WW2 and the US
advertisement

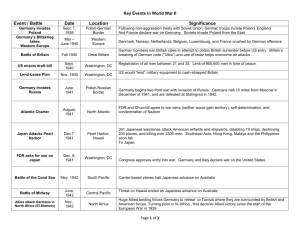
World War 2 Chapter 24 US 2 Mr. McLaughlin US Enters the War • The US had been preparing for war even though FDR claimed he wished to stay neutral • After the attack on Pearl Harbor, public opinion quickly changed and the US entered the war • Hitler declared war on the US to force the Americans to fight a two-front war (only time Hitler ever “declared war”) AXIS Strengths • Germany occupied several European and North African countries • Japan had extended its power throughout Southeast Asia, including China • Germany and Japan had large, well-trained Armies…neither was known for their desire to surrender ALLIED Strengths • ENORMOUS Russian Army • USA production capability • Axis troops were spread very thin across the World occupying many different countries US Preparation •Production Boom •Government Agencies •Economy •Army US Preparation • Production Boom: US wartime production quickly ends any lingering effects of the depression • Government Agencies: 1. Wartime Production Board 2. Office of War Mobilization • Economy: Increase income tax, Sell War Bonds, Institute Rationing, Freeze wages • Army: (1940)Selective Training and Service Act (1st ever peacetime draft) Bataan Death march • US and Filipino troops were defending the Philippines • Gen. MacArthur, realizing he was outnumbered, ordered an evacuation to the Bataan Peninsula • Trapped between the Japanese and the ocean the soldiers were forced to surrender • MacArthur left Bataan saying, “I shall return” • 70,000 survivors were forced to walk 60 miles, 10,000 died on the march • Conditions in camps were just as bad, thousands more died in captivity • Bataan Survivor Early Battles in the Pacific •Coral Sea •Midway •Guadalcanal Coral Sea • First Allied victory in the Pacific • Allies destroy 1 carrier and damage another • Significance: Allies stop the Japanese push toward Australia Midway • US had intercepted Japanese strategy • Japan planned to attack Alaska to force US troops to leave Hawaii and Midway islands unprotected • US Naval forces are waiting for the Japanese at Midway • 4 day battle: 4 Japanese aircraft carriers are sunk, major hit to the Japanese forces Guadalcanal •First Allied offensive •Japanese fought extremely hard, sign of things to come (refused surrender, committed suicide instead) •Allies take the island and never relinquish it Early Action in Europe • German and Italian forces controlled North Africa (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya) • Hitler wanted control of the Suez Canal and advance to the Middle East oil fields • Hitler’s North Africa commander is Erwin Rommel aka “Desert Fox”, well respected German General • The British pushed the Axis powers back at the Battle of El Alamein in Egypt to as far as Libya • The Allies had won a victory in N. Africa Stalingrad • Germany had pushed deep into Russia, threatening to take Moscow • Russia fought them back furiously through a difficult winter • The two sides clashed at Stalingrad near Russian oil reserves • Soviets surrounded the Germans who refused to surrender, Hitler’s orders • A brutal winter in 1943 forced the German surrender, over half of Germany’s most powerful 6th Army • The Allies had now felt victory in both Africa and Europe Quiz 1 1. Stalingrad 2. Coral Sea 3. Bataan 4. Midway 5. El Alamein A. B. C. D. E. US intercepts Japanese message and wins major naval battle here, turning point in Pacific Site of 87-mile march by surrendered US soldiers, many die Site of German surrender, its military was cut in half Axis forces, on route to the Suez Canal and Middle East are forced into a retreat here At this Naval battle Japanese forces are stopped from advancing to Australia US Homefront 1. 2. 3. What was the Office of War Information? What are Victory Gardens? What did west coast cities do at night to help the war effort? 4. Who is “Rosie the Riveter?” 5. Approx how many African-American soldiers served in WW2? 6. Explain the zoot-suit riots? 7. What is the difference between the “issei” and the “nisei?” 8. In what states were the Japanese relocation camps located? 9. What did the US do with Hawaii during the war? 10. What could young Japanese men do to show their loyalty to the US? North Africa • Allies now control Morocco and Algeria, giving them power over the Mediterranean Sea • They use this position to cut off supplies from Italy • May 1943, 250,000 Axis troops in Africa surrender Italy • July 1943, Allied Powers invade Sicily • Italy’s King removes Mussolini as PM but Mussolini is rescued by German forces and controls Northern Italy • Fighting was fierce, Italy signs armistice in Sept but fighting continues between German and Allied troops • German troops did not want to give up Italy, they do not finally surrender until June 1944 War in Atlantic • Read 815-816 • How do the Allies combat the German U-Boats? • Are they successful? D-Day! June 6, 1944 • AKA Operation Overlord • History’s largest naval invasion, D-Day June 6, 1944 • 160,000 troops landed on the beaches of France that day, 2 million within 3 months • 5,000 ships • Over 1,000 planes D-Day! June 6, 1944 • Allies bomb German strongholds in France to weaken them in advance • Once the invasion begins the Allies push towards Paris • Paris is liberated August 25th 1944 • From this point the US and British forces will drive toward Germany from the West while the Russians attack from the East Battle of the Bulge • 1. 