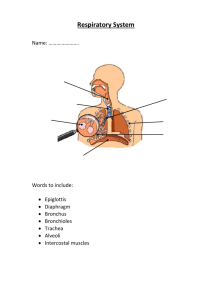
Circulatory System Red
advertisement
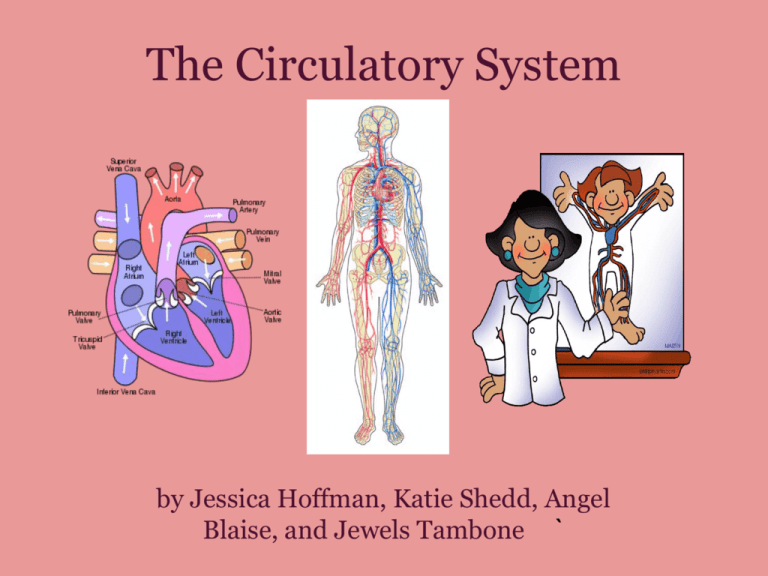
The Circulatory System by Jessica Hoffman, Katie Shedd, Angel Blaise, and Jewels Tambone ` The Structure of the Circulatory System: • Pulmonary Circuit: o Takes blood to the capillary beds in the lungs, then to the heart where it is pumped out the aorta and into the systemic circuit (1). • Systemic Circuit: Takes blood from aorta to blood vessels and down to the capillary beds in the different parts of the body where the oxygen is distributed among the cells (1). o The now deoxygenated blood is taken through the veins to the heart where it is pumped into the pulmonary circuit (1). o Blood Overview • Blood: A fluid connective tissue which maintains favorable conditions and delivers substances (including oxygen) to cells. Blood is composed of plasma, platelets, and red & white blood cells (1). Plasma: The liquid portion of blood which enables transportation for blood cells and platelets and everything that is absorbed by the small intestine (1) o Platelets: Release substances which initiate blood clotting (1) o Red Blood Cells: Transport oxygen from the lungs to the cells. Packed with hemoglobin (an iron-containing pigment that binds with oxygen & CO2) (1) o White Blood Cells: Target & engulf damaged, dead, & foreign cells. Lymphocytes destroy bacteria, viruses, & other disease agents (1). o Blood Vessel Structure Structure (from inside => out) Arteries: Endothelium, basement membrane, elastic tissue, smooth muscle, elastic tissue, outer coat Veins: Valve, endothelium, basement membrane, smooth muscle along with elastic fibers, outer coat Capillary: Endothelium, basement membrane The Main Blood Vessels (Function) Vena Cava- Main vein in the heart Aorta- The main artery in the heart Pulmonary Arteries- The blood vessels that brings blood to the lungs for oxygen Pulmonary Veins- Bring back the oxygenated blood back to the heart Systemic Veins- The Blood vessels that bring blood back from all parts of the body Systemic Arteries- The blood vessel that takes blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. Capillaries: Small blood vessels that distribute nutrients to cells in the body. all (1) Gas Exchange Trachea > Mainstem Bronchi > Terminal Bronchioles (w/o Alveoli) > Respiratory Bronchioles (w/ Alveoli) (4) • Bronchiole: A branch of the mainstem bronchi • Respiratory Bronchioles: Alveoli attached • Alveoli: Small thin-walled sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange takes place Gas Exchange • Ventilation: Brings air into alveoli • In the alveoli: o Oxygen diffuses from lungs to blood o Carbon dioxide from blood to lungs • At the ends of the bronchioles, where smaller molecules can go through gas exchange, blood cells and larger proteins cannot pass through the gaps between blood vessels. (4) Concentration Gradient in Alveoli • Ventilation: Maintains the concentration gradient of CO2 and O2 between the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries • The body needs to get rid of CO2 (a product of cell respiration) and needs to take in O2 (needed for cell respiration to make ATP) (2) • Low concentration of carbon dioxide in the alveoli > carbon dioxide can diffuse out of the blood in the capillaries and into the alveoli. (2) • High concentration of oxygen in the in the alveoli > oxygen can diffuse into the blood in the capillaries from the alveoli. (2) • Ventilation makes possible by getting rid of CO2 in alveoli and adding more oxygen (2) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5LjLFrmKTSA&feature=related References: 1) Biology The Unity and Diversity of life. 9TH ed. United States: THOMSON LEARNING (KY), 2001. Print. 2) "IB Biology Notes - Gas Exchange." IB Guides - Free International Baccalaureate Study Guides, Notes, Videos and Powerpoints. Web. 25 Oct. 2011. <http://www.ibguides.com/biology/notes/gas-exchange->. 3) "Alveoli Definition - Medical Dictionary Definitions of Popular Medical Terms Easily Defined on MedTerms." Medicine.net. Web. 25 Oct. 2011. <http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=2212>. 4) Black, Suzanne, James E. McLaren, and Neil A. Campbell. Biology: Exploring Life. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2009. Print.