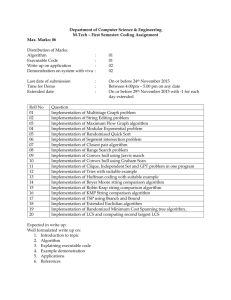
Reference JAVA
advertisement

Référence JAVA
1.
JAVA BASICS ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 2
1.1
2.
CLASSES, OBJECTS, VARIABLES, AND METHODS ........................................................................................................................................................... 2
JAVA PRIMITIVE VARIABLES ........................................................................................................................................................................ 3
2.1
3.
INTEGERS: BYTE, SHORT, INT, LONG ................................................................................................................................................................... 3
JAVA CONTROL STRUCTURES ....................................................................................................................................................................... 4
3.1
4.
SWITCH (THE JAVA CASE STATEMENT) .................................................................................................................................................................. 4
JAVA METHODS ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
4.1
5.
CONSTRUCTOR, ACCESSOR, AND MUTATOR METHODS ..................................................................................................................................................... 5
JAVA STATIC ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
5.1
6.
STATIC VARIABLES ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
JAVA INHERITANCE ................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
6.1
7.
EXTENDING CLASSES ................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
JAVA CASTING ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
7.1
7.2
7.3
7.4
7.5
7.6
7.7
7.8
7.9
7.10
7.11
7.12
7.13
7.14
7.15
7.16
7.17
7.18
7.19
7.20
7.21
8.
GETTING A STRING OUT OF AN ARRAYLIST ............................................................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A DOUBLE OUT OF AN ARRAYLIST (STORED IN THE ARRAYLIST AS A DOUBLE) .................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A STRING OUT OF A VECTOR ................................................................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A DOUBLE OUT OF A VECTOR (STORED IN THE VECTOR AS A DOUBLE) ........................................................................................................................ 8
STRING TO DOUBLE TO DOUBLE (USING DOUBLE CONSTRUCTOR) ........................................................................................................................................ 8
STRING TO DOUBLE TO DOUBLE....................................................................................................................................................................... 8
STRING TO DOUBLE (USING STATIC DOUBLE METHOD - JAVA 1.2 & LATER) ............................................................................................................................. 8
DOUBLE TO A NEW STRING (USING THE STRING CONSTRUCTOR) ......................................................................................................................................... 8
DOUBLE TO EXISTING STRING.......................................................................................................................................................................... 8
DOUBLE TO INT ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
GETTING A STRING OUT OF AN ARRAYLIST ............................................................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A DOUBLE OUT OF AN ARRAYLIST (STORED IN THE ARRAYLIST AS A DOUBLE) .................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A STRING OUT OF A VECTOR ................................................................................................................................................................. 8
GETTING A DOUBLE OUT OF A VECTOR (STORED IN THE VECTOR AS A DOUBLE) ........................................................................................................................ 8
STRING TO DOUBLE TO DOUBLE (USING DOUBLE CONSTRUCTOR) ........................................................................................................................................ 8
STRING TO DOUBLE TO DOUBLE....................................................................................................................................................................... 9
STRING TO DOUBLE (USING STATIC DOUBLE METHOD - JAVA 1.2 & LATER) ............................................................................................................................. 9
DOUBLE TO A NEW STRING (USING THE STRING CONSTRUCTOR) ......................................................................................................................................... 9
DOUBLE TO EXISTING STRING.......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
DOUBLE TO INT ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
STRING TO CHAR ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
JAVA THIS AND SUPER ........................................................................................................................................................................... 10
8.1
8.2
9.
THIS ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
SUPER ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 10
JAVA ACCESSABILITY .............................................................................................................................................................................. 11
9.1
10.
THE FOUR TYPES OF ACCESSABILITY FOR CLASSES, METHODS, AND VARIABLES ........................................................................................................................... 11
JAVA ABSTRACTS............................................................................................................................................................................. 13
10.1
USING AN ABSTRACT CLASS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 13
11.
JAVA INTERFACES ........................................................................................................................................................................... 14
12.
JAVA LOGGING .............................................................................................................................................................................. 16
13.
JAVA OBJECT ................................................................................................................................................................................ 17
14.
JAVA STRINGS ............................................................................................................................................................................... 19
15.
JAVA ARRAYS ................................................................................................................................................................................ 25
16.
JAVA ARRAYLISTS ............................................................................................................................................................................ 27
17.
JAVA LISTITERATORS ........................................................................................................................................................................ 29
18.
JAVA HASHMAPS ............................................................................................................................................................................. 31
19.
ITERATOR ................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
20.
CONSOLE INPUT ............................................................................................................................................................................ 34
Page 1
1.
Java Basics
1.1
classes, objects, variables, and methods
class
A grouping of "variables" and "methods".
