The Copper Reaction Cycle - The Big Science Notebook
advertisement

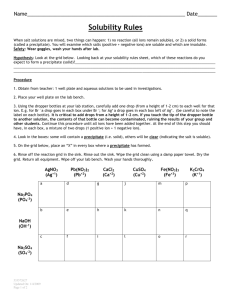
Hangzhou International School Chemistry Unit 4: Ions and their Reactions Quiz 4.3: Solubility and the Copper Reaction Cycle Name:_______________________________ Fill in each blank with the correct formula from the “compound bank.” A formula may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Cu Cu(NO3)2 Cu(OH)2 H2O NaNO3 NO2 HNO3 NaOH CuO 1. _______________was added to Cu(NO3)2 solution to produce a blue precipitate. 2. _______________ is a black precipitate. 3.________________ is called nitric acid. 4.________________ is a base. 5.________________ causes a brown gas to form when it is poured onto copper. 6.________________ quickly turns into copper (II) oxide when heated. 7.________________ is called copper (II) nitrate. 8.________________ is a blue solid that does not dissolve in water. 9.________________ reacts with nitric acid to release NO2 gas. 10._______________is present in the solution that separated from the CuO by decanting. (hint: we are going to collect some of this compound as a solid in a petri dish by letting the water from the solution evaporate.) Created by Thomas Robinson Hangzhou International School Chemistry Unit 4: Ions and their Reactions 11. Circle the elements that, when combined with sulfate, will form a precipitate. Ni Pb K Ba 12. Circle the formulas of the compounds which are not able to dissolve in water. LiOH CaS AgNO3 13. Circle the formulas of the soluble compounds. Fe2(CO3)3 Na3PO4 Pb(SO4)2 14. You are given a sample called “Solution X” and told that is has the Ca2+ ion in it. You are asked to precipitate the Ca2+ ion. Two other solutions, listed below, are available to you. Which one will you mix with Solution X in order to precipitate the Ca2+ ion? Give reasons for your answer. NaOH Na2SO4 Created by Thomas Robinson