Respiration
advertisement

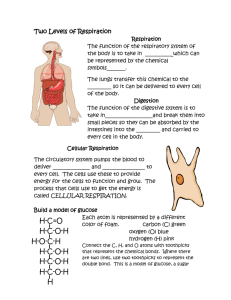
Respiration Unit B – Year 8 Do Now: • Copy down the following formula into your books: Glucose • Cells need energy to stay alive • This energy comes from glucose • Produced from the digestion of carbohydrates ATP Energy • Adenosine triphosphate – ATP Energy • Energy created by the breakdown of glucose • Contains 3 phosphates • Phosphates break to create energy Cells Need ATP Energy • All cells need ATP energy • Fermentation – creating ATP energy without oxygen • Most cells in your body will use glucose and oxygen to produce ATP energy Fermentation Experiment • You will be using yeast, sugar and water to create ATP energy • Answer the following questions: • What is the glucose in the experiment? • What would happen without the sugar? • What gas fills the balloon? Experiment: • Heat 100 mL of water to approximately 32°C. • Place about 3.5 g of yeast into the conical flask with the warm water • Each table will add a different amount of sugar into the yeast and water • After adding everything, place a balloon on top. • Measure the diameter of the balloon in 5 minute intervals. • We will then check on the products tomorrow Yeast Fermentation • What your final experiment should look like: Do Now: • Collect your experiment from the window and measure the balloon and write your observation of what occurred. • Now a quick review: Moving the Glucose and Oxygen Through Your Body • Small Intestines – Nutrients pass through the small intestines and are absorbed into the blood through the villi (or a single one is called villus) The Villi • Digested food passes through into tiny blood vessels called capillaries Circulatory System • Veins – carry blood towards the heart • Arteries – carry blood away from the heart How do capillaries help? Red Blood Cells • Red Blood Cells – Carry oxygen around the body • When we breathe in oxygen enters the small air sacs, called alveoli, in the lungs. Oxygen diffuses from there into the bloodstream. • These contain a red substance called haemoglobin, which joins onto oxygen and carries it around the body in the blood, then lets it go when necessary. Oxygen can diffuse into cells from the capillaries. Plasma • Glucose is obtained through digestion of the food we eat and then absorbed across the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream. • Glucose is carried round the body dissolved in blood plasma, the pale yellow liquid part of our blood. The dissolved glucose can diffuse into the cells of the body from the capillaries. Once in the cell glucose can be used in respiration. Moving through the Blood Glycolysis • Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid units. • Creates 2 ATP • This stage takes place in the cytoplasm; it does not require oxygen: Do Now: • What is the “goal” of cellular respiration? What does the body get out of it? • What are the two options that glucose can react with to create the needed energy? Anaerobic vs. Aerobic • Anaerobic – Reaction without oxygen • Aerobic – Reaction with oxygen • Aerobic Exercise gains more oxygen into the body • What are some examples of aerobic exercise? Activity • We will determine aerobic exercise difficulty using heartrate. • We will complete different activities and record heartrate after each exercise. Do Now: • Define and describe glycolysis • Which exercise were you producing the most ATP energy? • What do you believe a “pyruvate” is? How Fast is Cellular Respiration? • Depends on how fast you are taking in oxygen and using energy • Faster during aerobic exercise • Slower during sleep Kreb’s Cycle • 2nd step of cellular respiration • What do you notice is produced? • Hint: It’s a gas! Kreb’s Cycle • Pyruvic Acid is broken down with oxygen • Carbon dioxide is produced • Water is produced • Also produces 2 ATP energy NADH • Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide – an enzyme that is needed in the final step of cellular respiration, Electron Transport Train • You only need to remember NADH will carry electrons to the final stage Mitochondria • Part of the cell • Kreb’s Cycle takes place here • Continuous cycle for as long as the body is producing and needs ATP energy • Located inside the cytoplasm Eukoaryotes Cells Project • You are to create a board game about cellular respiration • We will finish talking about the electron transport chain tomorrow and wrap up the 3 steps in cellular respiration • Wednesday and Friday we will review • Next Monday your games are due • I will choose the