In the example below, Cat (line 1) is a class.
object
An "instance" or of a class. Below (line 14) we create a Cat named patches.
variable
Data stored in the class with a given name.
Below (line 2 & 3) we have the variables animalType and animalColor.
method
A grouping of java code with a name, list of zero to n variables in, and zero or one variables out.
Below (line 8) getCatsColor is a method.
1 class Cat {
2
private String animalType = "feline";
3
private String catColor;
4
Cat(String colorIn)
5
{
6
catColor = colorIn;
7
}
8
public String getCatsColor()
9
{
10
return catColor;
11
}
12
13
public static void main (String[] argsIn) {
14
Cat patches = new Cat("calico");
15
}
16 }
Page 2
2.
Java Primitive Variables
2.1
integers: byte, short, int, long
byte
Occupies 8 bits or 1 byte, which is:
-27 to 27-1 or -128 to 127.
Default value of 0.
short
Occupies 16 bits or 2 bytes, which is:
-215 to 215-1 or -32,768 to 32,767
Default value of 0.
int
Occupies 32 bits or 4 bytes, which is:
-231 to 231-1 or -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
Default value of 0.
long
Occupies 64 bits or 8 bytes, which is:
-263 to 263-1 or -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807.
Default value of 0.
Page 3
3.
Java Control Structures
3.1
switch (the Java case statement)
//note: shown using char.
//Primitive types char, byte, short, or int
// can be used in the switch.
switch (charToCheck)
{
case 'A' : System.out.print('A'); break;
//Print 'A' if charToCheck = 'A'
case 'B' : System.out.print('B'); break;
//Print 'B' if charToCheck = 'B'
default : System.out.print('D');
//Print 'D' if charToCheck does
//
not equal 'A' or 'B'
}
//note: if neither break were there,
// and if charToCheck = 'A',
// the code would print ABD
if else
if (x > 5)
{
System.out.println("x is greater than 5");
}
else
{
System.out.println("x is not greater than 5");
}
Page 4
4.
Java Methods
4.1
constructor, accessor, and mutator methods
constructor methods
Special method for creating new instance of a class. Must have the same name as the class it constructs. Below (line 4) is the constructor for Cat.
accessor methods
Methods that return variables. The accessor method name should start with "get". Below (line 8) is the accessor named getCatsColor.
mutator methods
Methods that alter variables. The mutator method name should start with "set". Below (line 12) is the accessor named setCatsColor.
1 class Cat {
2
private static String animalType = "feline";
3
private String catColor;
4
Cat(String colorIn)
5
{
6
setCatsColor(colorIn);
7
}
8
public String getCatsColor()
9
{
10
return this.catColor;
11
}
12
public String setCatsColor()
13
{
14
this.catColor;
15
}
16
17
public static void main (String[] argsIn) {
18
Cat patches = new Cat("calico");
19
}
20 }
Page 5
5.
Java Static
5.1
static variables
Variables that have the same value for the whole class, not just an instance. Below you can see the on line 12 and 13 how the instance (not static) variable
catColor is accessed. However, on line 14 you see the different way in which the static variable animalType is accessed.
1 class Cat {
2
public static String animalType = "feline";
3
public String catColor;
4
Cat(String colorIn)
5
{
6
catColor = colorIn;
7
}
8
9
public static void main (String[] argsIn) {
10
Cat patches = new Cat("calico");
11
Cat percy
= new Cat("black and white");
12
System.out.println("the cat named Patches color is " +
patches.catColor);
13
System.out.println("the cat named Percy
color is " +
percy.catColor);
14
System.out.println("Patches and Percy are both " +
Cat.animalType);
15
}
16 }
Page 6
6.
Java Inheritance
6.1
extending classes
class Cat {
public String className;
public String name;
public Cat()
{
className = "Cat";
name = "no name in";
}
public Cat(String nameIn)
{
className = "Cat";
name = nameIn;
}
public String getName()
{
return(name + " the " + className);
}
}
class Himalayan extends Cat{
public Himalayan()
{
className = "Himalayan";
}
public Himalayan(String nameIn)
{
className = "Himalayan";
name = nameIn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat percy = new Cat("Percy");
Himalayan cappuccino = new Himalayan("Cappuccino");
System.out.println(percy.getName());
//output is: Percy the Cat
System.out.println(cappuccino.getName());
//output is: Cappuccino the Himalayan
}
}
Page 7
7.
