Power Point Slides
advertisement
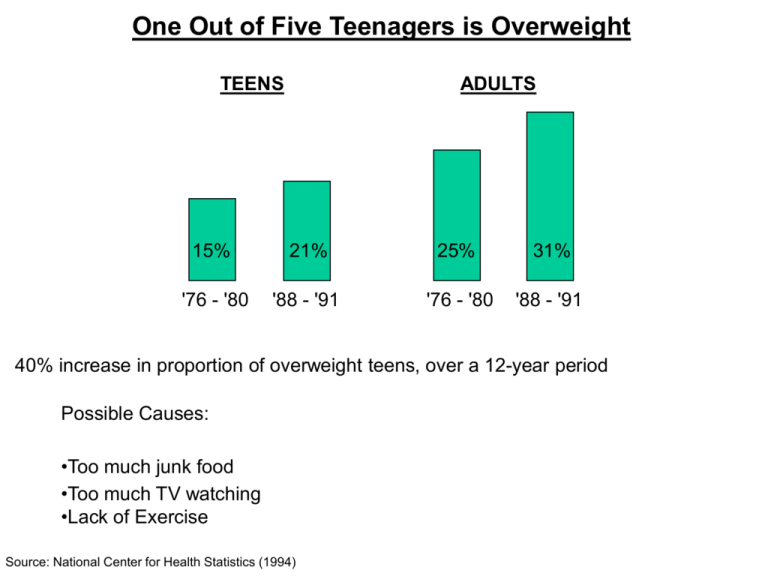
One Out of Five Teenagers is Overweight TEENS ADULTS 15% 21% 25% 31% '76 - '80 '88 - '91 '76 - '80 '88 - '91 40% increase in proportion of overweight teens, over a 12-year period Possible Causes: •Too much junk food •Too much TV watching •Lack of Exercise Source: National Center for Health Statistics (1994) FEATURES OF FORMAL OPERATIONAL THINKING • Attention to hypothetical ideas and possibilities • Scientific reasoning • Logical combination of ideas • Abstract thinking The Pendulum Problem A Piagetian test for formal operational thinking X Y Z 1 2 3 B C There are: • 3 weights (A, B, C) • 3 lengths of string (1, 2, 3) • 3 push positions (X, Y, Z) A Which makes the quickest arc? Source: Howard Gruber & J. Jacques Vonesce, The Essential Piaget. New York, Basic Books (1977). KOHLBERG'S STAGES OF MORAL JUDGMENT • PRECONVENTIONAL LEVEL (emphasis on avoiding punishments and getting awards) Stage 1: Heteronomous morality; ethics of punishment and obedience Stage 2: Instrumental purpose; ethics of market exchange • CONVENTIONAL LEVEL (emphasis on social rules) Stage 3: Interpersonal conformity; ethics of peer opinion Stage 4: Social system orientation: conformity to social system; ethics of law and order • POSTCONVENTIOANL LEVEL (emphasis on moral principles) Stage 5: Social contract orientation; ethics of social contract and individual rights Stage 6:Ethics of self-chosen universal principles Longitudinal Development of Moral Reasoning stage 1 stage 2 stage 3 stage 4 stage 5 Moral reasoning (percent) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Age (in Years) 26 28 30 32 34 36 Gilligans's Stages of Moral Development Stage Features Stage 1 Survival orientation Egocentric concern for self, lack of awareness of others' needs; "right" action is what promotes emotional or physical survival Stage 2 Conventional care Lack of distinction between what others want and what is right; "right" action is whatever pleases others best Stage 3 Integrated care Coordination or integration of needs of self and of others; "right" action takes account of self as well as others Developmental Changes in Information Processing Control processes Environmental stimuli (input) Sensory register (SR) Increased efficiency Attention Recognition Short-term memory (STM) Increased size Response (output) Rehearsal Organization Meaningfulness Long-term memory (LTM) Greater specific expertise Greater knowledge about problemsolving Summary of Adolescent Cognitive Development • Piaget’s formal operational stage • Scientific and abstract thinking develop • Information processing skills continue to improve • Moral development matures