Business Ethics & Business Professional Integrity
advertisement

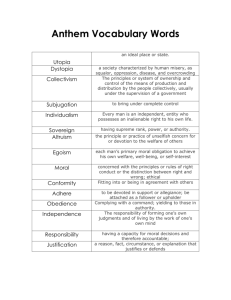
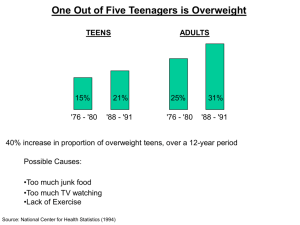
ACCOUNTING & INTEGRITY CAPACITY ACCOUNTABILITY Dr. Joseph A. Petrick Executive Director Institute for Business Integrity Wright State University 2007 Dayton Accounting Show The Ohio Society of CPAs May 23, 2007 Raj Soin College of Business Wright State University • The only Accounting Department in the country whose students have won the IMA National Case Competition on 5 different occasions. • Business student teams won the National Intercollegiate Ethics Bowl in 2002 and in 2004 were National runner-up champions. Agenda A. B. C. D. Accounting and Rebuilding Stakeholder Trust Integrity Capacity Model for Professional Development 1. Accounting Process Integrity Capacity 2. Accounting Judgment Integrity Capacity 3. Accounting Developmental Integrity Capacity 4. Accounting System Integrity Capacity Microeconomic and Macroeconomic Improvements 1. Improved Microeconomic Moral Accountability 2. Improved Macroeconomic Moral Accountability New Agenda for Responsible Leadership in Accounting Organizations & Accounting Ethics • • • • • • • • AICPA Standards & JEEP IMA Standards Global & Industry Standards SEC Standards SOX Accounting Oversight Board Independence Standards Board (ISB) State Societies of CPAs & NASBA Others: GAO, DOL, ASB, FASB among others. Corporate Reporting Supply Chain (DiPiazza: PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2002) Rebuilding Accounting Stakeholder Trust 1. Renewed Spirit of Transparency and Assurance a. Tier 1: Global GAAP b. Tier 2: Industry-Based Standards c. Tier 3: Company-Specific Information 2. Culture of Accountability 3. People of Integrity Integrity Capacity Theoretical Model The individual and collective capability for repeated process alignment of moral awareness, deliberation, character and conduct that demonstrates balanced judgment, enhances sustained moral development, and promotes supportive systems for moral decision making. Instrumental Value of Integrity Capacity Accounting Integrity Capacity Reputational Capital Sustainable Competitive Advantage, Public Trust & World-Class Performance Dimensions of Accounting Integrity Capacity 1. Accounting Process Integrity Capacity 2. Accounting Judgment Integrity Capacity 3. Accounting Developmental Integrity Capacity 4. Accounting System Integrity Capacity Accounting Process Integrity Capacity The alignment of individual and/or collective accounting moral awareness, deliberation, character, and conduct on a sustained basis, so that enhanced reputational capital results. Accounting Process Integrity Capacity MORAL AWARENESS Perception Sensitivity MORAL DELIBERATION Analysis Resolution MORAL CHARACTER Cognitive Readiness to Act Volitional Readiness to Act MORAL CONDUCT Responsible Sustainable Virtues That Build Professional & Organizational Character 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Intellectual Virtues Moral Virtues Social Virtues Emotional Virtues Political Virtues Accounting Judgment Integrity Capacity The balanced and inclusive use of key ethics theories and their subordinated cognate theoretical resources in the analysis and resolution of individual and/or collective accounting moral issues. Accounting Judgment Integrity Capacity (R2C2) Flexibility Build Virtuous Character Enhance Supportive Contexts Internal External Follow Right Rules Achieve Good Results Control Positive & Negative Zones of Accounting Professional Moral Judgment Integrity (R2C2) Negative Zone Abdicates Authority Positive Zone Shows Consideration Character Wastes Energy Context Envisions Changes Slows Production Acquires Resources Facilitates Interaction Disrupts Continuity Negative Zone Amoral Professionalism Collects Information Rules Initiates Action Neglects Possibilities Destroys Cohesion Maintains Structure Stifles Progress Provides Structure Offends Individuals Results Accounting Judgment Integrity Capacity Based on Four Human Nature Drives Negative Zone Context Positive Zone Character DRIVE TO BOND DRIVE TO LEARN Negative Zone Amoral Professionalism DRIVE TO DEFEND Rules DRIVE TO ACQUIRE Results ACCOUNTING PARTNER EXTREME CONCERN FOR PROFITS Flexibility Context (ADAPTABILITY) Character (INVOLVEMENT) Internal External Results (EFFECTIVENESS) Rule s (CONTINUITY) Control DILBERT CEO LACK OF JUDGMENT INTEGRITY CAPACITY Ranges of Moral Judgment Evaluation using R2C2 ™ Quantitative Ranges 0–1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 – 10 Qualitative Anchors Extremely Unacceptable Under-emphasis Unacceptable Under-emphasis