Java Casting
7.1
Getting a String out of an ArrayList
String StringName = (String)arrayListName.get(n);
7.2
Getting a double out of an ArrayList (Stored in the ArrayList as a Double)
double doubName = ((Double)arrayListName.get(n)).doubleValue();
7.3
Getting a String out of a Vector
String StringName = (String)vectName.get(n);
7.4
Getting a double out of a Vector (Stored in the Vector as a Double)
double doubName = ((Double)vectName.get(n)).doubleValue();
7.5
String to Double to double (using Double constructor)
double doubName = new Double(stringName).doubleValue;
7.6
String to Double to double
double doubName = Double.valueOf(stringName).doubleValue;
7.7
String to double (using static Double method - Java 1.2 & later)
double doubName = Double.parseDouble(stringName);
7.8
double to a new String (using the String constructor)
String stringName = new String(doubleName);
7.9
double to existing String
stringName = String.valueOf(doubleName);
7.10
double to int
double doubleName = 3;
int intName = (int)doubleName;
// intName becomes == 3
double anotherDoubleName = 3.3;
int anotherIntName = (int)anotherDoubleName;
//anotherIntName becomes == 3, not 3.3
7.11
Getting a String out of an ArrayList
String StringName = (String)arrayListName.get(n);
7.12
Getting a double out of an ArrayList (Stored in the ArrayList as a Double)
double doubName = ((Double)arrayListName.get(n)).doubleValue();
7.13
Getting a String out of a Vector
String StringName = (String)vectName.get(n);
7.14
Getting a double out of a Vector (Stored in the Vector as a Double)
double doubName = ((Double)vectName.get(n)).doubleValue();
7.15
String to Double to double (using Double constructor)
double doubName = new Double(stringName).doubleValue;
Page 8
7.16
String to Double to double
double doubName = Double.valueOf(stringName).doubleValue;
7.17
String to double (using static Double method - Java 1.2 & later)
double doubName = Double.parseDouble(stringName);
7.18
double to a new String (using the String constructor)
String stringName = new String(doubleName);
7.19
double to existing String
stringName = String.valueOf(doubleName);
7.20
double to int
double doubleName = 3;
int intName = (int)doubleName;
// intName becomes == 3
double anotherDoubleName = 3.3;
int anotherIntName = (int)anotherDoubleName;
//anotherIntName becomes == 3, not 3.3
7.21
String to char
char charName = stringName.charAt(2);
//must specify offset in string to get char from
Page 9
8.
Java This and Super
8.1
this
The current class instance. Can be used with variables (line 6) or methods (line 10).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Numbers {
private int aNumber = 42;
public int returnANumber()
{
return this.aNumber;
}
public int returnANumber(int intIn)
{
return (intIn * this.returnANumber());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Numbers numberTest = new Numbers();
System.out.println("The Number is " +
numberTest.returnANumber() );
//output is: The Number is 42
System.out.println("The Number is " +
numberTest.returnANumber(2) );
//output is: The Number is 84
18
19
20
21
22
8.2
}
}
super
Used to specify methods in the parent class.
class Cat {
public String name;
public Cat() {name = "no nameIn";}
public Cat(String nameIn) {name = nameIn;}
public String getName() {
return(name + " the Cat");
}
}
class Himalayan extends Cat {
public Himalayan() {}
public Himalayan(String nameIn) {
name = nameIn;
}
public String getName() {
return (name + " the Himalayan");
}
public String getNameAsCat() {
return super.getName();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Himalayan cappuccino = new Himalayan("Cappuccino");
System.out.println("The Himalayan name is " +
cappuccino.getName() );
//output is: The Himalayan name is
// Cappuccino the Himalayan
System.out.println("The Cat name is "
+ cappuccino.getNameAsCat() );
//output is: The Cat name is
// Cappuccino the Cat
Page 10
}
}
9.
Java Accessability
9.1
The four types of Accessability for classes, methods, and variables
public - Available to all classes.
protected - Available to the package & subclasses.
package - (aka friendly) implied default, no modifier, Available to package
private - Available only to own class, not inherited.
Note: accessability has the same basic rules for classes, methods, and variables.
Test class "Cat"
package com.fluffycat.feline;
class Cat {
public
String publicString
protected String protectedString
String packageString
private
String privateString
}
=
=
=
=
"public";
"protected";
"package";
"private";
Test class "Siamese"
package com.fluffycat.feline;
class Siamese extends Cat {
public void findOutAboutCat(Cat catToTest) {
String testPublic
= catToTest.publicString;
String testProtected =
catToTest.protectedString;
String testPackage
= catToTest.packageString;
//String testPrivate
=
//
catToTest.privateString;
//!can't access this
}
}
Test class "Cheeta"
package com.fluffycat.feline;
class Cheeta {
public void findOutAboutCat(Cat catToTest) {
String testPublic
=
catToTest.publicString;
String testProtected =
catToTest.protectedString;
String testPackage
=
catToTest.packageString;
//String testPrivate
=
// catToTest.privateString;
// !can't access this
}
}
Test class "Dog"
package com.fluffycat.canine;
Page 11
import com.fluffycat.cat.Cat;
class Dog {
public void findOutAboutCat(Cat catToTest) {
String testPublic
= catToTest.publicString;
//String testProtected =
// catToTest.protectedString;
// !can't access this
//String testPackage
=
// catToTest.packageString;
// !can't access this
//String testPrivate
=
// catToTest.privateString;
// !can't access this
}
}
Test class "SmallCatLikeDog"
package com.fluffycat.canine;
import com.fluffycat.cat.Cat;
class SmallCatLikeDog extends Cat{
public void findOutAboutCat(Cat catToTest) {
String testPublic
=
catToTest.publicString;
String testProtected =
catToTest.protectedString;
//String testPackage
=
// catToTest.packageString;
// !can't access this
//String testPrivate
=
// catToTest.privateString;
// !can't access this
}
}
Page 12
10.