2. 3. 4. Germany, its back against the wall begins its final counterattack Which side had more troops? Why was it called the Battle of the Bulge? How did Gen. McAuliff respond to a surrender request? What is the outcome? Yalta Conference • FDR, Stalin, Churchill • They agree to divide and occupy Germany for years to come • Stalin agrees to declare war on Japan if the US needs them Berlin • Allies inflict serious damage to German cities with a series of bombing raids • 30-60,000 civilian deaths • Churchill and US are both fearful of Stalin’s motives and want to win the “race” to Berlin • Gen Eisenhower refuses to change his plans and the Soviets reach Berlin 1st After Repair German Theater April 28th, 1944 Benito Mussolini is killed in Italy Hitler’s Fate • Mussolini had been captured and killed in Italy by Italian rebels on April 28th • Hitler, with the Allies storming the city of Berlin commits suicide in his bunker on April 30th (Eva Braun is with him and also commits suicide) • May 7, 1944: Germany officially surrenders • V-E Day!!!!! Island Hopping • War in the Pacific was largely a naval conflict, unlike Europe • Island Hopping: Rather than recapturing all of the Japanese held islands, the US would attack and seize strategic islands that would lead them to the mainland War in Pacific (Key Battles) • Tarawa • Saipan • Leyte Gulf • Iwo Jima • Okinawa Tarawa •Significance: US gains control of vital Japanese airstrip for future landings •Casualties were higher than expected, a sign of things to come Saipan • Significance: Decisive US victory • 350 Japanese planes are destroyed • 3,400 US deaths, 16,000 Casualties • US gains another important airstrip, close to the main island of Japan Leyte Gulf • Significance: US needed to recapture the Philippines • Largest Naval battle in the Pacific • Japanese lose 4 aircraft carriers and 3 battleships (Japan’s ability to fight a naval war is GREATLY damaged) • MacArthur made good on his promise, he had returned to the Philippines Iwo Jima • Significance: 6 week battle was one of the hardest fought in the war, US victory placed them just 750 miles from Japan • 20,000 Japanese are killed • Photographer Joe Rosenthal took one of the most memorable photos in US Military history after the Marines took Mount Surabachi • Iwo Jima (History Channel) Okinawa • Significance: Bloodiest, deadliest battle in the Pacific • Japanese began using Kamikaze missions during the battle • Japanese troops continued to refuse surrender and fought to the death • 110,000 Japanese troops were killed • Okinawa Video The death of FDR Franklin D. Roosevelt who had won re-election for an unprecedented 4th term in 1944 died on April 12th 1945 His Vice President, Harry Truman had been in office for only a few months when he was forced to take over He faced the most difficult decision of the war. Should he use the Atomic Bomb? What are his other options? 33rd President, Harry S Truman Manhattan Project • Since 1942 the US had been working on the Atomic Bomb • The man in charge of the project was Robert Oppenheimer • The 1st successful test of an Atomic Bomb took place in Alamogordo, NM on July 16, 1945 Hiroshima • August 6th, 1945, The plane Enola Gay delivers the 1st Atomic Bomb to the city of Hiroshima (Bomb was named “Little Boy” • Hiroshima was a military target where the US hoped civilian casualties would be low • The initial blast kills 100,000 people instantly “Little Boy” “Enola Gay” Hiroshima Dome Hiroshima Dome (Today) 65 Years Later Hiroshima (Present Day) Nagasaki • August 9th, 1945 • Japan refused surrender, the US still not wanting to invade Japan uses a 2nd Atomic Bomb named “Fat Man” • The Japanese were forced into a surrender, September 2nd, 1945 • V-J Day!!!!! • Atomic Bomb Movie Nagasaki Aftermath of the War • Truman saved countless American lives by not invading Japan, however he opened the door to the Atomic Age • World War 2 claimed the lives of up to 60 million people or more • The Soviet Union lost over 20 million alone • The cost of the war, although impossible to truly calculate, totals more than $1 Trillion • Cities across Europe were left in ruins, millions of homes were uninhabitable • Millions of children were left orphaned and thousands were misplaced and left homeless WW2 YouTube Videos • War in Europe • War in Pacific