Minimally Acceptable Emphasis Below Average Emphasis Average Emphasis Above Average Emphasis Optimal Emphasis Unacceptable Over-emphasis Extremely Unacceptable Over-emphasis Judgment Integrity Capacity Graph & Global Accounting Ethics Communication Accounting Developmental Integrity Capacity The organizational and extra-organizational cultural cognitive improvement of individual and/or collective accounting moral reasoning capabilities from a stage of selfinterested connivance, through a stage of external conformity, and onto a stage of internalized commitment to moral principles. Accounting Cultural Context: Moral Development Stages Principled Integrity HOUSE OF INTEGRITY Democratic Participation (Commitment) Allegiance to Authority HOUSE OF COMPLIANCE Popular Conformity (Conformity) Machiavellianism HOUSE OF MANIPULATION Social Darwinism (Connivance) Accounting System Integrity Capacity The development and alignment of the moral infrastructure within the organization and the shaping of the external moral environment of the accounting organization to provide a supportive context for sound moral decision making. Internal System Integrity Capacity Organizational Moral Environment • Compliance-Based Systems • • • • Prevent Criminal Misconduct U.S. Federal Sentencing Guidelines Sarbanes-Oxley Act Professional Association Standards • Integrity-Based Systems • Enable Responsible Conduct Compliance-Based Organization Internal Systems 1. Establish compliance standards and procedures 2. Assign high level individuals to oversee program 3. Exercise due care in delegating discretionary authority 4. Communicate and train Compliance-Based Organization Internal Systems 5. Monitor, audit, and provide safe reporting system 6. Enforce appropriate discipline with consistency 7. Respond to offences and prevent further misconduct 8. Comply with SOX requirements 9. Comply with professional standards Integrity-Based Organization Internal Systems 1. Moral Leadership at the Top 2. Ethics Needs Assessment & Compliance Standards in Place 3. Ethics in Strategy and Structure 4. Integrity Steering Committee 5. Statement of Values/Written Code of Conduct 6. Ethics Policy and Procedure Manuals Integrity-Based Organization Internal Systems 7. Ethics in Selection, Socialization, and Performance Subsystems 8. Ethics in Appraisal, Rewards/Recognition/Incentive, and Development Subsystems 9. Ethics in Communication Processes and Work Attitudes 10. Ethics Training and Education Programs 11. Ethics in Decision-Making/Meeting Processes Integrity-Based Organization Internal Systems 12. Organizational Integrity Advisor Responsibilities 13. Ethics Reporting, Whistleblower Protection and Conflict Resolution Processes 14. Enforcement Processes of Ethical Standards 15. Ethics Monitoring, Auditing & Improving Subsystems 16. Ethics System and Quality Work Process Control and Improvement External System Integrity Capacity 1. Domestic External Moral Environment • Corruption Elimination and/or Control • Industry & Professional Standards • Proactive Positive Stakeholder Relations & Triple Bottom Line Accountability 2. Global External Moral Environment • Corruption Elimination and/or Control • Industry & Professional Standards • Proactive Positive Stakeholder Relations & Triple Bottom Line Accountability Improved Microeconomic Moral Accountability A. Individual Accountability Improvement 1. Demonstrated Process Integrity Capacity 2. Demonstrated Judgment Integrity Capacity B. Partner Accountability Improvement 1. Demonstrated Developmental Integrity Capacity 2. Demonstrated System Integrity Capacity Improved Macroeconomic Moral Accountability Improved Macroeconomic Moral Accountability A. Professional Association/Industry Accountability Improvement 1. More rigorous quality control & enforcement 2. Partner with competent stakeholders for reform 3. Strengthen accounting professional education B. Political Economy Accountability Improvement 1. Financial markets & statistical variation 2. Types of capitalism/forms of economic democracy 3. International accounting harmonization New Agenda for Responsible Leadership in Accounting • National commission with task forces on improving microeconomic levels of integrity capacity accountability • International commission with task forces on improving macroeconomic levels of moral accountability • Integrity capacity building skills in mainstream accounting professional education ACCOUNTING & INTEGRITY CAPACITY ACCOUNTABILITY Dr. Joseph A. Petrick Executive Director Institute for Business Integrity Wright State University 2007 Dayton Accounting Show The Ohio Society of CPAs May 23, 2007