Java Abstracts
10.1
using an abstract class
abstract class Cat {
//abstract classes can have variables
String abstractClassName = "Cat";
//abstract classes can have methods
String getAbstractClassName() {
return abstractClassName;
}
//this must be implemented in any class extending Cat
abstract String getClassName();
}
//you can not extend from two classes at once
class Himalayan extends Cat{
String className = "Himalayan";
public Himalayan() {}
//must have this method,
// because Cat declared it as an abstract
String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//you can not instantiate an abstract class
//Cat percy = new Cat(); //does not work
Himalayan cappuccino = new Himalayan();
System.out.println(cappuccino.getAbstractClassName());
//output is: Cat
System.out.println(cappuccino.getClassName());
//output is: Himalayan
}
}
Page 13
11.
Java Interfaces
an example of using an interface
interface Fruit {
public boolean hasAPeel();
//has a peel must be implemented in any class implementing Fruit
//methods in interfaces must be public
}
interface Vegetable {
public boolean isARoot();
//is a root must be implemented in any class implementing Vegetable
//methods in interfaces must be public
}
class FandVUtility {
static String doesThisHaveAPeel(Fruit fruitIn)
{
if (fruitIn.hasAPeel())
return "This has a peel";
else
return "This does not have a peel";
}
static String isThisARoot(Vegetable vegetableIn)
{
if (vegetableIn.isARoot())
return "This is a root";
else
return "This is not a root";
}
static String doesThisHaveAPeelOrIsThisRoot(
Tomato tomatoIn)
{
if (tomatoIn.hasAPeel() && tomatoIn.isARoot())
return "This both has a peel and is a root";
else if (tomatoIn.hasAPeel() || tomatoIn.isARoot())
return "This either has a peel or is a root";
else
return "This neither has a peel or is a root";
}
}
class Tomato implements Fruit, Vegetable {
boolean peel = false;
boolean root = false;
public Tomato() {}
public boolean hasAPeel()
//must have this method,
// because Fruit declared it
{
return peel;
}
public boolean isARoot()
//must have this method,
// because Vegetable declared it
{
return root;
Page 14
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Part one: making a tomato
Tomato tomato = new Tomato();
System.out.println(FandVUtility.isThisARoot(tomato));
//output is: This is not a root
System.out.println(
FandVUtility.doesThisHaveAPeel(tomato));
//output is: This does not have a peel
System.out.println
(FandVUtility.doesThisHaveAPeelOrIsThisRoot
(tomato));
//output is: This neither has a peel or is a root
//Part two: making a fruit
//Fruit = new Fruit();
//can not instantiate an interface like
// this because Fruit is not a class
Fruit tomatoFruit = new Tomato();
//can instantiate by interface like
// this because Tomato is a class
//System.out.println(
// FandVUtility.isThisARoot(tomatoFruit));
//can not treat tomatoFruit as a Vegetable
// without casting it to a Vegetable or Tomato
System.out.println(
FandVUtility.doesThisHaveAPeel(tomatoFruit));
//output is: This does not have a peel
//System.out.println
// (FandVUtility.doesThisHaveAPeelOrIsThisRoot
// (tomatoFruit));
//can not treat tomatoFruit as a Vegetable
// without casting it to a Vegetable or Tomato
}
}
Page 15
12.
Java Logging
java.util.Logging
TestLogging - Shows the basic usage of java.util.Logging
//new logging api in Java 1.4
import java.util.logging.*;
public class TestLogging {
//set up a logger
static Logger testLog =
Logger.getLogger("Fluffycat.TestLog");
public static void main(String[] args) {
//test a warning log
testLog.warning("sample warning");
//test all priority levels to lowest
//default will only show
// SEVERE, WARNING, and INFO on your console
testLog.log(Level.SEVERE, "severe log");
testLog.log(Level.WARNING, "warning log");
testLog.log(Level.INFO, "info log");
testLog.log(Level.CONFIG, "config log");
testLog.log(Level.FINE, "fine log");
testLog.log(Level.FINER, "finer log");
testLog.log(Level.FINEST, "finest log");
testLog.log(Level.ALL, "all log");
}
}
Logging Output
May 14, 2002 10:33:18 AM
WARNING: sample warning
May 14, 2002 10:33:18 AM
SEVERE: severe log
May 14, 2002 10:33:18 AM
WARNING: warning log
May 14, 2002 10:33:18 AM
INFO: info log
TestLogging main
TestLogging main
TestLogging main
TestLogging main
Page 16
13.
