Eclipses Earth from Mars Imaging on Mars Back to Earth Back to Earth – Thank You!