Musical aesthetics and emotion
advertisement

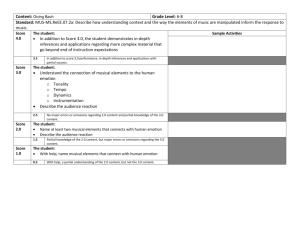
Musical Aesthetics & Emotion • Ways of characterizing emotions in music • The idea of musical preference • We all like some forms of music, and dislike other forms of music • Idea of individual difference response emotional response • The emotion response to music • Music engenders in listeners an emotional reaction • Emotional reaction presumably relatively constant across listeners Musical Preferences / Aesthetics • Individual difference factors that might underlie musical preferences • Personality • Preference for certain musical styles might be linked to quantifiable characteristics in temperament or personality • Physiological arousal • Individuals with particular physiological parameters will prefer music related to those physiological parameters • Social identity • Musical preference is a “badge” to communicate values, attitudes, and self-views Personality Structure and Musical Preferences Raymond Cattell’s 16PF Warmth: Desire to develop close relations with others Reasoning: The extent to which you solve numerical and verbal problems Emotional Stability: How calmly you Dominance: Tendency to influence respond to life’s demands and/or control others Liveliness: How freely you express yourself Rule Consciousness: How much value is placed on external rules Social Boldness: How much at ease you feel in social situations Sensitivity: Extent to which emotions and sentiments influence outlook Vigilance: The extent to which you are cautious of other’s motives Abstractedness: How much attention is given to abstract rather than concrete observations Privateness: How much you like to keep personal information to yourself Apprehension: How much you are prone to self-criticism Openness to Change: Extent you enjoy new situations/experiences Self-Reliance: How much you enjoy your own company and trust your own judgment Perfectionism: Need to rely on structure rather than leaving things to chance Tension: How easily situations can cause you frustraction Personality Structure and Musical Preferences Eysenck’s Personality Questionnaire (EPQ-R) • Extroversion / Introversion (E) • Extraversion is defined as outgoing, talkative, high on positive affect, in need of external stimulation • Neuroticism / Stability (N) • Neuroticism or emotionality is characterized by high levels of negative affect such as depression and anxiety • Psychotocism / Socialisation (P) • Psychotocism is associated not only with the liability of having a psychotic episode, but also with aggression. Psychotic behavior is rooted in toughmindedness, non-conformity, recklessness, hostility, etc. Personality Structure and Musical Preferences EPQ-R means and differences for preference for exaggerated bass McCown, Keiser, Mulhearn & Williamson (1997) Variable Psychotocism Males Females Mean 13.02 10.03 Extraversion Males Females 21.23 18.87 Neurotocism Males Females 15.21 19.66 Variable Gender p level .001 Mean # of bass choices Female 6.2 Male 9.4 Extraversion .05 Low High 6.7 9.5 Psychotocism .001 Low High 5.9 9.7 Personality Structure and Musical Preferences Dimensions of musical preference and their relation to musical attributes Rentfrow & Gosling (2003) Personality Structure and Musical Preferences Dimensions of musical preference and their relation to musical attributes Rentfrow & Gosling (2003) Musical Preferences and Social Identity Perceived normative characteristics of fans of different types of music North & Hargreaves (1999) Musical and Emotion • Possible reasons for the paucity of research on music and emotion • The difficulty of studying emotions in the laboratory in general • The dominant influence of cognitive science on music psychology • The difficulty of studying musical emotions • The academic study of music as promoting a particular way of listening to music Music and Emotion Emotion and Meaning in Music Meyer (1956) Absolutist view: The idea that musical meaning lies exclusively in the perception of the relations set out in the music itself Referentialist view: The idea that music ALSO communicates extramusical concepts of actions, emotional states, and so on. Music and Emotion A cognitive theory of emotions Mandler (1984) • Human cognition operates by means of perceptual-motor schemata through which expectancies are generated for upcoming events and future behaviors are planned • If you interrupt an ongoing schema, you get biological arousal • The biological reactions triggers a search for a cognitive interpretation of what happened, or a search for meaning • The arousal and interpretation join together in producing an emotional experience Music and Emotion The ITPRA theory • • • • • • • Huron (2005) Pre-outcome phase: Feelings that occur prior to the expected/unexpected event Post-outcome event: Feelings that after the expected/unexpected event Imagination Response: Imagining an outcome to a particular situation Tension Response: Prepare organism for impending event Prediction Response: Provide positive and negative inducements that encourage the formation of accurate expectations Reaction Response: The immediate protective response Appraisal Response: Provide positive and negative reinforcements related to biological value of the end state Music and Emotion Emotional ratings and musical attributes Hevner (1935, 1936) Musical attribute Minor mode Emotional descriptions Pathetic, doleful, sad, dreamy, tender, yearning Major mode Merry, joyous, gay, spiritual, lofty, dignified Music and Emotion Emotional ratings and musical attributes Cosa, Fine, & Bitti (2004) Musical attribute Major mode Emotional descriptions Happiness, serenity Perfect 4th Minor 7th Tonally strong Pleasant Minor 2nd Tritone Active, instable, motion Music and Emotion Emotion and brain activation attributes Koelsch et al. (2006) Music and Emotion Emotion and brain activation attributes Koelsch et al. (2006)