Java Object
java.lang.Object
General Notes
1. Every Class extends Object
2. You can not store a primitive in an Object variable.
Object objStringFive = new String("5");
//this works.
Object objDoubleFive = new Double("5");
//this works.
int fiver = 5;
Object objFive = fiver;
//this will not compile.
Object anotherObjFive = 5;
//this will not compile.
Object methods most used
Object cloneOfObject =
objectToClone.clone();
boolean isEqual =
objectToCompare.equals(objectToCompareTo);
Class runtimeClass =
objectToGetClassFrom.getClass();
int hashCodeOfObject =
objectToGetHashCodeOf.hashCode();
String stringValue =
objectToGetStringOf.toString();
Object methods for threads
objectWithThreadWaiting.notify();
//wakes up current thread
objectWithThreadWaiting.notifyAll();
//wakes up all threads
objectToMakeThreadWait.wait();
//current thread goes to sleep until notify() or notifyAll()
objectToMakeThreadWait.wait
(longTimeToWaitInMilliseconds);
//current thread goes to sleep until notify(),
// notifyAll(), or longTimeToWaitInMilliseconds elapses
objectToMakeThreadWait.wait(
longTimeToWaitInMilliseconds,
intTimeToWaitInNanoseconds);
//current thread goes to sleep until notify(),
// notifyAll(), or longTimeToWaitInMilliseconds +
// intTimeToWaitInNanoseconds elapses
Page 17
Object method for garbage collection
objectForGarbageCollection.finalize();
//called by garbage collector when no more
// object references exist
Page 18
14.
Java Strings
java.lang.String
the String constructors
//Note: Strings are immutable,
// so once a String is constructed it can not be changed.
// StringBuffer is like String, however it is mutable.
//construct an empty string
String emptyString = new String();
//constructors using a byte[]
String stringFromByteArray = new String(byteArrayIn);
String stringFromByteArray =
new String(byteArrayIn,
intOffsetToCopyFrom,
intLengthToCopy);
String stringFromByteArray =
new String(byteArrayIn,
encodingString);
String stringFromByteArray =
new String(byteArrayIn,
intOffsetToCopyFrom,
intLengthToCopy,
encodingString);
//constructors using a char[]
String stringFromCharArray =
new String(charArrayIn);
String stringFromCharArray =
new String(charArrayIn,
intOffsetToCopyFrom,
intLengthToCopy);
//constructor using a String
String stringFromString =
new String(stringIn);
//constructor using a StringBuffer
String stringFromStringBuffer =
new String(stringBufferIn);
Finding out about a String
int comparisonValue =
stringToCompare.compareTo(objectToCompareTo);
//note: objectToCompareTo must really be a String.
//returns an int value of zero if Strings are equivalent
//returns an int value less than zero if
Page 19
// stringToCompare is less than objectToCompareTo
//returns an int value greater than zero if
// stringToCompare is greater than objectToCompareTo
int comparisonValue =
stringToCompare.compareTo(stringToCompareTo);
//returns an int value of zero if Strings are equivalent
//returns an int value less than zero if
// stringToCompare is less than stringToCompareTo
//returns an int value greater than zero if
// stringToCompare is greater than stringToCompareTo
int comparisonValue =
stringToCompare.compareToIgnoreCase(stringToCompareTo);
//returns an int value of zero if
// Strings are equivalent, ignoring case
//returns an int value less than zero if
// stringToCompare is less than stringToCompareTo,
// ignoring case
//returns an int value greater than zero if
// stringToCompare is greater than stringToCompareTo,
// ignoring case
boolean doesStringAendWithStringB =
stringA.endsWith(stringB);
boolean isObjectEqualToString =
stringToCompare.equals(objectToCompare);
boolean isObjectEqualToString =
stringToCompare.equalsIgnoreCase(objectToCompare);
int stringHashcode =
stringToGetHashcodeFrom.hashcode();
int stringLength =
stringToGetLengthOf.length();
boolean doesRegionMatch =
stringAToCompare.regionMatches(
booleanShouldIgnoreCase,
intOfStringAoffsetToStartAt,
stringBToCompare,
intOfStringBoffsetToStartAt,
intLengthToCompare);
boolean doesRegionMatch =
stringAToCompare.regionMatches(
intOfStringAoffsetToStartAt,
stringBToCompare,
intOfStringBoffsetToStartAt,
intLengthToCompare);
Finding things in a String
int indexOfFoundCharacter =
