Lesson 4 -- Polarity and Bond Properties -
advertisement

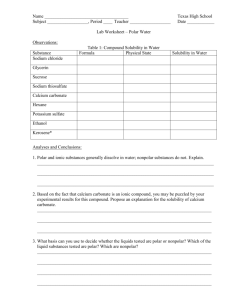
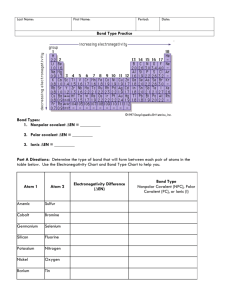
CHEMICAL BONDING WARM-UP Answer the following questions INDEPENDENTLY! Identify the shape: A D B E Draw the following and predict the Shape of the Following: (1) H2S (2) CBr4 C CHECK YOUR ANSWERS and DISCUSS ANYTHING YOU MISSED: Identify the shape: A) Bent B) Trigonal Pyramidal C) Linear D) Trigonal Planar E) Tetrahedral Draw the following and predict the Shape of the Following: (1) H2S - Bent (2) CBr4 -Tetrahedral HOMEWORK CHECK Check your homework answers against the keys provided on the next two slides. HOMEWORK REVIEW: VSEPR THEORY PRACTICE WORKSHEET TODAY’S OBJECTIVES WHAT YOU WILL LEARN TODAY Objectives Identify bond strengths based upon type of bond. Define polarity Apply VSEPR theory to predict the overall polarity of a molecule. Predict the properties of a molecule based on the type of molecule (Ionic, NPC, PC, Metallic) IDENTIFY BOND STRENGTHS BASED UPON TYPE OF BOND Bonds have lengths and strengths! Ionic bonds- Strongest of all bonds! Covalent Bonds Triple Bonds – shortest and stronger Double bonds Single bonds - longest and weakest of all the bonds. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond strength. CO2 CCl4 SrBr2 N2 CHECK YOUR ANSWERS ON THE NEXT SLIDE Arrange the following in order of increasing bond strength. CCl4 – WEAKEST – SINGLE COVALENT CO2 -- Double Covalent N2 --- Triple Covalent SrBr2 Ionic – STRONGEST!! DEFINE POLARITY DISCUSS WHAT THESE PICTURES HAVE IN COMMON What Does This Represent??? (Think Electronegativity!!) Polarity PUT THIS IN YOUR NOTES!!!!! Polarity is defined as the unequal distribution of electrons. But what does that actually mean? Polar molecules have a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end. Nonpolar molecules have a consistent charge throughout and thus no charged poles (ends). POLAR and NONPOLAR DO NOT MIX!!!! POLAR BONDS create special properties due to small charges. DEMO: BACK TABLE On the back table is a test tube filled with the following…. Water, Oil, and Food Coloring Which items are Polar and which are NON-Polar? (Hint: Research to determine the polarity of water) Check Your Answers On The Next Slide DEMO: BACK TABLE On the back table is a test tube filled with the following…. Water, Oil, and Food Coloring Which items are Polar and which are NON-Polar? Water and Food Coloring are BOTH POLAR as they mix together. The oil is NONPOLAR causing it to not mix with the water. Check Your Answers On The Next Slide APPLY VSEPR THEORY TO PREDICT THE OVERALL POLARITY OF A MOLECULE. How do you know if a molecule is polar? COPY THIS INTO YOUR NOTES Step 1: Draw Lewis Structure & Determine the shape Step 2: Predict the polarity of the molecule based on the following. Bent, and trigonal pyramidal molecules are ALWAYS polar. (think about WHY they are bent…lone pairs) Tetrahedral, trigonal planar, and linear are usually nonpolar. But can be polar, IF and ONLY IF there are 3 or more different elements. Ex. CH4 (NonPolar) vs. CH2F2 (Polar) Examples – Work As A Team Determine if the following molecules are polar or non-polar: NH3 CSeF2 CO2 Check Answers On The Next Slide --- Examples – Work As A Team Determine if the following molecules are polar or non-polar: NH3 Polar CSeF2 Polar CO2 Non-Polar You Try - Work Independently Determine if the following molecules are polar or nonpolar. NF3 SO2 CH2I2 You Try - Work Independently Determine if the following molecules are polar or nonpolar. NF3 POLAR SO2 POLAR CH2I2 POLAR PREDICT THE PROPERTIES OF A MOLECULE BASED ON THE TYPE (IONIC, NPC, PC, METALLIC) Copy this chart and complete as you read the next few slides Type of Bond IONIC METALLIC