best games and we will play next week in class Examples: • You may make it with or without the assistance of a computer Computer Based Games: • You may also make a computer based game such as: Your Game Must Include: • Vocabulary • Stages of cellular respiration • I am happy to print anything you need for your project • Please do not wait until the last minute! Do Now: • What is produced during glycolysis? • What is produced during Kreb’s cycle? Electron Transport Chain • Final stage of cellular respiration • Produces most ATP energy – 34 ATP energy (usually closer to 32) • NADH (abd FADH) carries electrons from Kreb’s cycle through the mitochondria • Membranes will turn the electrons into ATP energy! • And we are done….almost… ETC Stopping the Chain • If something were to “block” the chain, then your body would not be able to create enough ATP energy • Example: Cyanide can stop the chain Cellular Respiration Do Now: • Write the equation for cellular respiration and indicate in which each step the product is made. Photosynthesis • Process to produce oxygen and glucose • Occurs in plants Reaction • Nearly opposite from cellular respiration Chloroplast • The plant “version” of the mitochondria (but opposite) • Produces glucose (instead of using glucose) • Contains chlorophyll – captures light energy to help produce glucose Video: • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Eo7JtRA7lg Do Now: • Clear off your desks, you have a quiz! The 3 Systems: • Respiratory System – Brings oxygen into the body • Main Organ: Lung • Digestive System – Brings glucose into the body • Main Organ: Small Intestine • Circulatory System – Circulates blood through the body • Main Organ: Heart Breathing • Ventilation – Movement of air in and out of the lungs • Inhale – bring air into the lungs • Lungs get bigger • Exhale – release air from the lungs • Lungs get smaller • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LaOBcF6N7e4 Your lungs contain cells! • Mucus – sticky liquid leading down to the lungs created by cells • Traps dust, dirt and germs before it can enter the lungs • Ciliated Epithelial Cells – cleans mucus out of the respiratory system and into the gullet where it is swallowed • Cilia – Tiny hairs in the cells that cleans out the mucus Goblet Cell • Produces mucus and is located next to ciliated cells Do Now: • Determine the vocabulary word for each of the following definitions: • The process used to create glucose. • Part of the cell Kreb’s cycle takes place. • The process used to create ATP energy. • Part of the blood that moves oxygen around the body. • Part of the small intestine that takes glucose from the digestive system. Gas Exchange • Picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. • Red blood cells: • Bright red when filled with oxygen • Dark red when not Air Sacs • Thousands in the lungs • Contain tiny pockets called alveoli • Give large surface area for RBC to absorb oxygen • Excrete carbon dioxide Getting into the blood • Capillaries surround the pockets in the to collect the oxygen and release carbon dioxide Diffuse • Thin walls of the pockets allows the gas exchange to go in and out of the blood Diffusion in the Water • Underwater diffusion allows plants to get oxygen • Gills allow fish to get oxygen Activity: • Read the handout about fish and respiration. • Make a graph and answer the questions Do Now: • Please glue the diagram into your books. Lungs • Your lungs receive the air you breathe in through your nose. • When you breathe in, the lungs puff-out or inflate, and deflate when you breathe out. • From the air, they take the useful part - oxygen (a gas), and convert it for use in the body via the bloodstream. • The blood swaps carbon dioxide (the waste material) for oxygen in the lungs. This is why the lungs are often said to convert gases. • You have 2 lungs. • Your lungs are protected by your ribcage. • Close-up, they look like a wet sponge. • The left lung is smaller - to accommodate your heart • Your lungs are particularly vulnerable to breathing-in nasty substances - toxic chemicals, smoke from fires and cigarette smoke all damage your lungs. Trachea (windpipe) • Carries air to the lungs Lung Dissection • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9xhxALk9gm8 • Write down observations What did you observe? • Discuss with the person next to you what observations you made during the video Class Observations • What did you learn from the dissection? Do Now: • What are the 2 cells in the lungs? • What are their functions?