stringToFindCharacterIn.charAt(intOfCharacter);
//finds first occurance,
Page 20
//
returns -1 if character is not found
int indexOfFoundCharacter =
stringToFindCharacterIn.charAt(
intOfCharacter,
intOffsetToStartAt);
//finds first occurance starting at offset,
// returns -1 if character is not found
int indexOfFoundString =
stringToFindStringIn.charAt(stringToFind);
//finds first occurance,
// returns -1 if String is not found
int indexOfFoundString =
stringToFindStringIn.charAt(
stringToFind,
intOffsetToStartAt);
//finds first occurance starting at offset,
// returns -1 if String is not found
int indexOfFoundCharacter =
stringToFindCharacterIn.lastIndexOf(intOfCharacter);
//finds last occurance,
// returns -1 if character is not found
int indexOfFoundCharacter =
stringToFindCharacterIn.lastIndexOf(
intOfCharacter,
intOffsetToStartAt);
//finds last occurance starting at offset,
// returns -1 if character is not found
int indexOfFoundString =
stringToFindStringIn.lastIndexOf(
stringToFind);
//finds last occurance,
// returns -1 if String is not found
int indexOfFoundString =
stringToFindStringIn.lastIndexOf(
stringToFind,
intOffsetToStartAt);
//finds last occurance starting at offset,
// returns -1 if String is not found
boolean doesRegionMatch =
stringAToCompare.regionMatches(
booleanShouldIgnoreCase,
intOfStringAoffsetToStartAt,
stringBToCompare,
intOfStringBoffsetToStartAt,
intLengthToCompare);
boolean doesRegionMatch =
stringAToCompare.regionMatches(
intOfStringAoffsetToStartAt,
Page 21
stringBToCompare,
intOfStringBoffsetToStartAt,
intLengthToCompare);
boolean doesStringStartWithStringToFind =
stringToFindStringAtStart.startsWith(stringToFind);
boolean doesStringStartWithStringToFind =
stringToFindStringAtStart.startsWith(
stringToFind,
intOffsetToCheckAt);
Getting things out of Strings
char charAtIndex =
stringToGetCharFrom.charAt(intIndex);
String stringAandStringB =
stringA.concat(stringB);
byte[] byteArrayFromString =
stringToGetByteArrayFrom.getBytes();
byte[] byteArrayFromString =
stringToGetByteArrayFrom.getBytes(
stringCharacterEncoding);
stringToGetCharArrayFrom.getChars(
intOffsetToCopyFromInclusive,
intOffsetToCopyToExclusive,
characterArrayToCopyInto,
intOffsetInCharacterArrayToStartCopy);
String canonicalRepresentationOfStringA =
stringA.intern();
String stringWithReplacements =
stringToReplaceCharsIn.replace(
charToFind,
charToReplaceWith);
String substring =
string.substring(intBeginningIndexInclusive);
String substring =
string.substring(
intBeginningIndexInclusive,
intEndingIndexExclusive);
char[] charArrayFromString =
stringToGetCharArrayFrom.toCharArray();
String lowercaseString =
Page 22
stringToGetLowerCaseStringFrom.toLowerCase();
String lowercaseStringUsingLocale =
stringToGetLowerCaseStringFrom.toLowerCase(localeToUse);
//uses java.util.Locale
String stringAsString =
stringToReturnAsString.toString();
//returns String as a String
String uppercaseString =
stringToGetUpperCaseStringFrom.toUpperCase();
String lowercaseStringUsingLocale =
stringToGetUpperCaseStringFrom.toUpperCase(
localeToUse);
//uses java.util.Locale
String trimmedString = stringToTrim.trim();
//Removes all whitespaces.
//Whitespaces are: horizontal tabs, vertiacal tabs,
// line feeds, form feeds, carriage returns,
// file separators, group separators,
// record separators, unit separators,
//
Unicode space separators (not a no-break space),
// Unicode line separators, and Unicode
// paragraph separators.
valueOf()
String stringFromCharArray =
String.copyValueOf(charArray);
String stringFromCharArray =
String.copyValueOf(charArray,
intOffsetToCopyFrom,
intLengthToCopy);
String stringFromBoolean =
String.valueOf(booleanIn);
//returns "true" or "false"
String stringFromChar = String.valueOf(charIn);
String stringFromCharArray =
String.valueOf(charArrayIn);
String stringFromCharArray =
String.valueOf(charArrayIn,
intOffsetToCopyFrom,
intLengthToCopy);
String stringFromDouble = String.valueOf(doubleIn);
Page 23
String stringFromFloat = String.valueOf(floatIn);
String stringFromInt = String.valueOf(intIn);
String stringFromLong = String.valueOf(longIn);
String stringFromObject = String.valueOf(objectIn);
Page 24
15.