POLAR NONPOLAR Conduct Electricity Dissolve In water? State at Room Temp Properties of Ionic Substances Hard Brittle A solid at room temperature Very high melting points (≈800C) Very high boiling points Soluble in water (think SALT) Conduct electricity when dissolved in water or as a liquid. Properties of Metals Shiny Solid at room temperature. Very very high melting point (≈1000C) Very Very high boiling point Insoluble in water (does your gold necklace wash away when you shower?) Conduct electricity Malleable and ductile (think COPPER) Properties of Polar Molecules Typically a liquid at room temperature. Low melting points (≈20C) Medium boiling points Soluble in water (think SUGAR) Not a of conductor electricity Properties of Non-polar molecules Typically a gas at room temperature. Very low melting (≈-100C) Very low boiling points Insoluble in water (think Oxygen) Not a conductor of electricity. Here’s What You Should Have Learned Type of Bond IONIC METALLIC POLAR NONPOLAR Conduct Electricity Dissolve State at Room Temp Y Y N N Y N Y N Solid Solid Liquid Gas Steps for determining properties. Step 1: Draw the Lewis structures Step 2: Predict the shape Step 3: Based on the shape determine the polarity Step 4: Use polarity to determine properties Given CO2 Work Together To Answer The Following Questions: What is the overall shape? Using this shape, what type of bond is present? Ionic, Metallic, Polar or Nonpolar? Given the shape, determine the following: What is the state of matter at room temp? Will it conduct electricity Will it dissolve in water? Check Your Answers On The Next Slide Given CO2 Work Together To Answer The Following Questions: What is the overall shape? Linear Using this shape, what type of bond is present? Ionic, Metallic, Polar or Nonpolar? Nonpolar Given the shape, determine the following: What is the state of matter at room temp? Will it conduct electricity No Will it dissolve in water? No Gas PULLING IT ALL TOGETHER Copy and complete the following table, working together as a team Compound Type of Bond? (I, M, PC, PC) Shape State of Matter Conduct Electricity? Dissolve in Water? CO2 NPC Linear Gas No No PCl3 H2O CCl4 MgCl2 Cl2 CH2Cl2 NH3 AlCl3 Compound Type of Bond? (I, M, PC, NPC) Shape State of Matter Conduct Electricity? Dissolve in Water? CO2 NPC Linear Gas No No PCl3 PC Trig Pyramidal Liquid No Yes H2O PC Bent Liquid No Yes CCl4 NPC Tetrahedral Gas No No MgCl2 Ionic Lattice Solid Yes Yes Cl2 NPC Linear Gas No No CH2Cl2 PC Tetrahedral Liquid No Yes NH3 PC Trig Pyramidal Liquid No Yes AlCl3 Ionic Lattice Solid Yes Yes YOU TRY IT ----WORK INDEPENDENTLY !! Compound Type of Bond? Shape SrAt2 O3 SO3 HgZn GeH2Br2 ----- Type of Bond Conduct Electricity Dissolve State at Room Temp IONIC Y Y Solid METALLIC Y N Solid POLAR N Y Liquid NONPOLAR N N Gas State of Matter Conduct Electricity? Dissolve in Water? YOU TRY IT ----- Type of Bond Conduct Electricity Dissolve State at Room Temp IONIC Y Y Solid METALLIC Y N Solid POLAR N Y Liquid NONPOLAR N N Gas WORK INDEPENDENTLY !! Compound Type of Bond? Shape State of Matter Conduct Electricity? Dissolve in Water? SrAt2 Ionic Lattice Solid Yes Yes O3 PC Bent Liquid No Yes SO3 NPC Trig Planar Gas No No HgZn Metallic ----- Solid Yes No GeH2Br2 PC Tetrahedral Liquid No Yes Objectives (Today You’ve Learned How To….) Identify bond strengths based upon type of bond. Define Polarity Apply VSEPR theory to predict the overall polarity of a molecule. Predict the properties of a molecule based on the type of molecule (Ionic, NPC, PC, Metallic) HOMEWORK BONDING WORKSHEET (WHOLISTIC VIEW) HONORS…. OMIT INTERMOLECULAR FORCES SECTION UNTIL LATER UNIT 4 QUIZ When you’re finished, turn in paper and start on worksheet. Complete worksheet for homework!