Java Arrays
Declaring an array of primitives
int[] arrayName1;
//Declares an array of ints.
//note: All elements in an array are the same type
// int, String, Object, etc.
int arrayName2[];
//Also declares an array of ints.
int[] arrayName3 = new int[5];
//Creates an array of 5 ints,
// initializes all 5 ints to 0.
int[] arrayName4 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
//creates an array of 5 ints, values 1,3,5,7,9
//note: the subscripts of the elements are 0,1,2,3,4
System.out.println("arrayName4[0] = " + arrayName4[0]);
//prints arrayName4[0] = 1
System.out.println("arrayName4[4] = " + arrayName4[4]);
//prints arrayName4[4] = 9
System.out.println("arrayName4.length = " + arrayName4.length);
//prints arrayName4.length = 5
Declaring an array of objects
ClassName[] classArrayName1;
//Declares an array of ClassName.
ClassName[] classArrayName2 = new ClassName[5];
//Creates an array of 5 ClassName, initializes all 5 to null.
Declaring a matrix
int[] [] matrixName2 = new int[3] [7];
//an array of array
int[] [] [] matrixName3 = new int[3] [7] [4];
//an array of array of array
int[] [] [] [] matrixName4 = new int[3] [7] [4] [2];
//an array of array of array of array
You can swap array values like this
double temp = myArray[i];
myArray[i] = myArray[i+1];
myArray[i+1] = temp;
Array methods in java.util.Arrays
List list = Arrays.asList(arrayName);
boolean isEqual = Arrays.equals(arrayName, otherArrayName);
Arrays.fill(arrayName,
valueToFillWith);
Arrays.fill(arrayName,
fromIndex,
Page 25
toIndex,
valueToFillWith);
int foundAt =
Arrays.binarySearch(arrayName, valueToSearchFor);
//array must be sorted for this to work
Arrays.sort(Object arrayToSort)
//All elements in the array must have Comparable interface,
// and they must be comparable to each other.
Array methods in java.lang.System
System.arraycopy(fromArray,
fromOffsetInt,
toArray,
toOffsetInt,
countInt);
Array methods in java.lang.reflect.Array
Array.get(arrayName, positionInt);
Array.getDouble(arrayName, positionInt);
//also getBoolean(), getByte(), getChar(),
// getFloat(), getInt(), getLong(), getShort()
Array.getLength(arrayName);
Array.set(arrayName, positionInt, value);
Array.setDouble(arrayName, positionInt, doubleToSet);
//also setBoolean(), setByte(), setChar(),
// setFloat(), setInt(), setLong(), setShort()
Page 26
16.
Java ArrayLists
java.util.ArrayList
the ArrayList constructors
ArrayList ArrayListName = new ArrayList();
ArrayList ArrayListName = new ArrayList(5);
//The 5 sets the initial element capcaity.
The default is 10.
ArrayList ArrayListName = new ArrayList(collectionIn);
//creates a new ArrayList with the elements of a collection.
//Elements are read from the collection with an Iterator.
ArrayList methods to find out what is in the ArrayList
int arrayListSize = arrayListName.size();
boolean isArrayListEmpty = arrayListName.isEmpty();
int objectFirstFoundAt =
arrayListName.indexOf(objectToSearchFor);
int objectLastFoundAt =
arrayListName.lastIndexOf(objectToSearchFor);
boolean isObjectInArrayList =
arrayListName.contains(objectToSearchFor);
ArrayList methods to retrieve elements from the ArrayList
Object objectName =
(ClassTypeToCastTo) arrayListName.get(intOffsetToGetElementAt);
//note: Objects coming out of ArrayLists have lost
// their class type, and must be cast
ArrayList methods to alter what is in the ArrayList
boolean addWasGood =
arrayListName.add(objectToAdd);
//inserts at end
arrayListName.add(intOffsetToSetElementAt, objectToAdd);
//inserts at offset, no boolean returned
arrayListName.addAll(collectionToAdd);
arrayListName.addAll(intOffsetToAddCollectionAt, collectionToAdd);
arrayListName.set(intOffsetToSetElementAt, objectIn);
//replaces element at offset
arrayListName.remove(intOffsetToRemoveElementAt);
//deletes element at offset
arrayListName.removeRange
Page 27
(intOffsetToRemoveElementFromInclusive,
intOffsetToRemoveElementToExclusive);
//deletes from start offset up to the end offset
//note - element at the end offset is not deleted
arrayListName.clear();
ArrayList methods for Arrays
Object[] arrayToCopyArrayListInto = arrayListName.toArray();
Page 28
17.
Java ListIterators
java.util.ListIterator
creating a ListIterator
ListIterator listIteratorName = arrayListName.listIterator();
//creating a ListIterator for an ArrayList
ListIterator listIteratorName = linkedListName.listIterator();
//creating a ListIterator for a LinkedList
ListIterator listIteratorName = listName.listIterator();
//creating a ListIterator for a List
ListIterator methods to find out things about the ArrayList
boolean areThereMore = listIteratorName.hasNext();
int whereIsNext = listIteratorName.nextIndex();
boolean wereThereAny = listIteratorName.hasPrevious();
int whereIsPrevious = listIteratorName.previousIndex();
ListIterator methods to retrieve elements
ClassTypeToCastTo nextElement =
(ClassTypeToCastTo) listIteratorName.next();
ClassTypeToCastTo previousElement =
(ClassTypeToCastTo) listIteratorName.next();
ListIterator methods which alter what is in the underlying ArrayList, LinkedList, or List
arrayListName.add(elementToAdd);
//inserts before what next() would return
arrayListName.set(intOffsetToSetElementAt, objectIn);
//replaces element that was just returned by next() or previous(),
// can not be called after add.
arrayListName.remove(intOffsetToRemoveElement);
//deletes element that was just returned by next() or previous(),
// can not be called after add.
Using a ListIterator to traverse an existing ArrayList
ListIterator listIteratorName = arrayListName.listIterator();
while (listIteratorName.hasNext()) {
classTypeToCastTo nextElement =
(ClassTypeToCastTo) listIteratorName.next();
}
Page 29
Page 30
18.
Java HashMaps
java.util.HashMap
the HashMap constructors
HashMap hashMapName = new HashMap();
HashMap hashMapName = new HashMap(5);
//The 5 sets the initial element capcaity.
HashMap hashMapName = new HashMap(5, .9);
//The 5 sets the initial element capcaity.
//The .9 is the load factor.
// The default load factor is .75.
HashMap hashMapName = new HashMap(mapIn);
//creates a new HashMap with the elements of a map.
HashMap methods to find out what is in the HashMap
int HashMapSize = hashMapName.size();
boolean isHashMapEmpty = hashMapName.isEmpty();
boolean isObjectKeyInHashMap =
hashMapName.containsKey(objectToSearchForAsKey);
boolean isObjectValueInHashMap =
hashMapName.containsValue(objectToSearchForAsValue);
HashMap methods to retrieve elements from the HashMap
Object objectName =
(ClassTypeToCastTo) hashMapName.get(keyToGetObjectValueFor);
//note: Objects coming out of HashMaps have lost
// their class type, and must be cast
Set setOfAllKeys = hashMapName.keySet();
//The set is a "view",
// so changes to the original HashMap change the view,
// and changes to the view change the original HashMap.
Collection collectionOfAllValues = hashMapName.values();
//The collection is a "view",
// so changes to the original HashMap change the view,
// and changes to the view change the original HashMap.
Set setOfAllEntryValues = hashMapName.entrySet();
//note: "Returns a collection view of the mappings
// contained in this map"
// (Platform API Spec, See online refs)
//The collection is a "view",
// so changes to the original HashMap change the view,
// and changes to the view change the original HashMap.
Object cloneOfHashMap = hashMapName.clone();
Page 31
//Shallow copy of HashMap,
// objects in HashMap are not cloned.
HashMap methods to alter what is in the HashMap
Object objectReplacedForKey =
hashMapName.put(objectKey, objectToAdd);
//inserts object value for a specified key
//returns the object that is replaced for that key,
// null if nothing is repplaced
hashMapName.putAll(mapToAdd);
//adds a map into the HashMap
hashMapName.remove(keyObject);
//removes a key and value pair for a key
hashMapName.clear();
Page 32
19.
Iterator
/**
*Output:
Original contents of al: C A E B D F
Modified list backwards: F+ D+ B+ E+ A+ C+
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
al.add("C");
al.add("A");
al.add("E");
al.add("B");
al.add("D");
al.add("F");
System.out.print("Original contents of al: ");
Iterator<String> itr = al.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String element = itr.next();
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
ListIterator<String> litr = al.listIterator();
while (litr.hasNext()) {
String element = litr.next();
litr.set(element + "+");
}
// Now, display the list backwards.
System.out.print("Modified list backwards: ");
while (litr.hasPrevious()) {
String element = litr.previous();
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
}
}
Page 33
20.
Console Input
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public
test(){
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.print("Entrez votre string : ");
System.out.println("mon string est : " + ReadConsole());
}
public static String ReadConsole(){
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
String myString = "";
myString = reader.nextLine();
return myString;
}
}
Page 34